Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Trapezoid
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
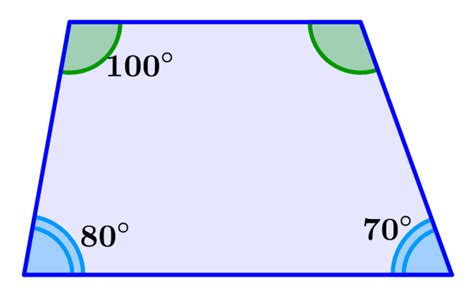
Table of Contents
Sum of Interior Angles of a Trapezoid: A Comprehensive Guide
The sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral, including a trapezoid, is always 360 degrees. This fundamental geometric principle is crucial for understanding various properties and applications of trapezoids in mathematics and beyond. This article delves deep into this concept, exploring its proof, practical applications, and related geometric concepts. We'll also look at how this property relates to other quadrilaterals and its significance in problem-solving.
Understanding Trapezoids
Before we dive into the sum of interior angles, let's refresh our understanding of trapezoids. A trapezoid (also known as a trapezium in some regions) is a quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides. These parallel sides are called bases, while the other two sides are called legs.
There are several types of trapezoids, including:
- Isosceles trapezoid: A trapezoid where the legs are congruent (equal in length). This type exhibits additional properties, such as congruent base angles.
- Right trapezoid: A trapezoid with at least one right angle (90 degrees).
- Scalene trapezoid: A trapezoid where all sides have different lengths.
Regardless of the type, the fundamental property we're focusing on – the sum of interior angles – remains constant: 360 degrees.
Proving the Sum of Interior Angles of a Trapezoid
Several methods can prove that the sum of interior angles of a trapezoid is 360 degrees. Let's explore two common approaches:
Method 1: Dividing the Trapezoid into Triangles
This method utilizes the known fact that the sum of angles in a triangle is 180 degrees. We can divide any trapezoid into two triangles by drawing a diagonal connecting two non-adjacent vertices.
- Draw a diagonal: Consider a trapezoid ABCD, where AB is parallel to CD. Draw a diagonal, say AC.
- Two triangles formed: This diagonal divides the trapezoid into two triangles: triangle ABC and triangle ACD.
- Sum of angles in each triangle: The sum of angles in triangle ABC is ∠BAC + ∠ABC + ∠BCA = 180 degrees. Similarly, the sum of angles in triangle ACD is ∠CAD + ∠ADC + ∠DCA = 180 degrees.
- Total sum of angles: Adding the angles of both triangles, we get: (∠BAC + ∠ABC + ∠BCA) + (∠CAD + ∠ADC + ∠DCA) = 360 degrees. Note that the angles of the trapezoid (∠A, ∠B, ∠C, ∠D) are represented in this sum.
Therefore, the sum of interior angles of the trapezoid ABCD is 360 degrees. This method works for all types of trapezoids.
Method 2: Using Parallel Lines and Transversals
This method leverages the properties of parallel lines and transversals.
- Parallel lines and transversals: In trapezoid ABCD, where AB || CD, consider lines AB and CD as parallel lines. The legs AD and BC act as transversals.
- Consecutive interior angles: Consecutive interior angles formed by a transversal intersecting parallel lines are supplementary (their sum is 180 degrees).
- Applying the property: ∠A + ∠D = 180 degrees and ∠B + ∠C = 180 degrees.
- Total sum: Adding these two equations, we get: ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360 degrees.
This proves that the sum of interior angles in any trapezoid is 360 degrees. This approach highlights the relationship between parallel lines and the angles of a trapezoid.
Applications of the 360-degree Property
The knowledge that the sum of interior angles of a trapezoid is 360 degrees has various practical applications:
- Solving for unknown angles: If you know three angles of a trapezoid, you can easily calculate the fourth angle by subtracting the sum of the known angles from 360 degrees.
- Construction and design: In architecture and engineering, understanding the angles of trapezoids is essential for creating stable and structurally sound designs. This is particularly relevant in designing roofs, bridges, and other structures involving trapezoidal shapes.
- Computer graphics and animation: Trapezoids are commonly used in computer graphics to represent various shapes. The understanding of angles is crucial for accurate rendering and manipulation of these shapes.
- Cartography and surveying: Trapezoids are frequently used in map projections and land surveying. Accurate angle calculations are necessary for creating precise maps and determining land boundaries.
- Tessellations: Trapezoids can be used to create tessellations (tilings) of a plane. Understanding their angles helps determine the arrangement and patterns of these tilings.
Relationship to Other Quadrilaterals
The 360-degree property isn't unique to trapezoids; it applies to all quadrilaterals. This includes:
- Parallelograms: Parallelograms (rectangles, squares, rhombuses) are special cases of trapezoids where both pairs of opposite sides are parallel. The sum of their interior angles is also 360 degrees.
- Rectangles: A rectangle is a parallelogram with four right angles. The sum of its angles is 4 * 90 degrees = 360 degrees.
- Squares: A square is a rectangle with four congruent sides. The sum of its angles is also 360 degrees.
- Rhombuses: A rhombus is a parallelogram with four congruent sides. The sum of its angles is 360 degrees.
- Kites: A kite is a quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent congruent sides. The sum of its angles remains 360 degrees.
Problem Solving with Trapezoids
Let's illustrate the application of the 360-degree property in problem-solving:
Problem: A trapezoid has angles of 70°, 110°, and 120°. Find the measure of the fourth angle.
Solution:
- Sum of known angles: 70° + 110° + 120° = 300°
- Fourth angle: 360° - 300° = 60°
Therefore, the fourth angle measures 60 degrees.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
While the sum of interior angles is a fundamental property, understanding trapezoids involves more advanced concepts:
- Area of a trapezoid: The area of a trapezoid is calculated using the formula: Area = (1/2) * (sum of bases) * height.
- Median of a trapezoid: The median of a trapezoid is a line segment connecting the midpoints of the legs. Its length is the average of the lengths of the bases.
- Isosceles trapezoid properties: Isosceles trapezoids possess unique properties, including congruent base angles and diagonals of equal length.
- Cyclic trapezoids: A cyclic trapezoid is a trapezoid that can be inscribed in a circle. In a cyclic trapezoid, the sum of opposite angles is 180 degrees.
Conclusion
The sum of interior angles of a trapezoid, always equaling 360 degrees, is a cornerstone of geometry. This fundamental property, readily provable through various methods, has wide-ranging applications in various fields. Understanding this principle is crucial for solving geometric problems, designing structures, and appreciating the intricate relationships within geometric shapes. Beyond this fundamental concept, exploring the diverse types of trapezoids and their unique properties opens up a deeper understanding of geometry's elegance and practical utility. This exploration helps build a solid foundation for more advanced geometric concepts and problem-solving capabilities. Remember to practice regularly and explore various problems involving trapezoids to solidify your understanding and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lcm Of 8 And 12 And 15
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Circumcenter Of A Triangle Is Equidistant From The
Mar 23, 2025
-
How Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Interdependent
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 2 5
Mar 23, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Homologous Structures
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Interior Angles Of A Trapezoid . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
