The Numerical Factor Of A Term
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
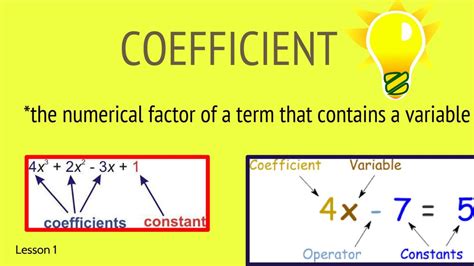
Table of Contents
The Numerical Factor of a Term: A Deep Dive into Mathematical Expressions
Understanding the numerical factor, also known as the coefficient, of a term is fundamental to mastering algebra and numerous other mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of numerical factors, exploring their role in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and ultimately, developing a strong foundation in mathematics. We'll cover various scenarios, from simple algebraic terms to more complex polynomial expressions, ensuring a thorough understanding for learners of all levels.
What is a Numerical Factor (Coefficient)?
A numerical factor, or coefficient, is the numerical part of a term in an algebraic expression. It's the number that multiplies a variable or a group of variables. For instance, in the term 3x, the numerical factor is 3. Similarly, in the term -5y², the numerical factor is -5. The coefficient can be a positive or negative integer, a fraction, a decimal, or even an irrational number like π (pi). It's crucial to understand that the coefficient is inherently linked to the variables it multiplies; it represents the scale or multiplier of those variables.
Identifying Coefficients in Different Expressions
Let's examine several examples to solidify our understanding of identifying coefficients:
-
Simple Algebraic Terms:
7a: The coefficient is 7.-2b: The coefficient is -2.0.5c: The coefficient is 0.5.-¼d: The coefficient is -¼.
-
Terms with Multiple Variables:
6xy: The coefficient is 6.-3xyz: The coefficient is -3.½ab²: The coefficient is ½.
-
Polynomial Expressions:
2x² + 5x - 7: The coefficients are 2, 5, and -7 respectively. Each term in the polynomial has its own coefficient.-4a³ + 2a² - a + 9: The coefficients are -4, 2, -1, and 9. Notice that when a variable doesn't have a visible coefficient, it's implicitly 1 (or -1 if negative).
The Significance of Coefficients
Coefficients play a vital role in various mathematical operations and concepts. Their significance extends beyond simple identification; they are the cornerstone of numerous algebraic manipulations and problem-solving techniques.
1. Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Coefficients are crucial for combining like terms. Like terms are terms that have the same variables raised to the same powers. When simplifying expressions, we add or subtract the coefficients of like terms while keeping the variables unchanged. For example:
3x + 5x = (3 + 5)x = 8x
Here, we add the coefficients 3 and 5 to simplify the expression.
2. Solving Equations
Coefficients are essential in solving equations. To isolate the variable, we often need to manipulate the coefficients through operations like division or multiplication. Consider the equation:
4x = 12
To find the value of x, we divide both sides by the coefficient 4:
x = 12/4 = 3
3. Understanding the Relationship between Variables
Coefficients show the relationship between variables. For example, in the term 5xy, the coefficient 5 indicates that the value of the term is five times the product of x and y. This relationship is fundamental to understanding and interpreting mathematical models and real-world applications.
4. Graphing Linear Equations
In linear equations of the form y = mx + c, where m is the coefficient of x, the coefficient m represents the slope or gradient of the line. The coefficient dictates the steepness and direction of the line on a graph. A larger coefficient indicates a steeper slope.
5. Polynomial Operations
Coefficients are central to polynomial operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. Understanding coefficients is critical for expanding brackets, factoring polynomials, and performing polynomial long division accurately.
Advanced Concepts Related to Coefficients
Let's explore some more advanced concepts involving coefficients:
1. Leading Coefficient
In a polynomial, the leading coefficient is the coefficient of the term with the highest degree. For example, in the polynomial 3x³ + 2x² - x + 5, the leading coefficient is 3 (the coefficient of x³). The leading coefficient plays a significant role in determining the end behavior of the polynomial function.
2. Constant Term
The constant term in a polynomial is the term without any variables. It's essentially a term where the coefficient is multiplied by a variable raised to the power of zero (x⁰ = 1). For example, in 2x² + 5x - 7, the constant term is -7.
3. Binomial Coefficients
Binomial coefficients appear in the binomial theorem and are represented using combinations. They dictate the coefficients in the expansion of a binomial raised to a power. For example, in the expansion of (a + b)³, the binomial coefficients are 1, 3, 3, and 1, resulting in the expansion: a³ + 3a²b + 3ab² + b³.
4. Coefficients in Matrices
Coefficients also appear in matrices, where they represent the numerical values within the matrix. These coefficients are crucial for matrix operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and finding determinants.
5. Coefficients in Differential Equations
Coefficients play a crucial role in differential equations. They are the numerical multipliers of the derivatives of the unknown function. Solving differential equations often involves manipulating and working with these coefficients to find solutions.
Practical Applications and Examples
Let's explore real-world applications where understanding coefficients is vital:
-
Physics: Coefficients are frequently used in physics equations. For instance, in Newton's second law of motion (F = ma), the mass (m) acts as a coefficient relating force (F) and acceleration (a).
-
Engineering: Coefficients are used extensively in engineering calculations and models. Structural engineers use coefficients in stress and strain calculations, while electrical engineers employ them in circuit analysis.
-
Economics: In economic models, coefficients represent the sensitivity of one variable to changes in another. For example, in a demand equation, a coefficient might represent the price elasticity of demand.
-
Computer Science: Coefficients are used in algorithms and data structures, particularly in numerical analysis and machine learning.
Conclusion
The numerical factor, or coefficient, is a fundamental concept in mathematics with far-reaching implications. From simplifying expressions to solving complex equations and understanding advanced mathematical concepts, a strong grasp of coefficients is essential for success in various fields. This article has explored the various aspects of coefficients, illustrating their importance and providing examples across different mathematical domains. By understanding the role and significance of coefficients, you can significantly improve your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities. Remember to practice regularly and apply your knowledge to diverse problems to solidify your understanding and build confidence in tackling more complex mathematical challenges. Through consistent effort and practice, you'll develop a deep understanding of this crucial mathematical building block.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is A Factor Of 5
Mar 25, 2025
-
List Three Similarities Between Dna And Rna
Mar 25, 2025
-
Light Wave Is Longitudinal Or Transverse
Mar 25, 2025
-
Arrange The Following Events In Chronological Order
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 42
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Numerical Factor Of A Term . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
