Sulfur Number Of Protons Neutrons And Electrons
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
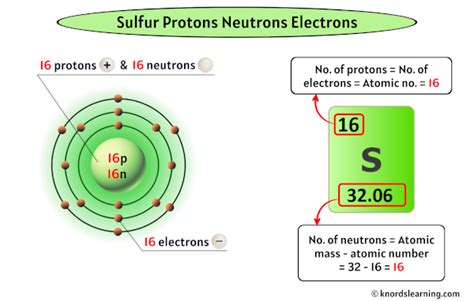
Table of Contents
Sulfur: Unpacking Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Sulfur, a vibrant yellow nonmetal with the chemical symbol S, plays a crucial role in various biological and industrial processes. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons, is fundamental to grasping its chemical behavior and applications. This article delves deep into the atomic composition of sulfur, exploring its isotopes, electron configuration, and the implications of its subatomic particles.
Understanding Atomic Structure
Before we delve into the specifics of sulfur, let's establish a foundational understanding of atomic structure. Every atom is composed of three fundamental subatomic particles:
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the atom's nucleus. The number of protons defines the element; it's the element's atomic number.
- Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles also residing in the atom's nucleus. Neutrons contribute to the atom's mass but not its charge.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus in electron shells or energy levels. The number of electrons generally equals the number of protons in a neutral atom.
The arrangement of these subatomic particles determines an atom's properties and how it interacts with other atoms.
Sulfur's Atomic Number and Protons
Sulfur's atomic number is 16. This means that every sulfur atom possesses 16 protons in its nucleus. This defining characteristic distinguishes sulfur from all other elements on the periodic table. The positive charge of these 16 protons is balanced by the negative charge of 16 electrons in a neutral sulfur atom.
Significance of the Atomic Number
The atomic number is critical for several reasons:
- Element Identification: It uniquely identifies sulfur as distinct from other elements.
- Chemical Properties: The number of protons directly influences the number of electrons, which in turn determines the atom's chemical reactivity and bonding behavior.
- Periodic Table Placement: The atomic number dictates sulfur's position within the periodic table, allowing us to predict its properties based on its placement among other elements.
Neutrons in Sulfur Isotopes
Unlike the fixed number of protons, the number of neutrons in a sulfur atom can vary. Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Sulfur has several naturally occurring isotopes, the most common being:
- Sulfur-32 (³²S): This is the most abundant isotope, comprising approximately 95% of naturally occurring sulfur. It has 16 protons and 16 neutrons.
- Sulfur-34 (³⁴S): This isotope has 16 protons and 18 neutrons.
- Sulfur-33 (³³S): This isotope has 16 protons and 17 neutrons.
- Sulfur-36 (³⁶S): This is a less abundant, stable isotope with 16 protons and 20 neutrons.
The different isotopes of sulfur have nearly identical chemical properties because the number of protons and electrons remains constant. However, their physical properties, such as mass, can differ slightly due to the varying number of neutrons.
Importance of Isotopes in Science
Isotopes find applications in various scientific fields:
- Radioactive Isotopes (though not naturally occurring in significant amounts): Radioactive isotopes of sulfur can be used as tracers in biological and environmental studies.
- Geochemical Analysis: The ratios of different sulfur isotopes in geological samples provide insights into the processes that formed those samples.
- Archaeological Dating: Sulfur isotopes can aid in dating certain geological and archeological artifacts.
Electrons in Sulfur: Electron Configuration and Shells
A neutral sulfur atom contains 16 electrons, mirroring the number of protons. These electrons are distributed in specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus, according to the principles of electron configuration. The electron configuration of sulfur is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁴.
Let's break down this configuration:
- 1s²: Two electrons occupy the first energy level (n=1) in the s orbital.
- 2s²: Two electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2) in the s orbital.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons occupy the second energy level (n=2) in the three p orbitals.
- 3s²: Two electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3) in the s orbital.
- 3p⁴: Four electrons occupy the third energy level (n=3) in the three p orbitals.
Valence Electrons and Chemical Reactivity
The electrons in the outermost shell, known as valence electrons, are crucial for determining an element's chemical reactivity. In sulfur, the four electrons in the 3p subshell are valence electrons. This configuration explains sulfur's ability to form two covalent bonds (sharing electrons) or to gain two electrons to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell) and a -2 charge. This is reflected in its common oxidation states of -2, +2, +4, and +6.
Sulfur's Chemical Bonding
Sulfur's ability to form covalent bonds is demonstrated in various compounds. It can form single, double, and even triple bonds with other atoms. This versatility enables sulfur to participate in a wide range of chemical reactions and form numerous compounds, which explains its presence in various substances, from proteins to industrial chemicals.
Applications of Sulfur and its Compounds
Sulfur's unique properties and reactivity make it essential in numerous industrial and biological applications:
- Sulfuric Acid Production: Sulfur is a crucial raw material for the production of sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), one of the most widely used industrial chemicals. Sulfuric acid has applications in fertilizer production, metal processing, and many other industries.
- Vulcanization of Rubber: Sulfur is vital in the vulcanization process, transforming natural rubber into durable and elastic materials.
- Pharmaceuticals and Medicine: Sulfur-containing compounds are present in various pharmaceuticals and have medicinal properties.
- Fertilizers: Sulfur is an essential nutrient for plant growth and is included in many fertilizers.
- Food Additives: Some sulfur compounds are used as food preservatives and antioxidants.
- Matches: Elemental sulfur is a component in the head of safety matches.
- Cosmetics: Some sulfur-based compounds are used in cosmetic products.
Sulfur in the Environment and Biological Systems
Sulfur plays a significant role in environmental processes:
- Sulfur Cycle: Sulfur is a crucial element in the biogeochemical sulfur cycle, where it undergoes various transformations between different chemical forms.
- Air Pollution: Sulfur dioxide (SO₂) released from burning fossil fuels contributes to acid rain and air pollution.
- Biological Roles: Sulfur is a crucial component of many amino acids, proteins, and enzymes in living organisms. It's vital for many biological processes.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Sulfur's Atomic Structure
Understanding the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in sulfur is paramount to comprehending its unique chemical behavior, its wide range of applications, and its impact on the environment and biological systems. From its role in industrial processes to its fundamental contribution to life itself, sulfur's significance is undeniable. The exploration of its isotopes and electron configuration further clarifies its reactivity and the diverse ways it interacts with other elements, shaping the world around us. The detailed knowledge of sulfur's atomic structure helps scientists in diverse fields to better understand and utilize this vital element. Furthermore, the ongoing research into sulfur's properties and applications continues to reveal new insights and potential uses for this versatile nonmetal.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Symmetry Lines Does A Square Have
Mar 17, 2025
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sulfur Number Of Protons Neutrons And Electrons . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
