What Is The Factor Of 61
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
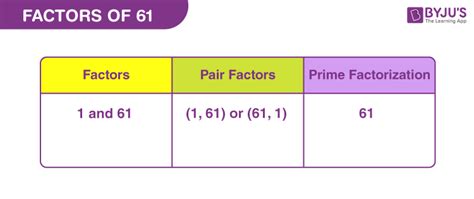
Table of Contents
What are the Factors of 61? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
The question, "What are the factors of 61?" might seem deceptively simple. However, exploring this seemingly basic question opens doors to understanding fundamental concepts in number theory, particularly prime numbers and factorization. This article will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader mathematical context, providing a comprehensive understanding of factors, prime numbers, and their significance.
Understanding Factors
Before we tackle the specific case of 61, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In other words, if we divide the number by its factor, the result is another whole number. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12, because each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
We can represent this mathematically: if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a = c, where 'c' is also an integer.
Finding Factors: A Systematic Approach
Finding factors for smaller numbers is often straightforward. We can simply test each number from 1 up to the number itself. However, for larger numbers, this approach becomes inefficient. There are more sophisticated algorithms used in computer science for factoring large numbers, particularly in cryptography, but for numbers like 61, a simple approach suffices.
The Prime Factorization of 61
Now, let's get to the heart of the matter: what are the factors of 61? The answer is surprisingly simple, yet profoundly significant in the world of mathematics. The only factors of 61 are 1 and 61.
This seemingly simple result points to a crucial concept: prime numbers.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Numbers
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's only divisible by 1 and itself. Prime numbers are considered the fundamental building blocks of all other numbers, as all composite numbers (numbers that are not prime) can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
61, as we've established, fits this definition perfectly. It's only divisible by 1 and itself, making it a prime number. This makes its factorization particularly straightforward: 61 = 1 x 61.
Distinguishing Prime Numbers from Composite Numbers
It's crucial to understand the difference between prime and composite numbers. Composite numbers, unlike prime numbers, have more than two factors. For instance, 12 (a composite number) has factors 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Therefore, it can be factored as 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3).
The Importance of Prime Numbers
The seemingly simple concept of prime numbers has far-reaching implications in various fields, including:
1. Cryptography
Prime numbers form the bedrock of modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms, such as RSA, rely on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime factors. The larger the prime numbers used, the more secure the encryption. The computational challenge of factoring extremely large numbers into their prime components underpins the security of online transactions and sensitive data.
2. Number Theory
Prime numbers are central to number theory, a branch of mathematics dedicated to the study of integers and their properties. Many unsolved problems in mathematics, such as the Riemann Hypothesis (concerning the distribution of prime numbers), continue to fascinate and challenge mathematicians worldwide.
3. Computer Science
Algorithms for finding prime numbers and factoring large numbers are crucial in computer science, particularly in areas like cryptography and data security. The efficiency of these algorithms directly impacts the speed and security of various applications.
4. Abstract Algebra
Prime numbers play a significant role in abstract algebra, providing a foundation for understanding modular arithmetic, group theory, and other abstract mathematical structures.
Methods for Determining Primality
While determining the primality of smaller numbers like 61 is relatively easy, testing for primality with larger numbers requires more sophisticated techniques. Some common methods include:
1. Trial Division
This method involves systematically dividing the number by all integers from 2 up to the square root of the number. If none of these integers divide the number evenly, it's a prime number. However, this method becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers.
2. Sieve of Eratosthenes
This is an ancient algorithm for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. It involves iteratively marking composite numbers, leaving only prime numbers unmarked. While efficient for finding primes up to a certain limit, it's not suitable for determining the primality of a single, arbitrarily large number.
3. Probabilistic Primality Tests
For very large numbers, probabilistic tests are often used. These tests don't guarantee primality with absolute certainty but provide a high probability of correctness. The Miller-Rabin test is a widely used example. These tests are significantly faster than deterministic tests for large numbers and are commonly used in cryptographic applications.
Beyond 61: Exploring Other Prime Numbers
Understanding the factors of 61 provides a foundation for exploring other prime numbers and their properties. The distribution of prime numbers, while seemingly random, follows fascinating patterns that continue to be studied by mathematicians. The prime number theorem, for example, provides an estimate of the number of primes less than a given number.
Conclusion: The Significance of Simplicity
While the question "What are the factors of 61?" appears simple at first glance, its answer opens up a world of mathematical concepts and applications. The fact that 61 is a prime number highlights the fundamental role these numbers play in mathematics, cryptography, computer science, and other fields. The seemingly simple act of factoring a number reveals deep-seated mathematical structures and their significant real-world implications. Understanding prime numbers, like 61, is not just an exercise in abstract mathematics; it’s a key to unlocking a wealth of knowledge across various disciplines. The exploration of 61’s factors leads to a richer appreciation of the fundamental building blocks that shape the world of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 4 6 And 10
Mar 14, 2025
-
Rule For Adding And Subtracting Integers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Determine Whether The Two Triangles Are Similar
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry In Square
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is 400 Square Feet In Feet
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Factor Of 61 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
