What Are The Factors For 67
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
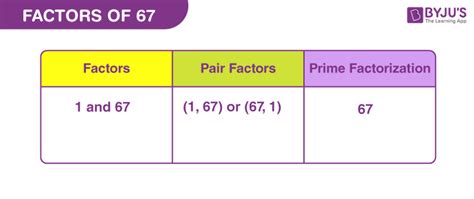
Table of Contents
Decoding the Factors of 67: A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Divisibility
The question "What are the factors of 67?" might seem deceptively simple. However, exploring this seemingly straightforward mathematical concept opens doors to a deeper understanding of prime numbers, divisibility rules, and the fundamental building blocks of arithmetic. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader context of prime factorization and its importance in various mathematical fields.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the factors of 67, let's establish a clear understanding of fundamental terminology. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides that number exactly without leaving a remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly. Divisibility, in turn, refers to the ability of one number to be divided by another without leaving a remainder.
The Unique Case of 67: A Prime Number
Now, let's address the primary question: what are the factors of 67? The answer is surprisingly concise: 1 and 67. This is because 67 is a prime number.
A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. This characteristic sets prime numbers apart from composite numbers, which have more than two divisors.
The primality of 67 can be verified through trial division. We can systematically check if any whole number from 2 to the square root of 67 (approximately 8.18) divides 67 without leaving a remainder. Since no such number exists, we confirm that 67 is indeed a prime number.
Prime Factorization and its Significance
The concept of prime numbers is fundamental to prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. For instance, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). This representation is unique for each composite number, meaning there's only one way to express it as a product of primes (ignoring the order of the factors).
While 67 doesn't undergo prime factorization itself (being prime), understanding prime factorization is crucial for comprehending number theory and its applications. It's a cornerstone in various mathematical disciplines, including:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are at the heart of modern encryption algorithms, such as RSA, which secure online transactions and communication. The difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime components forms the basis of the security of these systems.
-
Modular Arithmetic: This branch of mathematics, widely used in computer science and cryptography, heavily relies on prime numbers and their properties. Modular arithmetic involves performing arithmetic operations within a given modulus (a whole number). Prime numbers play a significant role in determining the properties of these operations.
-
Number Theory: Prime numbers are central to many unsolved problems in number theory, such as the twin prime conjecture (which postulates that there are infinitely many pairs of prime numbers that differ by 2) and Goldbach's conjecture (which states that every even integer greater than 2 can be expressed as the sum of two primes). These conjectures continue to drive research and advance our understanding of numbers.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers and their properties are vital in abstract algebra, a branch of mathematics that deals with algebraic structures like groups, rings, and fields. Prime ideals, a concept rooted in prime numbers, are crucial in studying these structures.
Testing for Primality: Algorithms and Methods
Determining whether a large number is prime can be computationally intensive. While trial division works for smaller numbers, it becomes inefficient for extremely large numbers. Several sophisticated algorithms have been developed to efficiently test for primality, including:
-
The Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm is a relatively simple method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It's effective for smaller ranges but becomes less efficient for very large numbers.
-
Probabilistic Primality Tests: These tests don't guarantee a definitive answer but offer a high probability of determining whether a number is prime. Examples include the Miller-Rabin test and the Solovay-Strassen test. These are frequently used in cryptography due to their speed.
-
Deterministic Primality Tests: These tests guarantee a correct answer, unlike probabilistic tests. The AKS primality test is a notable example; however, it is computationally more expensive than probabilistic tests.
The Importance of Prime Numbers in Real-World Applications
Beyond the theoretical realm, prime numbers have profound real-world applications:
-
Secure Communication: The security of online banking, e-commerce, and secure messaging relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components. Prime numbers form the foundation of many cryptographic algorithms used to protect sensitive data.
-
Hashing Algorithms: Prime numbers are employed in hash functions, which are used to create unique digital fingerprints of data. These fingerprints are crucial in data integrity checks and are used in various applications, including databases and blockchain technology.
-
Random Number Generation: Prime numbers play a crucial role in generating truly random numbers, which are essential in simulations, cryptography, and statistical analysis. Algorithms that leverage the properties of prime numbers help create sequences that are statistically unbiased.
-
Error Correction Codes: Prime numbers are used in error-correction codes, which are employed in data transmission and storage to detect and correct errors introduced during transmission or storage. These codes ensure data integrity and reliability.
Conclusion: The Significance of a Single Prime Number
While the factors of 67 might initially seem trivial—simply 1 and 67—the context of this seemingly simple question reveals the profound importance of prime numbers in mathematics and its applications. The primality of 67, and the properties of prime numbers in general, underpin many crucial aspects of modern technology and continue to drive mathematical research. Understanding prime numbers and their unique properties is essential for anyone interested in the foundations of mathematics and its impact on the world around us. This deep dive into the factors of 67 serves as a stepping stone to appreciating the elegance and power of prime numbers and their far-reaching consequences.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 300 M
Mar 17, 2025
-
Sulfur Number Of Protons Neutrons And Electrons
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Moral Of The Tortoise And The Hare
Mar 17, 2025
-
What Is The Melting Point In Celsius
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Crossing Over Happen In Mitosis
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Factors For 67 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
