What Are Prime Factors Of 14
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
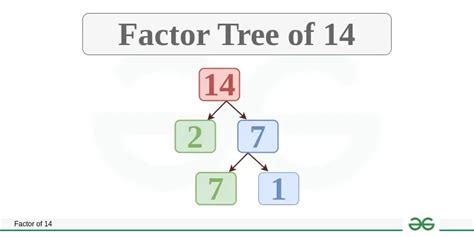
Table of Contents
Unpacking the Prime Factorization of 14: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What are the prime factors of 14?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the underlying concepts provides a robust understanding of prime numbers, factorization, and their significance in mathematics. This article delves into the prime factorization of 14, explaining the process, its implications, and related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the prime factorization of 14, we need a solid grasp of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. The number 1 is not considered prime; it's a unique number with its own special properties.
Key Characteristics of Prime Numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid centuries ago, demonstrating the endless expanse of prime numbers.
- Building Blocks of Numbers: Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other integers (whole numbers). Every composite number (a number that is not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of primes. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Prime Factorization: Breaking Down Numbers
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a composite number as a product of its prime factors. This process involves repeatedly dividing the number by the smallest prime number possible until you are left with only prime numbers. The result is a unique set of prime numbers, regardless of the order in which you perform the division.
Finding the Prime Factors of 14
Now, let's apply this to find the prime factors of 14.
-
Start with the smallest prime number, 2: 14 is an even number, so it's divisible by 2. 14 ÷ 2 = 7.
-
Consider the result, 7: 7 is a prime number (only divisible by 1 and 7).
Therefore, the prime factorization of 14 is 2 x 7. This means that 2 and 7 are the prime factors of 14. There are no other prime numbers that can be multiplied together to equal 14. This unique factorization is guaranteed by the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
The Significance of Prime Factorization
The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factors of a number has far-reaching consequences in various mathematical fields and applications.
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers play a crucial role in modern cryptography, particularly in public-key cryptography systems like RSA. These systems rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The security of these systems hinges on this computational challenge. The larger the numbers involved, the more computationally intensive it becomes to factor them, guaranteeing the security of sensitive data.
-
Number Theory: Prime factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties of integers. Many important theorems and conjectures in number theory relate to prime numbers and their distribution. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most significant unsolved problems in mathematics, deals with the distribution of prime numbers.
-
Algebra: Prime factorization helps simplify algebraic expressions and solve equations. By factoring polynomials, we can find their roots and gain insights into their behavior. This is fundamental to solving various algebraic problems and understanding the nature of equations.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for prime factorization are crucial in computer science, used in tasks like cryptography, data compression, and database management. The efficiency of these algorithms directly impacts the performance of these systems.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers are also significant in coding theory, specifically in error detection and correction codes. These codes use mathematical properties of prime numbers to ensure data integrity during transmission or storage.
Beyond 14: Exploring Other Factorizations
While we've focused on 14, let's examine the prime factorization of some other numbers to solidify our understanding:
Example 1: Prime Factorization of 36
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 is prime.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 36 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, which can also be written as 2² x 3².
Example 2: Prime Factorization of 100
- 100 ÷ 2 = 50
- 50 ÷ 2 = 25
- 25 ÷ 5 = 5
- 5 is prime.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 100 is 2 x 2 x 5 x 5, or 2² x 5².
Example 3: Prime Factorization of a Larger Number - 3780
Let's tackle a larger number to demonstrate a systematic approach.
- Divide by 2: 3780 ÷ 2 = 1890
- Divide by 2 again: 1890 ÷ 2 = 945
- Divide by 3: 945 ÷ 3 = 315
- Divide by 3 again: 315 ÷ 3 = 105
- Divide by 3 again: 105 ÷ 3 = 35
- Divide by 5: 35 ÷ 5 = 7
- 7 is prime.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 3780 is 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 x 5 x 7, or 2² x 3³ x 5 x 7.
Methods for Finding Prime Factors
Several methods can be used to find the prime factors of a number:
-
Trial Division: This involves systematically dividing the number by each prime number, starting from the smallest (2), until you reach a prime number. This method is straightforward but can be time-consuming for large numbers.
-
Factor Trees: This visual method helps break down a number into its prime factors step-by-step. Branches represent divisions, and the end points are the prime factors.
-
Algorithms: For very large numbers, sophisticated algorithms are employed. These algorithms utilize advanced mathematical techniques to significantly speed up the factorization process.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Prime Factors
The seemingly simple prime factorization of 14, yielding 2 x 7, serves as a gateway to a rich mathematical landscape. Understanding prime numbers and their factorization is not merely an academic exercise; it is fundamental to various fields, from cryptography securing our online interactions to advanced algorithms powering our technology. The journey from a simple factorization to appreciating its profound implications highlights the beauty and power of mathematics. The seemingly simple concept of prime factors underpins much of the digital world we inhabit, showcasing the quiet yet powerful influence of this fundamental mathematical principle. Further exploration into number theory, particularly the intricacies of prime number distribution and advanced factorization algorithms, will continue to unlock new insights and applications in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Factor Of 61
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factor Of 6
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is An Example Of Barter
Mar 13, 2025
-
What Is The Factor Of 68
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Do You Spell 12 In Words
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Prime Factors Of 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
