State The Total Number Of Valence Electrons In Ch2o
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
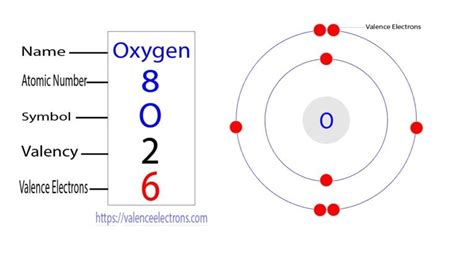
Table of Contents
Determining the Total Number of Valence Electrons in CH₂O (Formaldehyde)
Formaldehyde, with its chemical formula CH₂O, is a simple yet significant molecule in organic chemistry. Understanding its electronic structure is crucial for comprehending its reactivity and properties. A key aspect of this understanding involves determining the total number of valence electrons present in the molecule. This article will delve into the process of calculating this number, explaining the underlying principles and providing a comprehensive understanding of formaldehyde's electronic configuration.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before calculating the valence electrons in CH₂O, let's define what valence electrons are. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell (or energy level) of an atom. These electrons are crucial because they are involved in chemical bonding. Atoms tend to react in ways that achieve a stable electron configuration, often resembling that of a noble gas (a full outermost shell). This drive for stability governs the formation of chemical bonds.
Identifying Valence Electrons of Each Atom
To determine the total number of valence electrons in CH₂O, we need to know the number of valence electrons for each atom present in the molecule: carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O).
Carbon (C)
Carbon is located in group 14 (or IVA) of the periodic table. Group 14 elements typically have four valence electrons.
Hydrogen (H)
Hydrogen is located in group 1 (or IA) of the periodic table. Group 1 elements have one valence electron. Since there are two hydrogen atoms in CH₂O, we have a total of 2 hydrogen valence electrons (2 atoms x 1 electron/atom = 2 electrons).
Oxygen (O)
Oxygen is located in group 16 (or VIA) of the periodic table. Group 16 elements typically have six valence electrons.
Calculating the Total Valence Electrons in CH₂O
Now, we can sum up the valence electrons from each atom to find the total number of valence electrons in the formaldehyde molecule:
- Carbon (C): 4 valence electrons
- Hydrogen (H): 2 valence electrons (2 atoms x 1 electron/atom)
- Oxygen (O): 6 valence electrons
Total Valence Electrons = 4 + 2 + 6 = 12 valence electrons
Therefore, the formaldehyde molecule (CH₂O) has a total of 12 valence electrons.
Lewis Structure and Electron Distribution
The Lewis structure is a visual representation of the molecule's bonding and electron distribution. It shows how the valence electrons are arranged among the atoms, including bonding pairs and lone pairs. Constructing the Lewis structure for CH₂O helps confirm our valence electron count and illustrates how these electrons are involved in bonding.
Steps to Draw the Lewis Structure:
-
Count the total number of valence electrons: As calculated above, CH₂O has 12 valence electrons.
-
Identify the central atom: Carbon is typically the central atom in organic molecules, so it will be the central atom in our Lewis structure.
-
Connect atoms with single bonds: Connect the carbon atom to the two hydrogen atoms and the oxygen atom with single bonds. Each single bond consists of two electrons. This step uses 6 electrons (3 bonds x 2 electrons/bond).
-
Distribute remaining electrons: We have 6 electrons remaining (12 total - 6 used in bonds). These electrons are added as lone pairs to satisfy the octet rule (except for hydrogen, which only needs 2 electrons for a full shell). Oxygen needs to fulfill its octet, so we add 4 electrons as two lone pairs to the oxygen atom.
-
Check octets: Carbon has 8 electrons (2 from each single bond), each hydrogen has 2 electrons (one single bond), and oxygen has 8 electrons (2 from the single bond and 6 from the lone pairs). All atoms have satisfied the octet rule (or the duet rule for hydrogen).
The resulting Lewis structure shows a double bond between carbon and oxygen, and single bonds between carbon and each hydrogen atom. Oxygen has two lone pairs of electrons.
Formal Charges and Resonance Structures
While the Lewis structure with a carbon-oxygen double bond fulfills the octet rule, it's important to consider formal charges. Formal charge is the difference between the number of valence electrons in a free atom and the number of electrons assigned to that atom in a molecule. Calculating formal charges helps determine the most likely structure.
In the most common Lewis structure of formaldehyde, the formal charges on all atoms are zero. However, resonance structures can be drawn to show electron delocalization. These resonance structures contribute to the overall picture of electron distribution within the molecule and impact its properties. The actual structure of formaldehyde is a hybrid of these resonance structures.
Applications and Significance of Understanding Valence Electrons
Understanding the valence electrons in CH₂O is fundamental to comprehending its chemical behavior. The number of valence electrons dictates the type and number of bonds an atom can form, influencing the molecule's geometry, polarity, and reactivity. This understanding is crucial in various applications:
-
Organic Chemistry: Formaldehyde is a crucial building block in many organic syntheses. Knowing its electronic structure aids in predicting its reactivity and designing reactions.
-
Polymer Chemistry: Formaldehyde is a key component in the production of various polymers, including resins and plastics. Its electronic structure is critical in understanding polymer formation and properties.
-
Biochemistry: Formaldehyde plays a role in certain biochemical processes and is used as a preservative in some applications. Understanding its electronic structure helps explain its interactions with biological molecules.
-
Environmental Science: Formaldehyde is a common pollutant, and understanding its chemistry is crucial for developing strategies for its mitigation and environmental remediation.
Conclusion
Determining the total number of valence electrons in CH₂O (formaldehyde) involves a straightforward yet fundamental concept in chemistry. By understanding the number of valence electrons for each atom (carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen) and adding them together, we arrive at a total of 12 valence electrons. This calculation is essential for constructing accurate Lewis structures, predicting molecular geometry, and understanding the chemical reactivity and properties of formaldehyde. The implications extend to various fields, highlighting the importance of understanding fundamental chemical principles in numerous scientific and technological applications. The ability to calculate valence electrons is a cornerstone skill for anyone pursuing studies in chemistry, biochemistry, or related disciplines. Further exploration of concepts such as formal charges and resonance contributes to a more complete and nuanced understanding of molecular structure and behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Air A Compound Or A Mixture
Mar 25, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 16 And 9
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Sides Does A Rectangle Have
Mar 25, 2025
-
Litmus Paper Test For Acid And Base
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is The Percent Of 1 25
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about State The Total Number Of Valence Electrons In Ch2o . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
