Which Is A Characteristic Of A Mixture
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
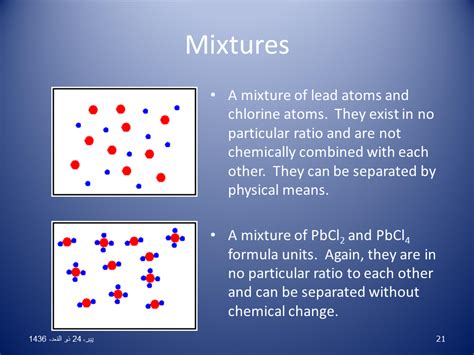
Table of Contents
Which is a Characteristic of a Mixture? A Deep Dive into the Properties of Mixtures
Mixtures are all around us, from the air we breathe to the food we eat. Understanding their characteristics is crucial in various fields, from chemistry and cooking to environmental science and material science. This comprehensive guide delves into the defining properties of mixtures, exploring their composition, behavior, and the ways they differ from pure substances.
Defining Mixtures: A Blend of Substances
A mixture is a substance comprising two or more components not chemically bonded. A key characteristic distinguishing mixtures from compounds is the lack of fixed proportions. Unlike compounds, where the elements combine in a specific ratio, mixtures can have varying ratios of their constituents. This variability is a cornerstone of their definition and leads to a range of observable properties.
Types of Mixtures: A Spectrum of Combinations
Mixtures exist in various forms, broadly categorized into:
-
Homogeneous Mixtures: These mixtures have a uniform composition throughout. At the macroscopic level, they appear as a single phase, meaning you can't visually distinguish the individual components. Examples include saltwater, air, and sugar dissolved in water.
-
Heterogeneous Mixtures: In contrast, heterogeneous mixtures exhibit non-uniform composition. Their components are visually distinguishable, existing as separate phases. Examples include sand and water, oil and water, and a salad.
The distinction between homogeneous and heterogeneous mixtures isn't always absolute; the scale of observation matters. Milk, for instance, appears homogeneous to the naked eye, but under a microscope, it reveals a heterogeneous mixture of fat globules and water.
Key Characteristics of Mixtures: Unveiling their Defining Properties
Several crucial characteristics differentiate mixtures from pure substances:
1. Variable Composition: The Hallmark of Mixtures
The ability to vary the proportions of components is a defining feature of mixtures. You can prepare saltwater solutions with varying concentrations of salt and water, each resulting in a different mixture. This contrasts sharply with compounds, where a change in the ratio of elements alters the substance's identity.
2. Retention of Individual Properties: Components Maintain Their Identity
A crucial aspect of mixtures is that their components retain their original properties. In a saltwater mixture, the salt retains its salty taste, and the water remains a liquid. This contrasts with chemical compounds, where the properties of the constituent elements change significantly upon bonding.
For instance, sodium (a highly reactive metal) and chlorine (a toxic gas) react to form sodium chloride (table salt), a completely different substance with distinct properties. In a mixture of sodium and chlorine (a highly dangerous proposition!), the properties of sodium and chlorine are retained – until a reaction is initiated, at which point a compound is formed.
3. Separation of Components: Utilizing Physical Methods
The components of mixtures can be separated using physical methods. These methods exploit differences in the physical properties of the components, such as boiling point, density, solubility, or particle size. Common separation techniques include:
- Filtration: Separates solids from liquids using a porous material.
- Evaporation: Separates a dissolved solid from a liquid by evaporating the liquid.
- Distillation: Separates liquids with different boiling points.
- Chromatography: Separates components based on their different affinities for a stationary and mobile phase.
- Decantation: Separates liquids of different densities by carefully pouring off the top layer.
- Centrifugation: Separates components with different densities by spinning them at high speeds.
- Magnetism: Separates magnetic materials from non-magnetic materials.
The ease of separation is a distinguishing factor between mixtures and compounds. Separating the components of a compound requires chemical reactions, breaking the chemical bonds holding the atoms together.
4. No Fixed Melting or Boiling Points: A Range of Transitions
Unlike pure substances, which have sharp melting and boiling points, mixtures typically melt and boil over a range of temperatures. This is because the individual components of a mixture have different melting and boiling points. The mixture's behavior reflects the collective properties of its constituents.
5. Properties Vary with Composition: A Consequence of Variable Ratios
The properties of a mixture, such as density, boiling point, and melting point, depend on the proportions of its components. A solution of 10% salt in water will have different properties than a solution of 50% salt in water. This dependence on composition underscores the variable nature of mixtures.
Examples of Mixtures in Everyday Life: A Ubiquitous Presence
Mixtures are ubiquitous in our daily lives, playing a vital role in numerous aspects of our existence. Consider the following examples:
- Air: A homogeneous mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen, oxygen, and argon.
- Seawater: A homogeneous mixture of water and various dissolved salts.
- Soil: A heterogeneous mixture of minerals, organic matter, and water.
- Milk: A heterogeneous mixture of water, fats, proteins, and carbohydrates.
- Blood: A heterogeneous mixture of cells, plasma, and other components.
- Concrete: A heterogeneous mixture of cement, sand, gravel, and water.
- Salad: A heterogeneous mixture of various vegetables.
- Coffee: A homogeneous mixture (after brewing) of water and dissolved coffee compounds.
- Soft drinks: Homogeneous mixtures of water, sugar, flavorings, and carbon dioxide.
- Brass: A homogeneous mixture (alloy) of copper and zinc.
Distinguishing Mixtures from Compounds: A Crucial Distinction
Understanding the difference between mixtures and compounds is fundamental in chemistry. While both involve combinations of substances, the nature of their bonding and properties significantly differentiates them.
| Feature | Mixture | Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding | No chemical bonds between components | Chemical bonds between atoms/molecules |
| Composition | Variable | Fixed |
| Separation | Physical methods | Chemical methods |
| Properties | Components retain original properties | New properties emerge; properties of components significantly altered |
| Melting/Boiling Point | Range of temperatures | Sharp melting and boiling points |
Applications of Mixture Understanding: Across Diverse Fields
The understanding of mixtures and their properties is essential in a wide range of applications:
- Material Science: Designing new materials with specific properties by combining different substances in specific ratios.
- Environmental Science: Analyzing the composition of air, water, and soil to assess environmental quality and pollution.
- Food Science: Creating food products with desirable textures, flavors, and nutritional content by mixing different ingredients.
- Medicine: Preparing drugs and solutions with precise concentrations of active ingredients.
- Chemical Engineering: Designing processes for separating and purifying substances from mixtures.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Mixtures
Mixtures are fundamental to our world, impacting various aspects of our lives. Their characteristics, particularly their variable composition and the retention of individual component properties, distinguish them from compounds. Understanding the different types of mixtures, methods for their separation, and the wide range of applications where they are encountered is crucial for anyone pursuing studies or careers in science, engineering, or related fields. This in-depth exploration provides a solid foundation for further investigations into the fascinating world of mixtures and their pervasive role in the natural and engineered world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Mountain Range Separates Europe From Asia
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Oxidized And Reduced In Cellular Respiration
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Greater Mb Or Gb
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is Water A Renewable Or A Nonrenewable Resource
Mar 09, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 12 And 9
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Is A Characteristic Of A Mixture . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
