Molecular Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2
Juapaving
Mar 30, 2025 · 5 min read
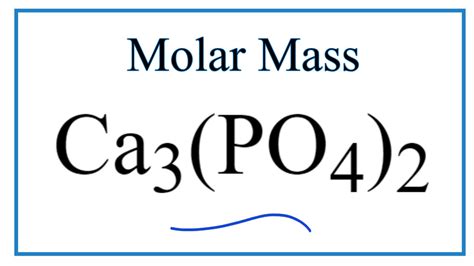
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into the Molecular Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂: A Comprehensive Guide
Calcium phosphate, specifically tricalcium phosphate (Ca₃(PO₄)₂), is a ubiquitous compound found in various biological and industrial applications. Understanding its molecular mass is crucial for numerous calculations in chemistry, biochemistry, and materials science. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, detailing the calculation process, its significance, and applications.
Understanding Molecular Mass
The molecular mass (also known as molecular weight) of a compound represents the total mass of all the atoms present in a molecule of that compound. It's expressed in atomic mass units (amu) or Daltons (Da). Calculating the molecular mass involves adding the atomic masses of each element present in the molecule, considering the number of atoms of each element.
Calculating the Molecular Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂
To calculate the molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, we need the atomic masses of calcium (Ca), phosphorus (P), and oxygen (O). These values can be found on the periodic table:
- Calcium (Ca): Approximately 40.08 amu
- Phosphorus (P): Approximately 30.97 amu
- Oxygen (O): Approximately 16.00 amu
Now, let's break down the calculation:
-
Calcium (Ca): There are three calcium atoms (3 Ca) in the formula unit. Therefore, the total mass contribution from calcium is 3 * 40.08 amu = 120.24 amu.
-
Phosphorus (P): There are two phosphorus atoms (2 P) in the formula unit. Thus, the total mass contribution from phosphorus is 2 * 30.97 amu = 61.94 amu.
-
Oxygen (O): There are eight oxygen atoms (8 O) in the formula unit (4 oxygen atoms per phosphate ion, and two phosphate ions). The total mass contribution from oxygen is 8 * 16.00 amu = 128.00 amu.
-
Total Molecular Mass: To find the total molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, we sum the mass contributions from each element: 120.24 amu + 61.94 amu + 128.00 amu = 310.18 amu
Therefore, the molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is approximately 310.18 amu. Slight variations may occur depending on the source of the atomic mass values used.
Significance of the Molecular Mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂
Knowing the molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is crucial for several reasons:
-
Stoichiometric Calculations: In chemical reactions involving Ca₃(PO₄)₂, the molecular mass is essential for converting between mass and moles. This is fundamental for determining reactant quantities, product yields, and limiting reagents.
-
Concentration Calculations: In solutions containing Ca₃(PO₄)₂, the molecular mass is used to calculate molarity, molality, and other concentration units. Precise concentration values are vital in many analytical and biological applications.
-
Material Science Applications: In materials science, the molecular mass helps determine the properties of materials containing Ca₃(PO₄)₂, such as density, crystallinity, and reactivity. This is critical for developing new biomaterials and ceramics.
-
Biomedical Applications: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is a key component in bone and teeth. Understanding its molecular mass is essential in studying bone metabolism, developing bone grafts, and designing drug delivery systems targeting bone tissue.
-
Agricultural Applications: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is a vital component of fertilizers. Its molecular mass is essential for calculating the nutrient content of fertilizers and optimizing their application rates for effective crop growth.
Applications of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ and the Importance of Molecular Mass Calculations
The applications of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ are incredibly diverse, spanning various scientific and industrial fields:
1. Biomedical Applications:
-
Bone Grafts and Implants: Tricalcium phosphate's biocompatibility and osteoconductive properties make it an ideal material for bone grafts and implants. Accurate molecular mass calculations are vital for designing scaffolds with the correct porosity and mechanical strength.
-
Drug Delivery: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ nanoparticles can be used as drug carriers, delivering therapeutic agents directly to bone tissue. Molecular mass calculations aid in optimizing particle size and drug loading capacity.
-
Dental Materials: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is used in dental cements and restorative materials due to its excellent bioactivity and strength. Precise molecular mass calculations ensure consistent material properties.
2. Industrial Applications:
-
Fertilizers: As a major source of phosphorus, Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is a key ingredient in fertilizers, improving crop yields. Knowing its molecular mass is crucial for determining fertilizer composition and application rates.
-
Ceramics: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is used in the production of high-strength ceramics due to its thermal stability and chemical inertness. Molecular mass is important for controlling the ceramic's properties and microstructure.
-
Food Additives: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ is sometimes used as a food additive, acting as a firming agent and source of calcium.
3. Environmental Applications:
- Water Treatment: Ca₃(PO₄)₂ can be used in water treatment to remove heavy metals and other pollutants. Molecular mass calculations are essential for determining the optimal dosage.
4. Research Applications:
-
Biomineralization Studies: Understanding Ca₃(PO₄)₂'s molecular mass is crucial for studying the process of biomineralization, where living organisms create mineralized tissues like bone and teeth.
-
Nanomaterials Research: Research into the synthesis and properties of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ nanoparticles relies heavily on accurate molecular mass calculations.
Beyond the Basics: Isotopes and Isotopic Mass
The molecular mass calculated above uses the average atomic masses of the elements from the periodic table. However, elements exist as isotopes, which are atoms of the same element with varying numbers of neutrons. This means they have slightly different masses. For very precise calculations, particularly in mass spectrometry or nuclear chemistry, using isotopic masses instead of average atomic masses might be necessary.
For example, calcium has several stable isotopes, each with a different mass. To calculate the molecular mass considering isotopes, you'd need to know the isotopic abundance of each calcium isotope and use the mass of each isotope in the calculation, weighted according to its abundance. This is a more complex calculation, often requiring specialized software.
Conclusion
The molecular mass of Ca₃(PO₄)₂, approximately 310.18 amu, is a fundamental parameter with significant implications across various scientific disciplines. Accurate determination of this value is critical for stoichiometric calculations, concentration measurements, material characterization, and a wide array of applications ranging from biomedical engineering to agricultural practices. Understanding both the basic calculation and the complexities introduced by isotopes enhances our ability to use this important compound effectively. Further exploration into the specific applications of Ca₃(PO₄)₂ will reveal even more instances where the precise calculation of its molecular mass is paramount for success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Exponents Worksheets Pdf With Answers 7th
Apr 01, 2025
-
Is Chlorine A Pure Substance Or Mixture
Apr 01, 2025
-
How Do You Write 19 In Roman Numerals
Apr 01, 2025
-
Why Is It Warmer When It Snows
Apr 01, 2025
-
A Positively Charged Ion Is Called
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Molecular Mass Of Ca3 Po4 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
