What Is The Factor Of 68
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
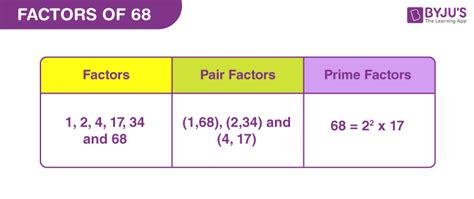
Table of Contents
Unraveling the Factors of 68: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but it opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory and its applications. This comprehensive guide will explore the factors of 68 in detail, explaining the process, revealing underlying mathematical principles, and showcasing the broader significance of factorization in various fields.
What are Factors?
Before diving into the specifics of 68, let's establish a clear understanding of what factors are. A factor of a number is any whole number that divides evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number and get a whole number as the result, then the second number is a factor of the first.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides evenly into 12.
Finding the Factors of 68: A Step-by-Step Approach
Now, let's tackle the task of finding the factors of 68. We can approach this systematically:
-
Start with 1 and the number itself: Every number has 1 and itself as factors. Therefore, 1 and 68 are factors of 68.
-
Check for divisibility by 2: Since 68 is an even number, it's divisible by 2. 68 / 2 = 34, so 2 and 34 are factors.
-
Check for divisibility by 3: To determine divisibility by 3, we add the digits of 68 (6 + 8 = 14). Since 14 is not divisible by 3, neither is 68.
-
Check for divisibility by 4: A number is divisible by 4 if its last two digits are divisible by 4. Since 68 is divisible by 4 (68 / 4 = 17), 4 and 17 are factors.
-
Check for divisibility by 5: A number is divisible by 5 if its last digit is 0 or 5. 68 does not end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
-
Check for divisibility by other prime numbers: We've covered the most common factors. To be thorough, we can continue checking for divisibility by prime numbers, but since we've already found 17, which is a prime number itself, and its pair 4, we have found all pairs.
Therefore, the factors of 68 are 1, 2, 4, 17, 34, and 68.
Prime Factorization of 68
Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. Prime factors are numbers greater than 1 that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.).
To find the prime factorization of 68, we can use a factor tree:
68
/ \
2 34
/ \
2 17
This shows that 68 can be expressed as 2 x 2 x 17, or 2² x 17. This is the prime factorization of 68. This representation is unique for every number and is fundamental in various mathematical applications.
The Significance of Factors and Factorization
Understanding factors and factorization is crucial in many areas:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the greatest common factor (GCF) of the numerator and denominator allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, if we have the fraction 34/68, we can simplify it by dividing both the numerator and denominator by their GCF, which is 34. This simplifies to 1/2.
-
Solving Algebraic Equations: Factoring is a vital technique in solving quadratic and other polynomial equations. Factoring allows us to break down complex equations into simpler ones that can be easily solved.
-
Cryptography: Factorization plays a central role in modern cryptography, particularly in RSA encryption, a widely used method for secure communication over the internet. The security of RSA relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors.
-
Number Theory Research: The study of factors and prime factorization is a core component of number theory, a branch of mathematics dedicated to the properties and relationships of numbers. Number theory has implications in various fields, including computer science, physics, and even music theory.
-
Combinatorics and Probability: The concept of factors is relevant in combinatorial problems where we need to consider the divisors of a number. It's also applied to probability problems involving scenarios with a finite number of outcomes that are multiples of a certain number.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Let's delve deeper into some concepts closely related to factors:
-
Greatest Common Factor (GCF): The GCF of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides evenly into all of them. Finding the GCF is essential for simplifying fractions and solving certain algebraic problems. For example, the GCF of 68 and 102 is 34.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. The LCM is useful for adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. For example, the LCM of 68 and 102 is 204.
-
Divisibility Rules: Understanding divisibility rules can speed up the process of finding factors. These rules provide quick ways to check if a number is divisible by smaller numbers (like 2, 3, 4, 5, etc.) without performing lengthy division.
-
Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). For example, 6 is a perfect number because its proper divisors are 1, 2, and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. The search for perfect numbers is an ongoing area of mathematical research.
Applications of Factorization in Real-World Scenarios
The principles of factorization aren't confined to abstract mathematical theories. They find practical application in various real-world scenarios:
-
Inventory Management: In warehouse or inventory management, efficiently organizing items often requires grouping them into sets based on factors of the total quantity.
-
Construction and Design: Many construction projects involve calculating dimensions based on factors, ensuring that materials are used efficiently. For example, dividing a space into equal sections is related to finding factors of the total area.
-
Scheduling and Time Management: Efficient scheduling often relies on finding common factors or multiples of time units (minutes, hours, days, etc.) to optimize workflow.
-
Data Organization and Analysis: In data analysis, factors can be used to create groups or categories for large datasets.
-
Music Theory: Understanding factors is important in music theory for working with rhythm and time signatures.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Factors
The seemingly simple act of finding the factors of a number like 68 unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and their practical applications. From simplifying fractions and solving equations to securing online communication and optimizing real-world processes, understanding factors and factorization is a cornerstone of mathematical literacy and problem-solving skills. The journey of exploring the factors of 68 has served as a gateway to appreciate the profound depth and widespread relevance of this fundamental concept in mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Find The Number Of Edges On This Solid
May 09, 2025
-
Are Hydrogen Bonds Weaker Than Covalent Bonds
May 09, 2025
-
Which Is A Point Mutation And Not A Frameshift Mutation
May 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Compounds
May 09, 2025
-
Which Statement About Dna Replication Is Correct
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 68 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.