Name Of A Seven Sided Polygon
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
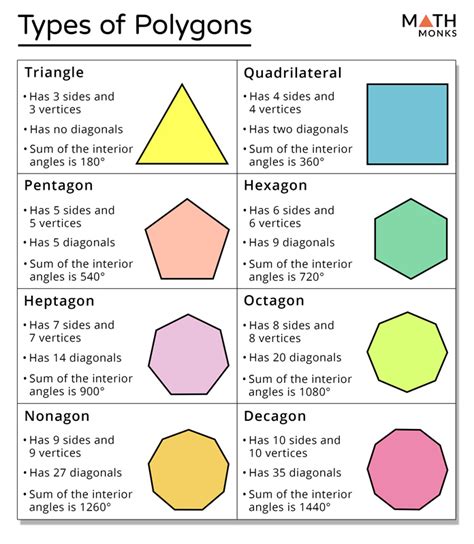
Table of Contents
The Heptagon: Unveiling the Secrets of the Seven-Sided Polygon
The world of geometry is filled with fascinating shapes, each with its unique properties and captivating history. Among these, the heptagon, a polygon with seven sides and seven angles, stands out for its intriguing characteristics and relative complexity compared to its more common counterparts like the square or hexagon. This comprehensive guide will delve into the depths of the heptagon, exploring its definition, properties, construction, applications, and its significance across various fields. We'll also touch upon some lesser-known facts and historical context surrounding this often-overlooked geometrical marvel.
Defining the Heptagon: A Deep Dive into Seven-Sided Shapes
A heptagon, also known as a septagon, is a two-dimensional closed geometric figure composed of seven straight sides and seven angles. The term "heptagon" derives from the Greek words "hepta," meaning seven, and "gonia," meaning angle. This etymology clearly points to its defining characteristic: its seven-sided structure. Understanding this fundamental definition is crucial before we explore its more intricate properties.
Regular vs. Irregular Heptagons: Key Distinctions
Heptagons can be classified into two main categories based on their side and angle measurements:
-
Regular Heptagon: A regular heptagon is a heptagon where all seven sides are of equal length, and all seven interior angles are equal. Each interior angle in a regular heptagon measures approximately 128.57 degrees. Constructing a perfect regular heptagon is famously challenging, and it cannot be constructed using only a compass and straightedge, unlike some other regular polygons.
-
Irregular Heptagon: An irregular heptagon is a heptagon where the lengths of its sides and the measures of its interior angles are not all equal. There is a vast diversity of irregular heptagons, each possessing its unique set of side and angle measurements.
Exploring the Properties of Heptagons: Angles, Diagonals, and More
Heptagons, like all polygons, possess several key properties that define their geometric behavior. Understanding these properties is essential for working with heptagons in various mathematical contexts.
Interior Angles: The Sum and Individual Measures
The sum of the interior angles of any polygon can be calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180°, where 'n' is the number of sides. For a heptagon (n=7), the sum of its interior angles is (7-2) * 180° = 900°. In a regular heptagon, each interior angle measures 900°/7 ≈ 128.57°. However, in an irregular heptagon, the interior angles will vary, but their sum will always remain 900°.
Exterior Angles: A Complementary Perspective
The exterior angles of a polygon are supplementary to its interior angles. The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon, including a heptagon, always equals 360°. In a regular heptagon, each exterior angle measures 360°/7 ≈ 51.43°.
Diagonals: Connecting the Vertices
A diagonal is a line segment that connects two non-adjacent vertices of a polygon. The number of diagonals in a polygon can be calculated using the formula n(n-3)/2, where 'n' is the number of sides. For a heptagon, this translates to 7(7-3)/2 = 14 diagonals. These diagonals play a crucial role in analyzing the properties and subdivisions of the heptagon.
Constructing a Heptagon: Methods and Challenges
Constructing a perfect regular heptagon is a famously challenging task. Unlike some regular polygons like the equilateral triangle or square, it cannot be constructed using only a compass and straightedge. This is due to the fact that the angle 360°/7 is not a constructible angle.
Approximate Constructions: Reaching for Precision
While a perfect geometric construction is impossible, there are various methods to construct approximate regular heptagons. These methods usually involve iterative processes or utilizing trigonometric calculations to achieve a high degree of accuracy. These approximations are often sufficient for practical applications where perfect precision is not critical.
Utilizing Technology: Computer-Aided Design (CAD)
Modern tools like CAD software can easily create precise regular heptagons. These programs utilize algorithms that calculate the necessary coordinates for each vertex, providing a highly accurate representation of the desired shape.
Heptagons in Real-World Applications: From Architecture to Nature
Despite its construction challenges, the heptagon appears in surprisingly many real-world applications and natural occurrences.
Architecture and Design: Seven-Sided Structures
While less common than other polygons, heptagons can be found in some architectural designs. Certain buildings and structures might incorporate heptagonal elements for aesthetic or functional reasons. Although it's not a frequently chosen shape, its unique visual appeal can contribute to a distinct architectural style.
Nature's Heptagons: Unexpected Appearances
While not as prevalent as hexagons (found in honeycombs), heptagonal shapes can occasionally appear in nature, albeit often in less perfect forms. Crystal structures and certain natural formations can exhibit approximate heptagonal symmetries.
Other Applications: From Logos to Games
Heptagons also find their way into less obvious applications. For example, some logos and designs incorporate heptagonal shapes to create a distinctive visual impression. They might also appear in games, puzzles, or other creative endeavors where unique geometric shapes are desired.
The Mathematical Significance of the Heptagon: Beyond the Basics
The heptagon's mathematical properties have intrigued mathematicians for centuries. Its non-constructibility with compass and straightedge has been a source of both challenge and fascination.
The Non-Constructibility Problem: A Historical Perspective
The impossibility of constructing a regular heptagon using only a compass and straightedge is a significant result in geometry. This non-constructibility stems from the fact that the angle 360°/7 cannot be expressed using only square roots, a fundamental limitation within the constraints of compass and straightedge constructions.
Advanced Mathematical Concepts: Exploring Connections
The heptagon's properties have led to the exploration of various advanced mathematical concepts, including those related to number theory, algebra, and complex numbers. These explorations contribute to a broader understanding of geometric properties and their relation to other mathematical fields.
Conclusion: The Enduring Appeal of the Seven-Sided Shape
The heptagon, despite being less familiar than its more commonly encountered polygonal counterparts, holds a unique place in geometry. Its intriguing properties, the challenges associated with its construction, and its surprisingly diverse range of real-world appearances make it a captivating subject of study. From its basic definition to its advanced mathematical implications, the heptagon presents a compelling case for the enduring allure of geometric shapes and their role in shaping our understanding of the world around us. Its non-constructibility highlights the boundaries of classical geometric methods, while its presence in various applications demonstrates its practical significance. The heptagon, therefore, deserves more recognition for its contributions to both the theoretical and practical aspects of mathematics and beyond.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Oxygen
Mar 28, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Letters Does Not Suffer Lateral Inversion
Mar 28, 2025
-
Is 53 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 15
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Percent Is 2 3 Of A Circle
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Name Of A Seven Sided Polygon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
