How Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Interdependent
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
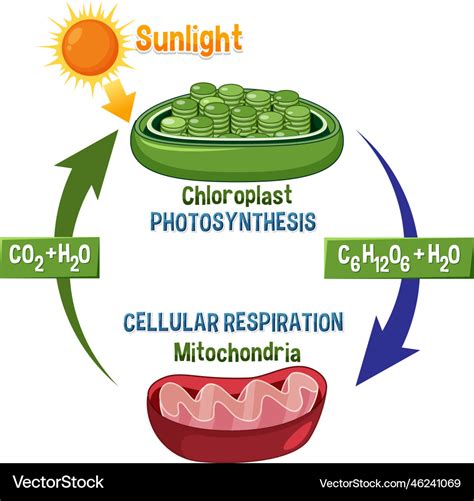
Table of Contents
How Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration are Interdependent: A Symbiotic Relationship Powering Life on Earth
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are two fundamental processes that underpin the existence of almost all life on Earth. While seemingly distinct, they are intricately intertwined in a remarkable symbiotic relationship, forming a cyclical exchange of energy and matter that sustains ecosystems and the biosphere as a whole. Understanding their interdependence is key to grasping the fundamental workings of life itself.
The Two Sides of the Energy Coin: A Brief Overview
Before delving into their interdependence, let's briefly review each process individually.
Photosynthesis: Capturing Sunlight's Energy
Photosynthesis, primarily performed by plants, algae, and some bacteria, is the process of converting light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This remarkable feat occurs within chloroplasts, specialized organelles containing chlorophyll, the pigment responsible for absorbing sunlight. The overall reaction can be summarized as:
6CO₂ + 6H₂O + Light Energy → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂
This equation shows that carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O) are utilized in the presence of light energy to produce glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), a sugar molecule that stores energy, and oxygen (O₂), a byproduct released into the atmosphere. This process is crucial because it forms the base of most food chains, providing energy for virtually all other organisms.
Key components and steps involved in Photosynthesis:
- Light-dependent reactions: This initial stage harnesses light energy to split water molecules (photolysis), releasing oxygen and generating ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate), energy-carrying molecules.
- Light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle): Utilizing the ATP and NADPH produced in the light-dependent reactions, carbon dioxide is fixed and converted into glucose, a process requiring a series of enzymatic reactions.
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Energy from Glucose
Cellular respiration is the process by which organisms break down glucose to release the stored chemical energy. This occurs in the mitochondria, the "powerhouses" of cells. The process can be summarized as:
C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
This equation demonstrates the opposite of photosynthesis: glucose and oxygen are consumed to produce carbon dioxide, water, and, crucially, ATP, the primary energy currency of cells. ATP fuels all cellular activities, from muscle contraction to protein synthesis.
Key stages of Cellular Respiration:
- Glycolysis: The initial breakdown of glucose in the cytoplasm, yielding a small amount of ATP and pyruvate.
- Pyruvate oxidation: Pyruvate is transported into the mitochondria and converted into acetyl-CoA.
- Krebs cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Acetyl-CoA enters a cycle of reactions, producing more ATP, NADH, and FADH₂ (flavin adenine dinucleotide), further energy-carrying molecules.
- Electron transport chain (ETC): Electrons from NADH and FADH₂ are passed along a chain of protein complexes, generating a proton gradient that drives ATP synthesis through chemiosmosis. Oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor, forming water.
The Interdependence: A Continuous Cycle of Energy Exchange
The interdependence of photosynthesis and cellular respiration becomes strikingly clear when we examine the inputs and outputs of each process. Observe the following:
-
Photosynthesis produces oxygen (O₂) and glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆), which are the inputs for cellular respiration. Plants produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, which is then used by animals and other organisms for cellular respiration. Similarly, the glucose created through photosynthesis serves as the primary energy source for most heterotrophic organisms (those that cannot produce their own food).
-
Cellular respiration produces carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O), which are the inputs for photosynthesis. The carbon dioxide released during cellular respiration is a vital component for photosynthesis, providing the carbon needed to build glucose molecules. Water, also a byproduct of cellular respiration, is utilized in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
This cyclical exchange forms a closed loop: photosynthesis utilizes the products of cellular respiration, and cellular respiration utilizes the products of photosynthesis. This cyclical nature creates a self-sustaining system where energy is continuously transformed and transferred throughout the ecosystem.
Beyond the Basic Exchange: A Deeper Look at the Interplay
The interdependence goes beyond the simple exchange of gases and glucose. Several other factors highlight this intricate relationship:
Environmental Impact and Regulation:
- Carbon Cycle Regulation: Photosynthesis and cellular respiration play crucial roles in regulating the Earth's carbon cycle. Photosynthesis removes carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, while cellular respiration releases it. This dynamic balance is essential for maintaining stable atmospheric carbon dioxide levels and mitigating climate change.
- Oxygen Levels: The oxygen produced by photosynthesis maintains atmospheric oxygen levels, crucial for the aerobic respiration of most organisms. Changes in photosynthetic rates can directly impact oxygen availability and influence the distribution and diversity of life.
Ecosystem Dynamics and Food Webs:
- Base of the Food Chain: Photosynthesis forms the base of most food chains. Plants, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy, which is then passed on to herbivores, carnivores, and decomposers. This energy flow depends entirely on the continuous process of photosynthesis.
- Nutrient Cycling: Decomposition of organic matter, a process often involving cellular respiration by decomposers, releases nutrients back into the environment, making them available for plants to utilize during photosynthesis. This continuous cycle of nutrient uptake and release maintains the health and productivity of ecosystems.
Evolutionary Significance:
- The Great Oxidation Event: The emergence of photosynthetic organisms billions of years ago fundamentally altered Earth's atmosphere, leading to the Great Oxidation Event, which dramatically increased oxygen levels. This paved the way for the evolution of aerobic respiration, a far more efficient energy-producing process than anaerobic respiration.
Human Impact and Disruptions:
- Deforestation and Climate Change: Human activities like deforestation significantly reduce the planet's photosynthetic capacity, impacting the Earth's carbon cycle and accelerating climate change. A decrease in photosynthetic activity also reduces oxygen production and disrupts the delicate balance of the ecosystem.
- Fossil Fuels and the Carbon Cycle: The burning of fossil fuels (ancient organic matter) releases vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, disrupting the natural balance between photosynthesis and cellular respiration. This imbalance contributes to global warming and climate change.
Conclusion: A Symbiotic Partnership for Life
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are not merely two separate processes; they represent a deeply intertwined symbiotic partnership that sustains life on Earth. Their interplay governs energy flow, nutrient cycling, atmospheric composition, and the overall health of ecosystems. Understanding this interdependence is not only crucial for grasping fundamental biological principles but also for addressing pressing environmental challenges like climate change and biodiversity loss. Protecting and promoting the balance between these two essential processes is paramount to maintaining a healthy and sustainable planet.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 9
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Inches Are In 70 Cm
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 9 And 12
Mar 25, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Ending In The
Mar 25, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 2 And 4
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Are Photosynthesis And Cellular Respiration Interdependent . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
