Si Unit Of Measurement For Acceleration
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
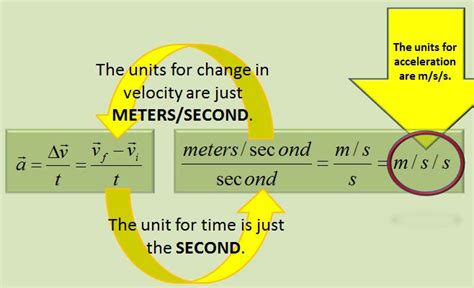
Table of Contents
The SI Unit of Measurement for Acceleration: Understanding m/s²
Acceleration, a fundamental concept in physics, describes the rate at which an object's velocity changes over time. Understanding its measurement is crucial for comprehending motion and forces in various fields, from classical mechanics to advanced astrophysics. This comprehensive guide delves into the SI unit of measurement for acceleration, the meter per second squared (m/s²), exploring its definition, applications, and significance in scientific calculations and real-world scenarios.
Defining Acceleration and its SI Unit
Acceleration is defined as the change in velocity divided by the change in time. Velocity, a vector quantity, includes both speed and direction. Therefore, a change in velocity can involve a change in speed, a change in direction, or both. This leads us to the mathematical representation of acceleration:
a = Δv / Δt
Where:
- a represents acceleration
- Δv represents the change in velocity (final velocity - initial velocity)
- Δt represents the change in time
The SI unit of acceleration directly stems from this definition. Since velocity is measured in meters per second (m/s) and time is measured in seconds (s), the unit of acceleration becomes meters per second squared (m/s²). This signifies that acceleration quantifies the change in velocity (m/s) occurring per unit of time (s), resulting in the unit m/s².
Why is it m/s² and not something else?
The units are a direct consequence of the formula. To get the unit of acceleration, we divide the unit of velocity (m/s) by the unit of time (s):
(m/s) / s = m/s²
This is not arbitrary; it reflects the physical reality of acceleration. The unit fundamentally conveys the rate at which velocity changes—how many meters per second the velocity changes every second.
Understanding the Magnitude and Direction of Acceleration
The SI unit, m/s², provides both magnitude and a direction component of acceleration, reflecting its vector nature. A positive value indicates acceleration in a particular direction (e.g., increasing velocity in the positive x-direction), while a negative value implies acceleration in the opposite direction (e.g., deceleration or decreasing velocity).
Consider these examples:
- 5 m/s²: This means the velocity increases by 5 meters per second every second.
- -2 m/s²: This means the velocity decreases by 2 meters per second every second (deceleration).
- 0 m/s²: This indicates no change in velocity; the object is moving at a constant velocity.
The direction of the acceleration vector is crucial, particularly in situations involving changes in direction. Even if the speed remains constant, a change in direction implies acceleration, as the velocity vector has changed. Circular motion provides an excellent example where the acceleration is always directed towards the center of the circle (centripetal acceleration), even if the speed remains constant.
Applications of the m/s² Unit Across Diverse Fields
The m/s² unit finds applications in a vast array of scientific and engineering disciplines:
1. Classical Mechanics:
The cornerstone of Newtonian physics, classical mechanics extensively uses acceleration in describing motion under various forces. From calculating the trajectory of projectiles to understanding the motion of planets around the sun, the m/s² unit plays a central role. Newton's second law, F = ma, directly links force (F), mass (m), and acceleration (a), highlighting the importance of the acceleration unit in understanding forces and their effects.
2. Automotive Engineering:
In automotive engineering, understanding acceleration is critical for designing and testing vehicles. Measuring acceleration during braking, acceleration tests, and handling maneuvers helps assess vehicle performance, safety, and driver experience. The m/s² unit is fundamental in quantifying and comparing the performance of different vehicles.
3. Aerospace Engineering:
Designing aircraft and spacecraft relies heavily on precise acceleration calculations. Understanding the forces involved during takeoff, landing, and orbital maneuvers requires accurate measurements and calculations using the m/s² unit. Furthermore, analyzing acceleration during atmospheric re-entry is essential for ensuring the safety of spacecraft.
4. Robotics:
In robotics, precise control of acceleration is crucial for smooth and efficient movement. Robots need to maneuver precisely and avoid collisions, and proper acceleration control is essential for achieving this. The m/s² unit allows for precise programming and control of robotic motion.
5. Sports Science:
Sports scientists use acceleration measurements to analyze athlete performance. Tracking the acceleration of athletes during sprints, jumps, and other activities helps assess their power, agility, and overall performance. This data informs training regimens and helps optimize athletic performance.
6. Medical Physics:
Medical imaging techniques, like MRI and CT scans, often involve the movement of components, and understanding the acceleration involved ensures precise image acquisition. In radiation therapy, precise control of the acceleration of radiation beams is vital for targeting cancerous tumors accurately.
Converting Units and Handling Different Unit Systems
While m/s² is the standard SI unit, other units for acceleration exist in different systems. Understanding how to convert between these units is essential for compatibility and accurate calculations.
Some commonly used alternative units include:
-
g (gravity): This unit represents the acceleration due to Earth's gravity, approximately 9.81 m/s². It's often used to express acceleration relative to gravity. For example, an acceleration of 2g implies an acceleration of 2 * 9.81 m/s² = 19.62 m/s².
-
km/h²: This unit is occasionally used, particularly in contexts like vehicle acceleration. It's essential to convert to m/s² for consistency in calculations with SI units.
-
ft/s²: Used in the imperial system of units, conversion to m/s² is necessary for consistent calculations in scientific contexts.
Converting between units requires using appropriate conversion factors. For instance, to convert from km/h² to m/s², you need to convert kilometers to meters and hours to seconds.
Advanced Concepts and Applications of Acceleration
Beyond its basic definition, acceleration plays a vital role in more advanced concepts:
-
Uniform vs. Non-uniform Acceleration: Uniform acceleration means constant acceleration (constant change in velocity over time), while non-uniform acceleration involves a changing acceleration rate.
-
Jerk: Jerk is the rate of change of acceleration, representing the smoothness or abruptness of acceleration changes. It's significant in areas like vehicle design, where minimizing jerk improves ride comfort.
-
Relative Acceleration: In scenarios with multiple moving objects, calculating relative acceleration helps understand their motion concerning each other.
-
Centripetal Acceleration: As mentioned earlier, this type of acceleration is vital in understanding circular motion and the forces involved in keeping an object moving in a circle.
Conclusion: The Importance of m/s² in Scientific Understanding
The SI unit for acceleration, m/s², is more than just a unit; it's a fundamental tool for understanding and quantifying motion, forces, and their effects across various scientific disciplines. Its clear definition, straightforward conversion methods, and applicability in diverse fields solidify its importance in scientific calculations and real-world applications. Mastering this unit is essential for anyone engaging with physics, engineering, and related fields. From calculating the trajectory of a rocket to analyzing an athlete's sprint, the meter per second squared serves as a cornerstone of our understanding of the dynamic world around us.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Attractive Force Of Water Molecules Is Called The
Mar 06, 2025
-
Find The Difference 2 X 10 3 X 4
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Square Root Of 20
Mar 06, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Does P Have
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Si Unit Of Measurement For Acceleration . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
