What Are The Common Factors Of 54
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 5 min read
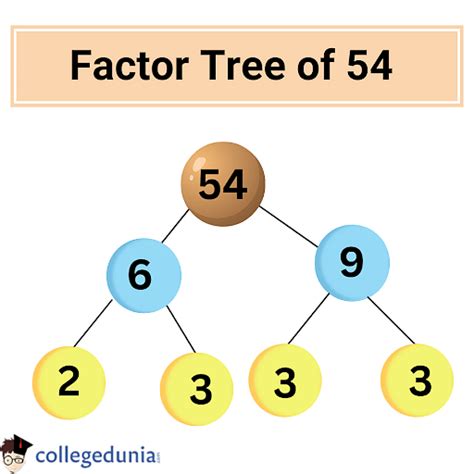
Table of Contents
What are the Common Factors of 54? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise, but it delves into the fascinating world of number theory and has practical applications in various fields, from cryptography to computer science. This article explores the common factors of 54, providing a comprehensive understanding of the process and the underlying mathematical principles. We'll go beyond simply listing the factors, exploring the concepts of prime factorization, greatest common divisor (GCD), and least common multiple (LCM), showcasing their relevance and practical use.
Understanding Factors
Before we delve into the specifics of 54, let's solidify our understanding of factors. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly, leaving no remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
Finding all the factors of a number is a fundamental step in many mathematical problems. It's the building block for understanding more advanced concepts like prime factorization and the greatest common divisor.
Prime Factorization: The Building Blocks
Prime factorization is a crucial technique in number theory. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors. This representation is unique for every number (except for the order of the factors).
Let's find the prime factorization of 54:
- We start by dividing 54 by the smallest prime number, 2: 54 ÷ 2 = 27.
- Now, we look at 27. It's not divisible by 2, but it is divisible by 3: 27 ÷ 3 = 9.
- 9 is also divisible by 3: 9 ÷ 3 = 3.
- Finally, we have reached a prime number, 3.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 54 is 2 x 3 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3³. This representation is incredibly useful because it reveals the fundamental building blocks of the number 54.
Finding the Factors of 54
Using the prime factorization (2 x 3³), we can systematically find all the factors of 54. We do this by considering all possible combinations of the prime factors:
- Using only 2: 2
- Using only 3: 3, 9, 27
- Using 2 and 3: 6, 18, 54
- Using only 1: 1
Therefore, the factors of 54 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18, 27, and 54.
Common Factors: Sharing Divisors
If we are considering multiple numbers, we can identify their common factors. These are the factors that are shared by all the numbers in the set. For instance, if we were to consider the numbers 54 and another number, say 36, we would need to find the factors shared by both.
Let's find the prime factorization of 36:
36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
Now let's compare the prime factorizations of 54 (2 x 3³) and 36 (2² x 3²):
- Both have a factor of 2.
- Both have factors of 3.
To find the common factors, we look at the lowest power of each common prime factor:
- The lowest power of 2 is 2¹.
- The lowest power of 3 is 3².
Therefore, the common factors of 54 and 36 are found by combining these:
- 1 (2⁰ x 3⁰)
- 2 (2¹ x 3⁰)
- 3 (2⁰ x 3¹)
- 6 (2¹ x 3¹)
- 9 (2⁰ x 3²)
- 18 (2¹ x 3²)
The common factors of 54 and 36 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides all the numbers in a set without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is a crucial step in simplifying fractions and solving various mathematical problems.
For the numbers 54 and 36, the GCD is 18, as it is the largest number that divides both 54 and 36.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive number that is a multiple of all the numbers in a set. LCM is frequently used in problems involving fractions, cycles, and periodic phenomena.
To find the LCM of 54 and 36, we can use the prime factorizations:
54 = 2 x 3³ 36 = 2² x 3²
The LCM is found by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
LCM(54, 36) = 2² x 3³ = 4 x 27 = 108
Applications of Common Factors and GCD/LCM
The concepts of common factors, GCD, and LCM have a wide range of applications across various fields:
- Fraction Simplification: Finding the GCD allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms.
- Scheduling: LCM is used to determine the time when events with different periodicities will occur simultaneously (e.g., scheduling buses with different routes).
- Cryptography: Number theory, including prime factorization and GCD, plays a crucial role in modern cryptography.
- Computer Science: Algorithms involving GCD and LCM are used in various computer science applications, including optimization problems.
- Geometry: GCD and LCM are applicable in geometric problems dealing with areas, volumes, and proportions.
Beyond 54: Generalizing the Process
The methods we used for finding the factors and GCD/LCM of 54 can be generalized to any integer. The prime factorization remains the cornerstone of these calculations. By understanding the prime factorization of a number, we can easily determine its factors, common factors with other numbers, and the GCD and LCM. This systematic approach eliminates guesswork and provides a clear path to solving problems involving factors and divisors.
Conclusion
Understanding the common factors of a number like 54 is far more than just a basic arithmetic exercise; it's a gateway to a deeper appreciation of number theory. Through prime factorization, we can systematically identify all the factors, common factors, GCD, and LCM, providing tools that have practical implications across numerous disciplines. Whether simplifying fractions, scheduling events, or securing data, the principles explored here form the foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques. The seemingly simple act of finding the factors of 54 opens a door to a rich world of mathematical exploration and its diverse applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Mixed Number For 5 2
Mar 19, 2025
-
Rounding Percentages To The Nearest Tenth
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Happens To Acceleration When Mass Is Doubled
Mar 19, 2025
-
The Hottest Layer Of The Earth Is The
Mar 19, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Rough Er And Smooth Er
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Common Factors Of 54 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
