What Are The Factors Of 225
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
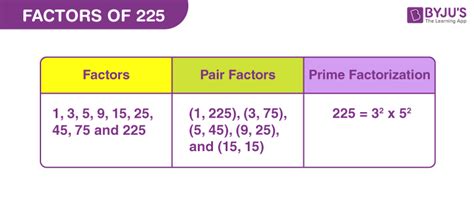
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Factors of 225: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the factors of 225?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, prime factorization, and the fundamental building blocks of mathematics. While the immediate answer might seem straightforward, exploring the methods and concepts behind finding these factors reveals a richer understanding of numerical relationships and their properties. This article will delve deep into the factors of 225, exploring various methods for finding them, discussing their significance in mathematics, and connecting them to broader mathematical concepts.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we embark on finding the factors of 225, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is an integer that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if we divide a number by one of its factors, the result is another whole number. Divisibility is the property of one number being exactly divisible by another.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder. Understanding divisibility rules for common numbers (like 2, 3, 5, and 10) can significantly speed up the process of finding factors.
Method 1: The Brute Force Approach – Systematic Division
The most straightforward, albeit time-consuming for larger numbers, method is to systematically test each integer from 1 up to the number itself to see if it divides 225 without a remainder. This is known as the brute force approach.
Let's try this for 225:
- 1 divides 225 (225/1 = 225)
- 2 does not divide 225 (remainder)
- 3 divides 225 (225/3 = 75)
- 4 does not divide 225 (remainder)
- 5 divides 225 (225/5 = 45)
- 6 does not divide 225 (remainder)
- ...and so on.
While this method works, it's inefficient for larger numbers. We can optimize it by only checking up to the square root of the number. If a number has a factor larger than its square root, it must also have a factor smaller than its square root.
Method 2: Prime Factorization – The Elegant Solution
Prime factorization is a significantly more elegant and efficient method. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
To find the prime factorization of 225:
- Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 225 is not divisible by 2 (it's odd).
- Try the next prime number, 3: 225 is divisible by 3 (225/3 = 75).
- Continue with 3: 75 is also divisible by 3 (75/3 = 25).
- Try the next prime number, 5: 25 is divisible by 5 (25/5 = 5).
- We've reached another prime number, 5: 5 is divisible by 5 (5/5 = 1).
Therefore, the prime factorization of 225 is 3 x 3 x 5 x 5, or 3² x 5².
Method 3: Factor Tree – A Visual Representation
A factor tree provides a visual way to perform prime factorization. We start with the number 225 and branch it into two of its factors. We continue branching until all the branches end in prime numbers.
225
/ \
3 75
/ \
3 25
/ \
5 5
This factor tree clearly shows that the prime factorization of 225 is 3 x 3 x 5 x 5, or 3² x 5².
Finding All Factors from the Prime Factorization
Once we have the prime factorization (3² x 5²), we can systematically find all the factors of 225. We consider all possible combinations of the prime factors:
- Using only 3s: 3⁰ = 1, 3¹ = 3, 3² = 9
- Using only 5s: 5⁰ = 1, 5¹ = 5, 5² = 25
- Combining 3s and 5s: 3¹ x 5¹ = 15, 3¹ x 5² = 75, 3² x 5¹ = 45, 3² x 5² = 225
Therefore, the factors of 225 are 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 25, 45, 75, and 225.
Significance of Factors in Mathematics
Understanding factors is fundamental to various areas of mathematics:
- Number Theory: Factors are crucial for studying prime numbers, divisibility, and other number-theoretic properties.
- Algebra: Factoring polynomials relies on finding the factors of numerical coefficients and variables.
- Calculus: Finding factors is essential in simplifying expressions and solving equations.
- Cryptography: Factorization of large numbers forms the basis of many modern encryption algorithms.
Applications of Factorization Beyond Pure Mathematics
The concept of factorization extends beyond the theoretical realm of mathematics and finds applications in various practical fields:
- Computer Science: Algorithms for factorization are critical for data compression and encryption techniques.
- Engineering: Factorization can simplify complex calculations and models in various engineering disciplines.
- Data Analysis: Understanding factors is helpful for analyzing and interpreting data sets.
Advanced Concepts Related to Factors
Several advanced mathematical concepts build upon the basic understanding of factors:
- Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The largest number that divides two or more integers without leaving a remainder.
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): The smallest number that is a multiple of two or more integers.
- Modular Arithmetic: A system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). Factorization plays a crucial role in modular arithmetic.
Conclusion: The Richness of Factorization
The seemingly simple question of finding the factors of 225 has led us on a journey through various methods, concepts, and applications within mathematics and beyond. From the brute-force approach to the elegance of prime factorization, understanding factors provides a deeper appreciation for the fundamental building blocks of numbers and their intricate relationships. The significance of factorization extends far beyond simple division, impacting various fields and continuing to inspire mathematical exploration. The factors of 225 – 1, 3, 5, 9, 15, 25, 45, 75, and 225 – represent more than just a list of divisors; they represent a gateway to a vast and fascinating world of mathematical concepts and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Vertical Columns On The Periodic Table Are Called
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 1000
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Combination Of All The Forces Acting On An Object
Mar 15, 2025
-
Difference Between Laptop And Notebook Computer
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 42
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors Of 225 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
