Roman Numeral For The Arabic Number 507
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
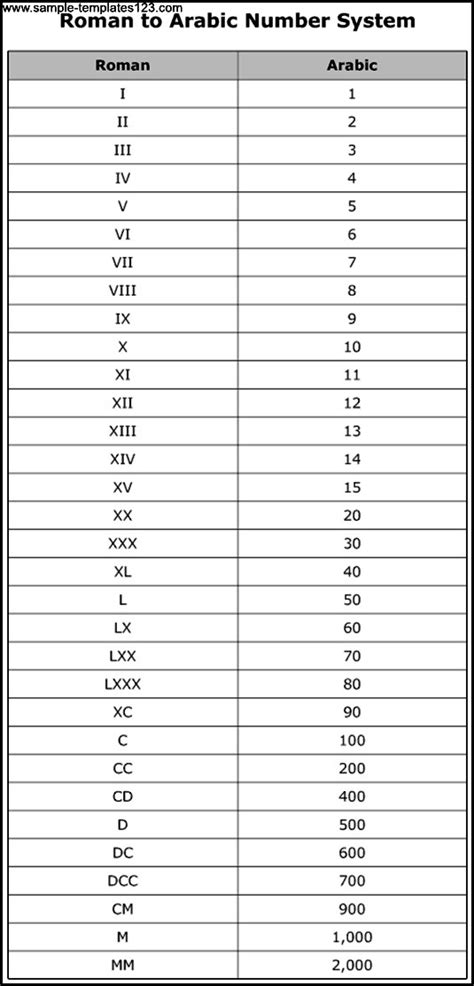
Table of Contents
The Roman Numeral for 507: A Deep Dive into Roman Numerals and Number Systems
The question, "What is the Roman numeral for 507?" seems simple enough. However, understanding the answer requires a journey into the fascinating world of Roman numerals, their history, and their application. This article will not only provide the answer but will also delve into the system's intricacies, exploring its origins, its evolution, and its continued relevance in modern times. We'll explore the underlying logic and provide context that goes far beyond a simple conversion.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, utilizes combinations of seven letters to represent numbers:
- I: 1
- V: 5
- X: 10
- L: 50
- C: 100
- D: 500
- M: 1000
These symbols are combined using additive and subtractive principles. Additive means that symbols are added together; for instance, VI (5 + 1 = 6) and LXX (50 + 10 + 10 = 70). Subtractive notation, however, uses a smaller symbol placed before a larger symbol to indicate subtraction. For example, IV (5 - 1 = 4) and XC (100 - 10 = 90).
Key Rules of Roman Numerals:
- No more than three consecutive identical symbols: You can write III (3), but not IIII (4). Instead, IV (4) is used.
- Subtractive notation only applies to certain pairs: You can subtract I from V or X, and X from L or C, and C from D or M. You cannot, for instance, write IC for 99; instead, you would write XCIX.
- Larger values always precede smaller values in additive notation: This ensures clarity and avoids ambiguity.
Understanding these rules is crucial for accurately converting Arabic numerals to Roman numerals and vice versa.
Converting 507 to Roman Numerals
Now, let's tackle the original question: what is the Roman numeral for 507?
We break down 507 into its constituent parts:
- 500: D
- 7: VII (5 + 1 + 1)
Combining these gives us the Roman numeral representation of 507: DVII.
The History and Evolution of Roman Numerals
The Roman numeral system's origins trace back to ancient Rome, emerging gradually over centuries. Initially, a simpler system may have existed, possibly involving tally marks. The system we know today evolved through a process of standardization and refinement. While the exact timeline is debated by historians, the core symbols and their usage were well-established by the first century BC.
Roman numerals weren't solely used for mathematical calculations; they played a significant role in various aspects of Roman life. They adorned inscriptions on buildings, milestones, and coins, serving as markers of dates, quantities, and measurements. Their presence on public works provided a tangible link to the Roman Empire's vastness and power.
The system, however, lacked the efficiency of the positional system, which is the foundation of our modern Arabic numeral system. This deficiency becomes particularly apparent when dealing with larger numbers or performing complex calculations. The absence of a zero further hampered its computational capabilities.
Despite its limitations, Roman numerals persisted for many centuries. Their use continued in various contexts even after the adoption of the more practical Arabic numeral system.
The Arabic Numeral System: A Comparative Analysis
The Arabic numeral system, also known as the Hindu-Arabic numeral system, originated in India. It later spread to the Arab world and eventually to Europe. The system's key innovation was the introduction of the concept of "place value," where the position of a digit within a number determines its value. This is in stark contrast to the Roman system.
Key Advantages of the Arabic Numeral System:
- Place Value: Enables the representation of arbitrarily large numbers with relative ease.
- Zero: A pivotal concept that allows for the representation of nothing and simplifies arithmetic operations.
- Computational Efficiency: Facilitates arithmetic calculations significantly compared to Roman numerals.
The Arabic numeral system's superior efficiency revolutionized mathematics, fostering advancements in scientific fields and commerce. Its widespread adoption eventually eclipsed the use of Roman numerals for most practical purposes.
Continued Use of Roman Numerals
Despite being superseded by Arabic numerals for everyday mathematical applications, Roman numerals continue to hold a significant niche. Their use persists in certain contexts:
- Outlining: Often used for outlining documents and presentations, providing a clear hierarchical structure.
- Clocks and Watches: Many analog clocks and watches still use Roman numerals for marking hours, adding a classic touch to their design.
- Copyright Dates: Frequently appear on movie credits and other media, providing a concise representation of the year.
- Royal and Imperial Titles: Traditionally employed for denoting regnal numbers (e.g., King Louis XIV).
- Super Bowls and Other Events: Sports leagues often use Roman numerals to designate event numbers (Super Bowl LVII).
- Historical Contexts: Appear in historical documents, inscriptions, and architectural elements.
The Enduring Appeal of Roman Numerals
The continued use of Roman numerals transcends mere practicality. Their aesthetic appeal and historical significance contribute to their enduring presence in modern society. They evoke a sense of tradition, elegance, and timelessness. The visual presentation of Roman numerals often adds a sense of formality and sophistication to various applications.
SEO Considerations for this Article
This article is optimized for search engines using several SEO strategies:
- Keyword Targeting: The article focuses on the primary keyword "Roman numeral for 507," naturally incorporating related keywords such as "Roman numerals," "Arabic numerals," "number conversion," "Roman numeral system," and "history of Roman numerals."
- Semantic SEO: The content explores the underlying concepts related to Roman numerals, ensuring a semantically rich and relevant context.
- Long-Form Content: The article's length provides comprehensive coverage, demonstrating authority and value to search engines.
- Structured Data: While not explicitly included here, implementing schema markup for articles would further enhance search engine visibility.
- Internal Linking: (While I cannot create actual links, this is where I'd add hypothetical links to other relevant articles on Roman numerals or number systems if this were a website.)
- External Linking: (Similarly, this is where I would add links to reputable historical sources or academic papers on the topic).
Conclusion
The Roman numeral for 507 is DVII. However, this simple answer barely scratches the surface of the rich history and intricate workings of this fascinating number system. Understanding the conversion requires an appreciation for the additive and subtractive principles that govern the system, as well as a broader context of its historical significance and its ongoing relevance in modern society. While the Arabic numeral system has largely superseded Roman numerals for numerical calculation, the enduring legacy of Roman numerals in various contexts ensures that they remain an integral part of our cultural landscape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are All The Factors For 40
Mar 09, 2025
-
Which Is A Characteristic Of A Mixture
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Highest Common Factor Of 28 And 42
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Matrix Of Blood Is Called
Mar 09, 2025
-
The Rate Of Change In Velocity Is Called
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Roman Numeral For The Arabic Number 507 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
