What Is A Factor Of 5
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
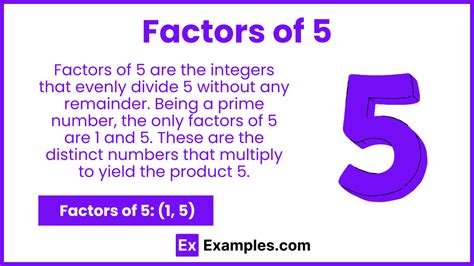
Table of Contents
What is a Factor of 5? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is a factor of 5?", opens the door to a fascinating exploration of number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. While the immediate answer might seem obvious, understanding the concept thoroughly involves delving into prime numbers, divisibility rules, and the fundamental theorem of arithmetic. This article provides a comprehensive overview, suitable for both beginners and those seeking a deeper understanding of factors and their significance.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we specifically address the factors of 5, let's establish a firm grasp of the core concepts. A factor (also known as a divisor) of an integer is a whole number that divides that integer exactly without leaving a remainder. In other words, if 'a' is a factor of 'b', then b/a is a whole number. This leads us to the concept of divisibility. An integer 'b' is divisible by an integer 'a' if and only if 'a' is a factor of 'b'.
For example:
- Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12. Each of these numbers divides 12 without leaving a remainder.
- Factors of 15: 1, 3, 5, and 15.
- Factors of 17: 1 and 17. 17 is a prime number, meaning its only factors are 1 and itself.
The Unique Factors of 5: A Prime Number Perspective
Now, let's focus on the number 5. What are its factors? The only whole numbers that divide 5 without leaving a remainder are 1 and 5 itself. This makes 5 a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself.
This seemingly simple characteristic of 5 has profound implications in number theory and cryptography. The uniqueness of its factors contributes to its importance in various mathematical applications.
Why is 5 a Prime Number? A Deeper Look at Divisibility
To fully understand why 5 is prime, let's revisit the concept of divisibility. We can test for divisibility by checking whether 5 is divisible by any number from 2 to 4 (we exclude 1 and 5 itself, as these are always factors).
- Divisibility by 2: 5 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number.
- Divisibility by 3: 5 is not divisible by 3 because 5 divided by 3 equals 1 with a remainder of 2.
- Divisibility by 4: 5 is not divisible by 4 because 5 divided by 4 equals 1 with a remainder of 1.
Since 5 is not divisible by any whole number other than 1 and itself, it satisfies the definition of a prime number.
The Significance of Prime Numbers: Building Blocks of Numbers
Prime numbers are often called the "building blocks" of integers. This is because of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. This representation is unique, regardless of the order of the prime factors.
For example:
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3)
- 15 = 3 x 5
- 36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 (or 2² x 3²)
This theorem highlights the fundamental role that prime numbers play in the structure of the number system. Understanding prime factorization is crucial for many mathematical concepts, including cryptography and efficient algorithms. The prime factorization of a number reveals essential information about its properties and divisibility.
Factors of 5 in Different Contexts
The simple nature of the factors of 5 doesn't diminish its significance. Let's examine how the concept of factors of 5 appears in different areas:
1. Modular Arithmetic:
Modular arithmetic is a system of arithmetic for integers, where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value, called the modulus. The modulus is often denoted as 'n'. In modular arithmetic, we often deal with remainders. For example, in modulo 5 arithmetic (mod 5), the numbers 5, 10, 15, etc., are all equivalent to 0 because they have a remainder of 0 when divided by 5. This concept is crucial in cryptography and computer science.
2. Number Bases:
The number 5 plays a role in different number bases. For instance, in base 5 (quinary), the digits represent multiples of powers of 5. The factors of 5 are inherently involved in converting numbers between different bases.
3. Geometry and Patterns:
The number 5 appears frequently in geometric patterns, such as pentagons and pentagrams. The properties of 5 and its factors influence the characteristics of these shapes and their symmetries.
4. Cryptography:
Prime numbers, such as 5, are essential in many cryptographic algorithms. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors forms the basis of the security of some encryption methods. While 5 itself is a small prime number, the principles extend to much larger primes.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
Understanding the factors of 5 leads to a deeper appreciation of related mathematical concepts:
1. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
The GCD of two or more integers is the largest positive integer that divides each of the integers without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is a fundamental operation in number theory and has applications in simplifying fractions and solving Diophantine equations. Since 5 is a prime number, finding its GCD with another number is straightforward. If the other number is divisible by 5, the GCD is 5; otherwise, it's 1.
2. Least Common Multiple (LCM):
The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all of the integers. The LCM is closely related to the GCD. Finding the LCM of 5 and another number involves considering the prime factorization of both numbers.
3. Prime Factorization:
As mentioned earlier, prime factorization is the process of decomposing a composite number into its prime factors. The prime factorization of a number is unique, meaning there is only one way to represent it as a product of prime numbers (ignoring the order). Prime factorization is crucial in many mathematical computations.
Practical Applications and Conclusion
While the factors of 5 might seem rudimentary at first glance, their significance extends far beyond basic arithmetic. The prime nature of 5 and its role in divisibility, modular arithmetic, and number theory contribute significantly to advanced mathematical concepts and practical applications in various fields. From cryptography to computer science, the understanding of factors and prime numbers forms the foundation of many complex algorithms and systems. The seemingly simple question, "What is a factor of 5?", ultimately leads to a much deeper appreciation of the intricate structure and beauty of number theory. The exploration of this seemingly simple question has broadened our understanding of number theory and its relevance in various domains, underscoring the importance of even the most fundamental mathematical concepts. Further exploration into these topics will continue to reveal the profound impact that prime numbers, and in this case, the factors of 5, have on mathematics and technology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Square Root Of 15 A Rational Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
Which Of These Is A Polysaccharide
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 7 As A Decimal
Mar 26, 2025
-
Differentiate Between Codominance And Incomplete Dominance
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is 0 75 As A Percent
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Factor Of 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
