Nucleus Is The Powerhouse Of The Cell
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 6 min read
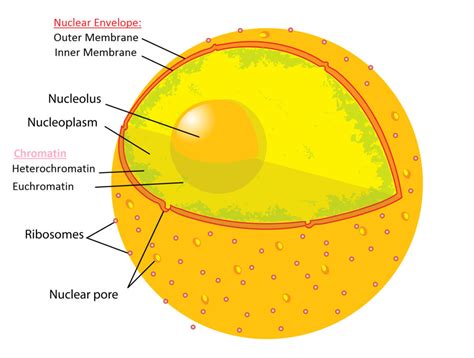
Table of Contents
Debunking the Myth: The Nucleus – More Than Just the Cell's Powerhouse
The ubiquitous phrase, "the nucleus is the powerhouse of the cell," is a common misconception perpetuated through simplified biology education. While the nucleus plays a vital role in cellular function, attributing it solely as the "powerhouse" is a gross oversimplification. The true powerhouse, responsible for generating the cell's energy currency (ATP), is actually the mitochondria. This article delves deeper into the intricate functions of the nucleus, clarifying its critical role in cellular life and debunking the persistent myth.
Understanding the Nucleus: The Cell's Control Center
The nucleus, a defining characteristic of eukaryotic cells, acts as the cell's control center, housing the genetic material, or DNA, organized into chromosomes. This DNA contains the blueprints for all cellular processes, essentially dictating the cell's identity, function, and lifecycle. Think of it as the cell's library, storing vast amounts of information crucial for its operation. But its function extends far beyond simply storing information; the nucleus is actively involved in regulating gene expression, transcription, and replication, all of which are fundamental for cellular life.
The Nuclear Envelope: A Protective Barrier
The nucleus isn't just a free-floating mass of DNA; it's enclosed within a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope. This envelope acts as a protective barrier, separating the genetic material from the cytoplasm, the bustling environment where cellular processes occur. The nuclear envelope is studded with nuclear pores, which are highly selective gateways regulating the transport of molecules between the nucleus and cytoplasm. This controlled transport ensures the proper regulation of gene expression and cellular function.
Nucleolus: The Ribosome Factory
Within the nucleus lies a dense, irregularly shaped structure called the nucleolus. The nucleolus isn't membrane-bound but is a crucial site for ribosome biogenesis. Ribosomes are the protein synthesis machinery of the cell, translating the genetic code into functional proteins. The nucleolus synthesizes ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and assembles the ribosomal subunits that are then transported to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. The activity of the nucleolus is directly related to the cell's protein synthesis demands, increasing in size and activity during periods of high protein production.
Chromatin and Chromosomes: The Genetic Material
The DNA within the nucleus isn't simply a disorganized tangle. Instead, it's meticulously organized into a complex structure called chromatin. Chromatin consists of DNA wrapped around histone proteins, forming a compact structure that allows for efficient storage and regulation of genetic information. During cell division, chromatin condenses into distinct structures called chromosomes, making them easier to manage and distribute to daughter cells. The precise organization of chromatin and chromosomes is vital for accurate replication and gene expression.
The Nucleus's Role in Gene Expression: Transcription and Beyond
The nucleus is far from a passive storage unit; it's the central hub for gene expression. Gene expression involves two major steps: transcription and translation. Transcription, occurring within the nucleus, is the process of copying a DNA sequence into a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. This mRNA molecule then carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the cytoplasm, where translation takes place.
Transcription Factors: Orchestrating Gene Expression
Transcription isn't a random process; it's tightly regulated by various proteins known as transcription factors. These factors bind to specific DNA sequences, either activating or repressing the transcription of nearby genes. This precise control ensures that only the necessary genes are expressed at the appropriate time and in the appropriate amounts. The intricate network of transcription factors allows the cell to respond dynamically to its environment and internal signals.
RNA Processing: Refining the Message
The mRNA molecule produced during transcription isn't immediately ready for translation. It undergoes several processing steps within the nucleus, including RNA splicing, capping, and polyadenylation. RNA splicing removes non-coding regions (introns) from the pre-mRNA, leaving only the coding regions (exons) to be translated. Capping and polyadenylation protect the mRNA molecule from degradation and help it to be efficiently translated in the cytoplasm. These processing steps ensure the fidelity of the genetic message.
The Nucleus in Cell Cycle Regulation and Cell Division
The nucleus plays a crucial role in the cell cycle, the ordered series of events leading to cell growth and division. The integrity of the nuclear envelope and the accurate replication and segregation of chromosomes are essential for ensuring the fidelity of cell division. Errors in these processes can lead to genetic instability and potentially cancer.
DNA Replication: Duplicating the Genetic Material
Before cell division, the entire genome must be accurately replicated to provide each daughter cell with a complete set of chromosomes. This replication occurs within the nucleus, involving complex enzymatic machinery ensuring high fidelity. The process is tightly regulated to prevent errors and maintain genome stability.
Mitosis and Meiosis: Distributing the Chromosomes
During mitosis, the process of cell division in somatic cells, the replicated chromosomes are precisely segregated into two daughter nuclei, each receiving a complete copy of the genome. Meiosis, the process of cell division in germ cells, involves two rounds of division, resulting in four haploid daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The nucleus plays a central role in ensuring the accurate segregation of chromosomes during both mitosis and meiosis.
Beyond the Powerhouse: The Nucleus's Multifaceted Roles
The nucleus is far more than a mere "powerhouse"; its diverse functions are fundamental to the cell's survival and function. It's the central control center, orchestrating gene expression, regulating cellular processes, and ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information during cell division. While mitochondria generate the energy needed for cellular processes, the nucleus directs the intricate symphony of cellular activities, making it the true conductor of the cellular orchestra.
Nuclear Lamina: Structural Support
The nuclear lamina is a protein meshwork lining the inner nuclear membrane, providing structural support and anchoring chromatin. It plays a role in organizing the genome and regulating gene expression. Disruptions in the nuclear lamina can contribute to various diseases.
Nuclear Matrix: Organization and Function
The nuclear matrix is a network of protein fibers within the nucleus that provides structural support and helps organize chromatin. It plays a role in various nuclear functions, including transcription and DNA replication.
Nuclear Bodies: Specialized Compartments
Various specialized compartments, often referred to as nuclear bodies, exist within the nucleus. These bodies include Cajal bodies, PML bodies, and paraspeckles, each with distinct functions related to RNA processing, gene regulation, and other cellular processes.
Conclusion: Redefining the Cell's Command Center
The notion of the nucleus as the "powerhouse of the cell" is a simplification that neglects its complex and multifaceted roles. The nucleus is the cell's true command center, orchestrating gene expression, regulating cellular processes, and ensuring the faithful transmission of genetic information. Its intricate structure and diverse functions are crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and overall organismal health. This accurate understanding of the nucleus is essential for appreciating the full complexity of eukaryotic cellular life. Further research continues to reveal the nuanced intricacies of nuclear function, constantly refining our understanding of this vital organelle. Moving forward, a more accurate portrayal of the nucleus will undoubtedly benefit scientific advancement and education alike.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Surface Area Of A Hemisphere Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
Put Numbers In Order From Least To Greatest
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Energy Levels Does Sodium Have
Mar 25, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between An Alternator And A Generator
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is Air A Compound Or A Mixture
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Nucleus Is The Powerhouse Of The Cell . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
