What Is The Melting Point In Celsius
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 6 min read
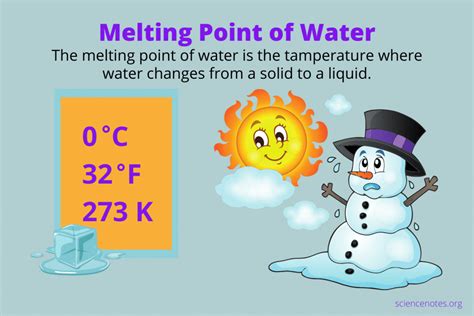
Table of Contents
What is the Melting Point in Celsius? A Comprehensive Guide
The melting point, a fundamental property of matter, represents the specific temperature at which a solid transitions into a liquid state. Understanding melting points is crucial in various scientific fields, from materials science and chemistry to geology and meteorology. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of melting points, explaining what they are, how they're determined, and the factors that influence them. We'll specifically focus on expressing these points in Celsius, the most widely used temperature scale globally.
Understanding the Phase Transition: Solid to Liquid
At a molecular level, the melting point signifies the temperature at which the kinetic energy of the molecules within a solid surpasses the intermolecular forces holding them in a fixed, ordered structure. As heat is applied, the molecules vibrate more vigorously. Once the temperature reaches the melting point, this vibrational energy overcomes the attractive forces, allowing the molecules to break free from their rigid lattice and move more freely, characteristic of the liquid phase. This transition is reversible; upon cooling, the liquid will solidify at the same temperature, its freezing point. For pure substances, the melting and freezing points are identical.
Factors Affecting Melting Points
Several factors contribute to the variance in melting points observed across different substances:
-
Intermolecular Forces: The strength of the attractive forces between molecules is a primary determinant. Stronger forces, such as hydrogen bonds (found in water) or ionic bonds (found in salts), lead to higher melting points because more energy is needed to overcome these interactions. Weaker forces like van der Waals forces result in lower melting points.
-
Molecular Weight: Generally, as molecular weight increases, so does the melting point. Larger molecules have more surface area for intermolecular interactions, strengthening the attractive forces and requiring more energy to initiate melting.
-
Molecular Shape and Symmetry: The shape and symmetry of molecules influence their packing efficiency in the solid state. Substances with highly symmetrical molecules often pack more efficiently, leading to stronger intermolecular forces and higher melting points.
-
Impurities: The presence of impurities in a substance typically lowers its melting point. Impurities disrupt the regular arrangement of molecules in the solid lattice, weakening the intermolecular forces and making it easier for the substance to transition to the liquid phase. This principle is exploited in techniques like cryoscopy, used to determine the molar mass of a solute.
-
Pressure: Pressure also influences the melting point. For most substances, increased pressure raises the melting point, as it hinders the expansion that occurs during melting. However, water is a notable exception; its melting point decreases slightly with increasing pressure. This anomalous behavior is due to the unique structure of ice, where the molecules are less densely packed than in liquid water.
Measuring and Reporting Melting Points in Celsius
The melting point of a substance is typically determined experimentally using a melting point apparatus. This apparatus usually involves heating the sample at a controlled rate and observing the temperature at which melting begins and ends. The reported melting point is often a range, reflecting the slight variations in temperature during the melting process. For example, a substance might be reported to have a melting point of 110-112 °C. The range arises from factors such as impurities, heating rate, and the sensitivity of the measuring instrument.
The Celsius scale, officially known as the degree Celsius (°C), is widely used for expressing melting points, especially in scientific literature and everyday applications. It's defined by the freezing and boiling points of water at standard atmospheric pressure: 0 °C for freezing and 100 °C for boiling.
Examples of Melting Points in Celsius:
Here are some examples of commonly known substances and their melting points in Celsius:
- Water (H₂O): 0 °C (at standard pressure)
- Ice (H₂O): 0 °C (at standard pressure)
- Sodium Chloride (NaCl): 801 °C
- Iron (Fe): 1538 °C
- Aluminum (Al): 660 °C
- Gold (Au): 1064 °C
- Silver (Ag): 962 °C
- Copper (Cu): 1085 °C
- Platinum (Pt): 1768 °C
- Tungsten (W): 3422 °C
The exceptionally high melting point of tungsten underscores the strength of metallic bonding in this element. Conversely, the relatively low melting point of water highlights the significance of hydrogen bonding.
Applications of Melting Point Determination
The determination of melting points has numerous practical applications across diverse fields:
-
Material Science: Melting point analysis is crucial in identifying and characterizing materials. It's used to assess the purity of substances, as impurities generally lower the melting point. This is vital in the production and quality control of various materials, including polymers, metals, and pharmaceuticals.
-
Chemistry: Melting point determination is a fundamental technique in organic chemistry for identifying and purifying compounds. The comparison of experimental melting points with literature values provides a powerful method for substance identification.
-
Pharmaceutical Industry: The melting point is a critical quality control parameter in the pharmaceutical industry. It helps ensure the purity and consistency of drug formulations, contributing to their efficacy and safety.
-
Geology: Melting points of minerals provide valuable insights into geological processes. The melting point of rocks and minerals under various conditions of pressure and temperature is crucial for understanding the formation and evolution of Earth's crust and mantle.
-
Food Science: Melting points play a role in the food industry, influencing the texture and properties of food products. For example, the melting point of fats and oils impacts their behavior in cooking and baking.
-
Forensic Science: Melting point analysis can be a helpful tool in forensic investigations, aiding in the identification of unknown substances.
Melting Point Depression and its Significance
As mentioned earlier, impurities typically lower the melting point of a substance. This phenomenon is known as melting point depression. The extent of the depression is proportional to the concentration of the impurity. This principle is utilized in various applications, including:
-
Cryoscopy: This technique uses the melting point depression to determine the molar mass of an unknown solute. By measuring the change in melting point of a solvent upon the addition of a solute, the molar mass of the solute can be calculated using established relationships.
-
Eutectics: A eutectic is a mixture of two or more components that melts at a lower temperature than any of its constituents. The eutectic point represents the lowest melting point attainable for a given mixture composition. Eutectic mixtures are utilized in various applications, such as soldering and alloy production.
Conclusion: Melting Point – A Key Property of Matter
The melting point, expressed in Celsius or other temperature scales, is a fundamental physical property providing valuable insights into the nature of materials. Its determination has widespread applications across diverse scientific and technological fields. Understanding the factors influencing melting points, methods for their measurement, and the implications of melting point depression is essential for numerous scientific and industrial processes. From characterizing new materials to ensuring the quality of pharmaceuticals, the significance of the melting point in Celsius continues to be pivotal in various aspects of our world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Melting Point In Celsius . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
