The Left Ventricle Has The Thickest Walls Because It
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
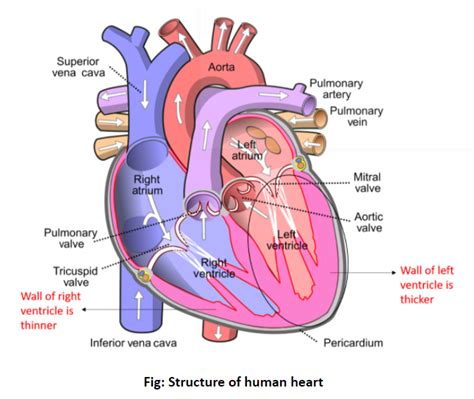
Table of Contents
The Left Ventricle Has the Thickest Walls Because It… Pumps Blood to the Entire Body
The human heart, a remarkable organ, tirelessly works to pump blood throughout our bodies. This intricate process relies on four chambers: two atria and two ventricles. While all four play crucial roles, the left ventricle stands out due to its exceptionally thick walls. But why? The answer lies in the immense workload it undertakes: propelling oxygenated blood to every part of the body. This article delves deep into the anatomical and physiological reasons behind the left ventricle's robust structure, exploring the circulatory system's mechanics and the implications of variations in left ventricular thickness.
Understanding the Heart's Chambers and Their Functions
Before we dive into the specifics of the left ventricle, let's review the roles of all four heart chambers:
- Right Atrium: Receives deoxygenated blood returning from the body through the superior and inferior vena cava.
- Right Ventricle: Receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium and pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation via the pulmonary artery.
- Left Atrium: Receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the pulmonary veins.
- Left Ventricle: Receives oxygenated blood from the left atrium and pumps it to the entire body through the aorta.
The Left Ventricle: The Powerhouse of the Circulatory System
The left ventricle's primary function is to pump oxygen-rich blood into the systemic circulation—the vast network of blood vessels supplying the entire body. This is a significantly more demanding task than pumping blood to the lungs (the right ventricle's job). The systemic circulation encompasses a far greater distance and requires overcoming much higher resistance. This explains the left ventricle's significantly thicker walls.
The Mechanics of Systemic Circulation
The systemic circulation involves a complex interplay of pressure, resistance, and blood flow. The left ventricle needs to generate sufficient pressure to overcome the considerable resistance presented by the extensive network of systemic arteries and arterioles. This pressure is crucial for efficient blood delivery to even the most distant tissues and organs. The greater the resistance, the more pressure the left ventricle must generate.
The Role of Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR)
Systemic vascular resistance (SVR) is a major factor influencing the left ventricle's workload. SVR refers to the resistance that blood encounters as it flows through the systemic circulation. Factors influencing SVR include:
- Blood viscosity: Thicker blood increases resistance.
- Blood vessel diameter: Constriction of blood vessels (vasoconstriction) increases resistance, while dilation (vasodilation) decreases it.
- Total blood vessel length: Longer blood vessels increase resistance.
A higher SVR necessitates a more powerful contraction from the left ventricle to maintain adequate blood flow. This increased workload over time leads to the hypertrophy (thickening) of the left ventricle's walls.
The Anatomy of a Thick Left Ventricular Wall
The left ventricle's wall thickness isn't just about increased muscle mass; it's a sophisticated adaptation involving several key anatomical features:
-
Increased Myocardial Thickness: The myocardium, the heart's muscular layer, is significantly thicker in the left ventricle compared to the other chambers. This greater mass allows for a stronger contraction, generating the necessary pressure for systemic circulation.
-
Specialized Cardiac Muscle Cells: The left ventricular myocardium contains specialized cardiac muscle cells optimized for forceful contractions. These cells are larger and more densely packed compared to those in other chambers, contributing to the ventricle's powerful pumping ability.
-
Myocardial Fiber Arrangement: The arrangement of myocardial fibers within the left ventricle further contributes to its strength and efficiency. The complex organization of these fibers optimizes force transmission during contraction, ensuring efficient ejection of blood into the aorta.
-
Robust Collagen Network: The left ventricle's wall is reinforced by a strong collagen network providing structural support and preventing excessive stretching during contraction. This collagen matrix is essential for maintaining the ventricle's integrity under high pressure.
Consequences of Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
While left ventricular hypertrophy is often an adaptive response to increased workload, it can also be a sign of underlying cardiovascular problems. Excessive hypertrophy can lead to several complications:
-
Heart Failure: The thickened heart muscle may become less efficient at pumping blood, leading to heart failure. This can manifest as shortness of breath, fatigue, and edema (swelling).
-
Arrhythmias: Hypertrophy can disrupt the heart's electrical conduction system, leading to irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias).
-
Sudden Cardiac Death: In severe cases, excessive left ventricular hypertrophy can increase the risk of sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosing Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Several diagnostic tools are used to assess left ventricular wall thickness and identify potential problems:
-
Echocardiogram: A non-invasive ultrasound test that provides detailed images of the heart's structure and function, allowing accurate measurement of left ventricular wall thickness.
-
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Measures the heart's electrical activity and can reveal abnormalities associated with hypertrophy.
-
Cardiac MRI: A more advanced imaging technique providing detailed anatomical and functional information about the heart.
Lifestyle Factors and Left Ventricular Health
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a crucial role in preventing excessive left ventricular hypertrophy and associated complications. Key factors include:
-
Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity strengthens the heart muscle and improves cardiovascular health.
-
Balanced Diet: A diet low in saturated and trans fats, sodium, and cholesterol reduces the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
-
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the strain on the heart.
-
Smoking Cessation: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
-
Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
The left ventricle's exceptionally thick walls are a testament to its critical role in propelling oxygenated blood throughout the body. This anatomical adaptation is a direct response to the high pressure and resistance encountered in systemic circulation. Understanding the complexities of left ventricular function, the implications of hypertrophy, and the importance of maintaining cardiovascular health are crucial for preventing and managing heart-related conditions. While hypertrophy can be a natural adaptive response, excessive thickening can lead to significant complications. Therefore, regular health check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are essential for maintaining a healthy heart and ensuring its long-term functionality. This nuanced understanding allows for informed decision-making regarding cardiovascular health and highlights the vital importance of proactive measures to safeguard this essential organ. The intricate workings of the left ventricle underscore the remarkable design and functionality of the human circulatory system.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Magnesium
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 12 And 36
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Organelles Are Found Only In Plant Cells
Mar 06, 2025
-
At What Temperature Does Water Boil Celsius
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Will Result In A Chemical Change
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Left Ventricle Has The Thickest Walls Because It . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
