What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 42
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 6 min read
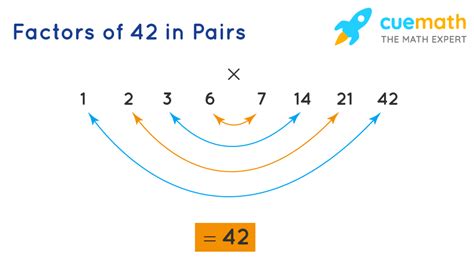
Table of Contents
What is the Greatest Common Factor of 42? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it unlocks a world of understanding in number theory and has practical applications in various fields. This article delves deep into determining the greatest common factor of 42, exploring different methods, and expanding on the broader concepts of GCF and its significance.
Understanding the Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
The greatest common factor (GCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the biggest number that perfectly divides all the numbers in a given set. For example, the GCF of 12 and 18 is 6 because 6 is the largest number that divides both 12 and 18 without leaving a remainder.
Finding the GCF is a fundamental concept in mathematics used in various areas like simplifying fractions, solving algebraic equations, and even in cryptography.
Finding the GCF of 42: Methods and Explanation
To find the GCF of 42, we need to identify all its factors and then select the largest one that is also a factor of any other number (if we were considering multiple numbers). Let's explore different approaches:
1. Listing Factors
The most straightforward method is to list all the factors of 42 and identify the greatest one. The factors of 42 are the numbers that divide 42 without leaving a remainder:
- 1: 42 ÷ 1 = 42
- 2: 42 ÷ 2 = 21
- 3: 42 ÷ 3 = 14
- 6: 42 ÷ 6 = 7
- 7: 42 ÷ 7 = 6
- 14: 42 ÷ 14 = 3
- 21: 42 ÷ 21 = 2
- 42: 42 ÷ 42 = 1
From this list, we can see that the largest factor of 42 is 42. Therefore, the GCF of 42 (considering only 42 itself) is 42.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a powerful technique for finding the GCF, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers. It involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself.
The prime factorization of 42 is: 2 x 3 x 7
This means that 2, 3, and 7 are the prime factors of 42. Since we are only considering the number 42, the GCF is simply the product of all its prime factors, which is 42 itself.
3. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is an efficient method for finding the GCF of two or more numbers. It's particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers where listing factors becomes cumbersome. While we are only dealing with the number 42 here, let's illustrate the Euclidean Algorithm for the sake of completeness and future application. Suppose we wanted to find the GCF of 42 and another number, say 56.
The algorithm involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCF.
- Divide the larger number (56) by the smaller number (42): 56 ÷ 42 = 1 with a remainder of 14.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (42) and the smaller number with the remainder (14): 42 ÷ 14 = 3 with a remainder of 0.
- Since the remainder is 0, the GCF is the last non-zero remainder, which is 14.
Therefore, the GCF of 42 and 56 is 14. However, as we are focusing solely on 42, the GCF remains 42.
The Significance of GCF in Mathematics and Beyond
The concept of GCF extends far beyond simple arithmetic exercises. Its applications are widespread across numerous mathematical domains and practical fields:
-
Simplifying Fractions: The GCF is crucial for simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 42/56 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF (14), resulting in the simplified fraction 3/4.
-
Algebra: GCF plays a vital role in factoring algebraic expressions. Finding the GCF of terms in an expression allows for simplification and solving equations.
-
Number Theory: GCF is a fundamental concept in number theory, forming the basis for numerous theorems and algorithms. Concepts like least common multiple (LCM) are directly related to GCF.
-
Cryptography: GCF and related concepts are used in cryptographic algorithms to ensure data security.
-
Computer Science: GCF algorithms are used in computer science for various tasks, including optimizing computations and data structures.
-
Real-World Applications: GCF finds practical applications in various areas such as:
- Geometry: Finding the dimensions of the largest square that can tile a rectangle.
- Measurement: Converting units of measurement.
- Project Management: Optimizing resource allocation.
Exploring the Relationship between GCF and LCM
The greatest common factor (GCF) and the least common multiple (LCM) are closely related concepts. The LCM is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers in a given set. For any two positive integers 'a' and 'b', the relationship between their GCF and LCM is given by:
a x b = GCF(a, b) x LCM(a, b)
This formula provides a handy way to find the LCM if the GCF is known, and vice versa. For example, if we know the GCF of 42 and another number (let's use 56 again, as before) is 14, we can find their LCM:
42 x 56 = 14 x LCM(42, 56) 2352 = 14 x LCM(42, 56) LCM(42, 56) = 2352 / 14 = 168
Therefore, the LCM of 42 and 56 is 168. This formula highlights the interconnectedness of these fundamental concepts in number theory.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous GCF of 42
While the seemingly simple question of "What is the greatest common factor of 42?" might appear trivial at first glance, the exploration reveals a wealth of information about the fundamental concepts of number theory. Understanding the GCF, its various methods of calculation (listing factors, prime factorization, Euclidean algorithm), and its profound connections with other mathematical concepts and real-world applications unveils its significance in a multitude of fields. The GCF of 42, when considered alone, is simply 42, but the journey to understanding how to arrive at that answer, and the broader implications of the GCF itself, makes this seemingly basic question a rich starting point for mathematical exploration. The concepts and techniques discussed here are not just limited to 42; they are widely applicable to a range of numbers and mathematical problems, providing a robust foundation for advanced mathematical studies and practical problem-solving.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Word Ending With On
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 80
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Much Atp Does Anaerobic Respiration Produce
Mar 15, 2025
-
Determine The Equation Of The Circle Graphed Below
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Percent Is 50 Of 60
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Greatest Common Factor Of 42 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
