The Part Of The Earth Where Life Exists
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
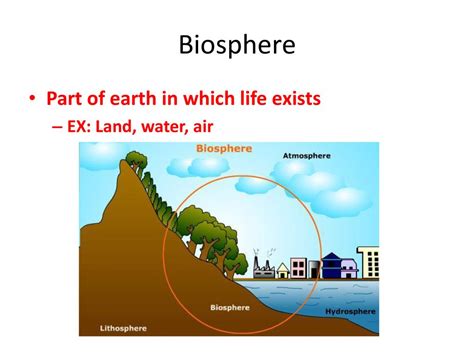
Table of Contents
The Biosphere: Where Life Thrives on Earth
The Earth, our vibrant and dynamic planet, is a unique celestial body in the vast universe. What sets it apart isn't just its size, composition, or location, but the incredible phenomenon that blankets its surface: life. This life, in all its astonishing diversity and complexity, exists within a relatively thin layer known as the biosphere. Understanding the biosphere, its components, its delicate balance, and the threats it faces is crucial for appreciating the fragility and importance of life on Earth.
Defining the Biosphere: A Realm of Life
The biosphere is the zone of life on Earth, encompassing all living organisms and their interactions with the physical environment. It's not a neatly defined layer like the Earth's crust or atmosphere, but rather a complex, interconnected system spanning across various spheres: the lithosphere (Earth's rocky outer layer), the hydrosphere (all the water on Earth), and the atmosphere (the gaseous layer surrounding the planet). Life extends from the deepest ocean trenches to the highest mountain peaks, from the frozen polar regions to the scorching deserts, demonstrating remarkable adaptability and resilience.
The Extent of Life: From the Deepest Depths to the Highest Peaks
While we often associate life with lush forests and vibrant coral reefs, life's reach extends far beyond these familiar ecosystems. Microscopic organisms, extremophiles, thrive in seemingly inhospitable environments. Deep-sea hydrothermal vents, miles beneath the ocean surface, support unique ecosystems powered by chemosynthesis, independent of sunlight. Similarly, certain microorganisms can survive in the extreme cold of Antarctic ice or in the scorching heat of geothermal springs. The limits of the biosphere are constantly being redefined as scientists discover life in previously unexplored environments.
The Interconnectedness of Biosphere Components
The biosphere isn't a collection of isolated ecosystems; it's a vast, interconnected web of life. The interactions between living organisms and their physical surroundings are intricate and essential for the functioning of the entire system. This intricate dance involves:
1. The Role of the Atmosphere: A Protective Shield and Vital Resource
The atmosphere provides crucial protection from harmful solar radiation and regulates the Earth's temperature, making it habitable for life. It's also a vital source of gases like oxygen and carbon dioxide, essential for respiration and photosynthesis. The atmospheric composition itself is constantly being shaped by biological processes, demonstrating the intricate interplay between the biosphere and atmosphere. The carbon cycle, for example, is a prime illustration of this connection, with plants absorbing carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and releasing oxygen, while animals consume oxygen and release carbon dioxide through respiration.
2. The Hydrosphere: The Water Cycle and Life's Foundation
Water is fundamental to life, and the hydrosphere – encompassing oceans, lakes, rivers, and groundwater – plays a critical role in the biosphere. The water cycle, driven by solar energy, constantly circulates water, transporting nutrients and shaping landscapes. Oceans regulate global temperature and provide habitat for a vast array of marine organisms. Freshwater ecosystems, including rivers and lakes, are equally crucial, supporting diverse terrestrial and aquatic life. The availability of water is a key determinant of the distribution and abundance of life across the planet.
3. The Lithosphere: A Foundation for Life and Nutrient Cycling
The lithosphere, the solid Earth's outer layer, provides a physical foundation for life. Soils, formed through the weathering of rocks and the decomposition of organic matter, are crucial for plant growth. Rocks and minerals provide essential nutrients for living organisms, and the weathering of rocks releases these nutrients into the environment. The lithosphere also plays a role in regulating the global carbon cycle, acting as a reservoir for carbon dioxide. The processes of weathering and erosion are integral to the movement of nutrients and the shaping of ecosystems.
Biodiversity: The Tapestry of Life
The biosphere boasts incredible biodiversity, encompassing the vast array of life forms on Earth. This biodiversity is essential for the resilience and stability of ecosystems. Each species plays a unique role, contributing to the overall functioning of the biosphere. The loss of biodiversity, therefore, poses a significant threat to the stability of the entire system.
Ecosystem Services: The Benefits of a Thriving Biosphere
A healthy biosphere provides numerous ecosystem services that benefit humankind. These services include:
- Provisioning services: These include food, freshwater, timber, and fuel.
- Regulating services: These include climate regulation, water purification, and disease control.
- Supporting services: These include nutrient cycling, soil formation, and primary production.
- Cultural services: These include recreation, tourism, and spiritual enrichment.
Threats to the Biosphere: Human Impact and Climate Change
The biosphere is currently facing unprecedented threats, largely due to human activities. These threats include:
1. Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion are leading to significant habitat loss and fragmentation. This results in the loss of biodiversity and the disruption of ecosystem services.
2. Pollution
Pollution from various sources, including industrial emissions, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste, is contaminating air, water, and soil, harming both human health and the environment.
3. Climate Change
Climate change, driven by the release of greenhouse gases, is causing global warming and altering weather patterns. This is affecting ecosystems worldwide, leading to shifts in species distributions, increased frequency of extreme weather events, and rising sea levels.
4. Overexploitation of Resources
Overfishing, overhunting, and unsustainable resource extraction are depleting natural resources and threatening the survival of many species.
Protecting the Biosphere: A Collective Responsibility
Protecting the biosphere is a crucial challenge that requires a concerted global effort. This requires:
1. Conservation Efforts
Establishing protected areas, restoring degraded habitats, and implementing sustainable land management practices are essential for conserving biodiversity and protecting ecosystems.
2. Sustainable Resource Management
Adopting sustainable practices in agriculture, fisheries, and forestry is essential for ensuring the long-term availability of natural resources.
3. Mitigation of Climate Change
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions through the transition to renewable energy, improving energy efficiency, and adopting sustainable transportation systems is crucial for mitigating climate change.
4. Promoting Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the importance of the biosphere and the threats it faces is essential for fostering a sense of responsibility and promoting individual action.
The Future of the Biosphere: A Call to Action
The biosphere is a complex and dynamic system that is essential for the survival of life on Earth. The threats it faces are serious, but it is not too late to take action. By working together, we can protect the biosphere and ensure that future generations can enjoy the benefits of a healthy planet. This requires a fundamental shift in our relationship with the environment, moving towards a more sustainable and equitable approach that prioritizes the long-term health of the planet over short-term economic gains. The future of the biosphere, and indeed the future of humanity, depends on our collective actions today. The urgent need for global cooperation, innovative solutions, and a renewed commitment to environmental stewardship is paramount in ensuring a vibrant and thriving biosphere for generations to come. The Earth's biosphere is a precious and irreplaceable resource; its preservation is not just an environmental imperative, but a moral one.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 7 As A Percent
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Sum Of All Body Chemistry
Mar 21, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Chemical Change
Mar 21, 2025
-
Mixed Number To Decimal Conversion Calculator
Mar 21, 2025
-
Volume Of One Drop Of Water
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Part Of The Earth Where Life Exists . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
