How Many Energy Levels Does Sodium Have
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
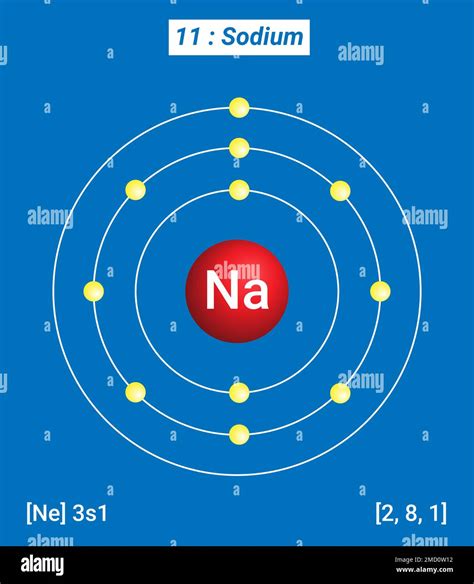
Table of Contents
How Many Energy Levels Does Sodium Have? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Sodium (Na), a ubiquitous element crucial for life, presents a fascinating case study in atomic structure and electron configuration. Understanding its energy levels is key to understanding its chemical behavior and properties. This article will delve deep into the energy levels of sodium, exploring its electronic configuration, quantum numbers, and the implications for its reactivity and applications.
Understanding Energy Levels in Atoms
Before focusing specifically on sodium, let's establish a fundamental understanding of atomic energy levels. Atoms are composed of a nucleus containing protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons occupying specific energy levels or shells. These shells are not arbitrarily arranged; they are governed by quantum mechanics, a branch of physics dealing with the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level.
Each energy level can hold a limited number of electrons. The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the lower its energy level. As we move further from the nucleus, the energy levels increase. These energy levels are not continuous; they are quantized, meaning electrons can only occupy specific, discrete energy levels and not exist in between.
The principal quantum number (n) designates the energy level, starting with n=1 for the lowest energy level (closest to the nucleus) and increasing for higher energy levels. The higher the value of n, the greater the distance of the electron from the nucleus and the higher its energy.
Subshells and Orbitals
Within each principal energy level (n), there are subshells, designated by the azimuthal quantum number (l). The value of l can range from 0 to n-1. Each subshell corresponds to a different type of orbital. For example:
- l = 0: s subshell (spherical orbital) – can hold up to 2 electrons
- l = 1: p subshell (dumbbell-shaped orbitals) – can hold up to 6 electrons
- l = 2: d subshell (complex shapes) – can hold up to 10 electrons
- l = 3: f subshell (even more complex shapes) – can hold up to 14 electrons
Sodium's Electronic Configuration and Energy Levels
Sodium has an atomic number of 11, meaning it possesses 11 protons and, in its neutral state, 11 electrons. To determine its energy levels, we follow the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first. The electronic configuration of sodium is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹.
Let's break down this configuration in terms of energy levels:
- Energy Level 1 (n=1): This level contains the 1s subshell, which holds two electrons (1s²).
- Energy Level 2 (n=2): This level contains the 2s and 2p subshells. The 2s subshell holds two electrons (2s²), and the 2p subshell holds six electrons (2p⁶).
- Energy Level 3 (n=3): This level contains the 3s subshell, which holds the remaining electron (3s¹).
Therefore, sodium has three principal energy levels occupied by its electrons. It's crucial to note that while higher energy levels exist theoretically, they are unoccupied in the ground state of a sodium atom.
Visualizing Sodium's Electron Configuration
Imagine a simplified model:
- The nucleus is at the center.
- The first energy level (n=1) is a small sphere close to the nucleus, containing two electrons.
- The second energy level (n=2) is a larger sphere further from the nucleus, containing eight electrons.
- The third energy level (n=3) is an even larger sphere, containing a single electron.
This simplified model, though not entirely accurate in representing the quantum mechanical nature of electron orbitals, helps visualize the electron distribution in sodium's atom.
Implications of Sodium's Energy Levels: Chemical Reactivity
Sodium's outermost electron in the 3s orbital is relatively loosely bound to the nucleus. This single electron in the valence shell is responsible for sodium's high reactivity. It readily loses this electron to achieve a stable octet configuration (like the noble gas neon), forming a +1 ion (Na⁺). This electron transfer is the basis for sodium's participation in ionic bonds, which are crucial in many chemical compounds and biological processes.
The ease with which sodium loses its valence electron contributes to its:
- Low ionization energy: The energy required to remove the outermost electron is relatively low.
- High reactivity: It readily reacts with other elements, particularly nonmetals like chlorine (forming sodium chloride, NaCl), oxygen, and water.
- Electropositivity: It has a strong tendency to lose electrons and form positive ions.
Sodium's Role in Biological Systems and Industrial Applications
The unique electronic configuration and the ease with which sodium loses an electron are fundamental to its importance in various biological and industrial processes.
Biological Significance:
- Nerve Impulse Transmission: Sodium ions (Na⁺) play a crucial role in the transmission of nerve impulses. The movement of Na⁺ ions across cell membranes generates electrical signals essential for communication within the nervous system.
- Muscle Contraction: Similar to nerve impulse transmission, the movement of sodium ions is crucial for muscle contraction.
- Fluid Balance: Sodium ions contribute to maintaining the osmotic balance between the intracellular and extracellular fluids in the body.
Industrial Applications:
- Sodium Lamps: Sodium vapor lamps are highly efficient and produce a characteristic yellow-orange light used in street lighting.
- Sodium-Sulfur Batteries: These batteries utilize sodium and sulfur electrodes and offer high energy density.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): A crucial chemical used in various applications, from soap manufacturing to paper production. The production of NaOH involves the electrolysis of sodium chloride solutions.
Beyond the Basics: Quantum Mechanical Description
The simplified model of energy levels provides a useful conceptual understanding, but a more accurate description requires the application of quantum mechanics. This involves solving the Schrödinger equation for a multi-electron atom, which is complex and requires sophisticated mathematical tools. However, some key concepts are important:
- Quantum Numbers: These numbers (n, l, m<sub>l</sub>, m<sub>s</sub>) precisely define the properties of each electron within the atom.
- Orbitals: Electrons are not simply particles orbiting the nucleus; they are described by wave functions that determine the probability of finding an electron in a specific region of space (an orbital).
- Electron-Electron Repulsion: The interaction between electrons within the same atom influences their energy levels and distribution. This repulsion is not considered in the simple model but is crucial for accurate predictions of atomic properties.
Conclusion
Sodium's three occupied energy levels, characterized by its electronic configuration 1s²2s²2p⁶3s¹, determine its unique chemical behavior and reactivity. The loosely bound valence electron is responsible for its tendency to readily lose an electron, forming a stable cation (Na⁺). This property is crucial for sodium's diverse biological roles and industrial applications. While a simple model provides a basic understanding, a complete description requires the intricacies of quantum mechanics, providing a deeper appreciation of the subtle interplay of forces governing atomic structure and behavior. Understanding sodium's energy levels provides a foundation for comprehending its significance in various aspects of science, technology, and everyday life. Further exploration into quantum mechanics unveils a more nuanced and complete picture of this seemingly simple element's remarkable properties.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements Are Correct
Mar 26, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 2 And 9
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is 54 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
Unit Of Measurement For Specific Heat Capacity
Mar 26, 2025
-
Cod Chemical Oxygen Demand Vs Bod
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Energy Levels Does Sodium Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
