The Hottest Layer Of The Earth Is The
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
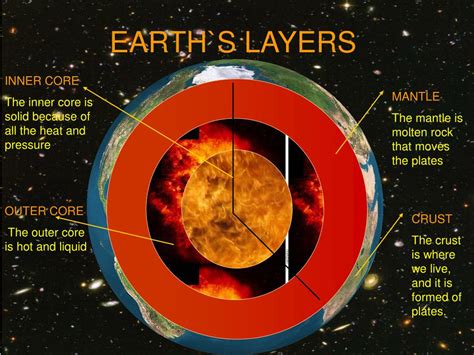
Table of Contents
The Hottest Layer of the Earth Is the Inner Core
The Earth, our vibrant and dynamic home, is far more than just the surface we inhabit. Beneath our feet lies a complex system of layers, each with its unique characteristics and contributing to the planet's overall functionality. While the surface is constantly reshaped by weather and geological events, the heart of our planet burns with intense heat, reaching temperatures unimaginable to us on the surface. The question, "What is the hottest layer of the Earth?" has a definitive answer: the inner core.
Delving into the Earth's Interior: A Layered Planet
Before focusing on the scorching inner core, let's briefly explore the Earth's layered structure. This understanding provides context for appreciating the extreme conditions found at the planet's center. The Earth's layers, from outermost to innermost, are:
1. Crust: The Earth's Brittle Shell
The crust is the outermost solid shell of the Earth, relatively thin compared to the other layers. It’s composed of various types of rock and is further divided into oceanic crust (thinner and denser) and continental crust (thicker and less dense). This layer is where we live, build our cities, and cultivate our land. The crust is dynamic, constantly changing through plate tectonics, volcanic eruptions, and earthquakes.
2. Mantle: A Viscous, Rocky Layer
Beneath the crust lies the mantle, a significantly thicker layer comprising primarily silicate rocks rich in iron and magnesium. The mantle is not a solid mass but rather behaves like a highly viscous fluid, exhibiting slow, convective movement over geological timescales. This movement is a crucial driver of plate tectonics, responsible for continental drift and the formation of mountain ranges. Temperatures within the mantle increase with depth, reaching thousands of degrees Celsius.
3. Outer Core: A Liquid Sea of Iron
The outer core, a layer of molten iron and nickel, is a swirling, electrically conductive fluid. It's the movement of this liquid metal that generates the Earth's magnetic field, a crucial protective shield against harmful solar radiation. The intense heat and pressure in the outer core maintain the iron in its liquid state, despite the substantial pressures.
4. Inner Core: A Solid Sphere of Iron and Nickel
Finally, at the very heart of our planet lies the inner core, a solid sphere of mostly iron and nickel. This is the hottest layer of the Earth, with estimated temperatures ranging from 5200°C (9392°F) to 5700°C (10300°F) – hotter than the surface of the Sun. The immense pressure at the Earth's center, approximately 3.6 million times the pressure at sea level, is responsible for keeping this iron-nickel alloy solid despite the extreme heat.
The Inner Core: A Realm of Extreme Conditions
The inner core's extreme conditions are a result of several factors:
-
Residual Heat from Planet Formation: A significant portion of the inner core's heat is residual heat from the Earth's formation billions of years ago. The accretion of dust and gas during the planet's early stages generated immense heat, which is still slowly dissipating.
-
Radioactive Decay: Radioactive isotopes within the Earth's interior, such as uranium, thorium, and potassium, undergo radioactive decay, releasing heat as a byproduct. This process continues to contribute to the inner core's high temperature.
-
Gravitational Compression: The immense pressure at the Earth's center due to the weight of overlying layers also contributes to the heat generation. The compression of material generates friction and heat.
-
Heat Transfer from the Mantle: Heat from the mantle is also transferred to the core through convection currents, further contributing to its temperature.
The Inner Core's Composition and Properties
The inner core's composition is primarily iron and nickel, with trace amounts of other elements likely present. The high pressure prevents the iron from solidifying into a crystalline structure, instead forming a highly dense, almost perfect sphere. While predominantly solid, scientists believe the inner core may exhibit a slight degree of plasticity, allowing for slow movement and deformation over extremely long timescales.
Understanding the Inner Core's Significance
The inner core plays a crucial role in several aspects of the Earth's dynamics:
-
Magnetic Field Generation: The interaction between the solid inner core and the liquid outer core is believed to be a key component in generating the Earth's magnetic field through a process known as the geodynamo. This magnetic field protects us from harmful solar winds and cosmic radiation.
-
Plate Tectonics: While the mantle's convection plays a dominant role in plate tectonics, the heat emanating from the core contributes to this process by driving mantle convection.
-
Seismic Wave Studies: Studies of seismic waves that travel through the Earth provide essential insights into the inner core's properties. The way these waves refract and reflect allows scientists to estimate the inner core's size, composition, and temperature.
Ongoing Research and Future Discoveries
Scientists continue to refine their understanding of the Earth's inner core through advanced seismic imaging techniques, computational modelling, and laboratory experiments that simulate the extreme conditions of the Earth's interior. Future research is expected to provide even more precise details about the inner core's composition, temperature variations, and its role in shaping our planet's dynamics. Further investigations may reveal more about the subtle movements within the inner core and their impact on the Earth's magnetic field. The study of the inner core is a dynamic field, with ongoing research continuously expanding our knowledge of this fascinating and extreme environment.
The Inner Core's Influence on Life on Earth
The seemingly remote inner core exerts a surprising influence on life on Earth. Its role in generating the Earth's magnetic field is critical to shielding us from harmful solar radiation, which could otherwise strip away our atmosphere and render the planet uninhabitable. The heat from the inner core also drives mantle convection, a process that influences plate tectonics and volcanic activity. These geological processes, while sometimes destructive, also contribute to the cycling of nutrients and the formation of landscapes that support life.
Mysteries of the Inner Core
Despite significant advancements, many mysteries surrounding the inner core remain unsolved. These include:
-
Precise composition: While predominantly iron and nickel, the exact proportions of these elements and the presence of trace elements still require further investigation.
-
Crystal Structure: Understanding the precise crystal structure of the inner core under such extreme pressure remains a challenge.
-
Growth and Evolution: The processes that govern the inner core's growth and evolution over geological time scales are not fully understood.
-
Relationship with the Outer Core: The exact mechanisms of interaction between the inner and outer cores in generating the Earth's magnetic field are still being actively researched.
Conclusion: The Heart of Our Planet
The inner core, the hottest layer of the Earth, is a realm of extreme conditions that profoundly impacts life on the surface. Its immense heat, largely a remnant of planetary formation and ongoing radioactive decay, drives dynamic processes that shape our planet's landscape and protect life. Though hidden deep beneath our feet, this fiery heart plays a critical role in sustaining the conditions that make life on Earth possible. Continuing research into the inner core will undoubtedly unveil even more fascinating insights into our planet's dynamic history and its future evolution. The exploration of this extreme environment is a testament to humanity's quest for knowledge and our ongoing effort to understand the complexities of the world around us. The Earth's inner core, though unseen, remains a captivating subject of scientific inquiry, continually revealing new and exciting discoveries.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet In 50 Yards
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Pure Air A Substance Or Mixture
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is 1 8 In A Percent
Mar 19, 2025
-
Only Moveable Bone In The Skull
Mar 19, 2025
-
Brain Or Heart Which Is More Important
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Hottest Layer Of The Earth Is The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
