Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
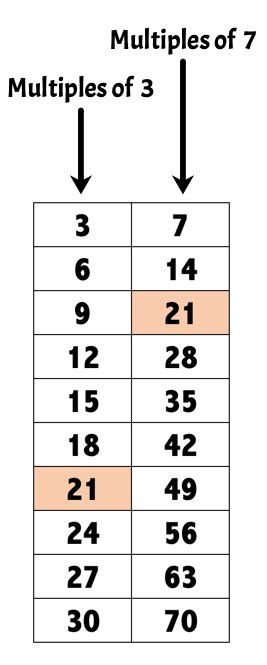
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 3 and 7: A Deep Dive
The concept of the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental element in mathematics, particularly within number theory and arithmetic. Understanding LCMs is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex mathematical problems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the LCM of 3 and 7, providing a step-by-step explanation, exploring different methods for calculation, and highlighting its significance in broader mathematical contexts. We'll go beyond a simple answer, exploring the underlying principles and showcasing the practical relevance of this seemingly basic concept.
Understanding the Fundamentals: What is LCM?
Before we tackle the specific case of 3 and 7, let's establish a solid foundation. The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 4 and 6. Multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20... Multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 12, hence the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 7: Three Proven Methods
Now, let's focus on finding the LCM of 3 and 7. We'll explore three common and effective methods:
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward approach, particularly suitable for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest number present in both sequences is 21. Therefore, the LCM of 3 and 7 is 21.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
Since 3 and 7 are both prime numbers and have no common factors, their LCM is simply the product of these prime factors: 3 x 7 = 21.
Method 3: Using the Formula (For Two Numbers)
For two numbers, a and b, a convenient formula exists to calculate the LCM:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
Where GCD(a, b) represents the Greatest Common Divisor of a and b.
In the case of 3 and 7:
- GCD(3, 7) = 1 (Since 3 and 7 have no common divisors other than 1)
- LCM(3, 7) = (3 x 7) / 1 = 21
This formula elegantly connects the LCM and GCD, showcasing the inherent relationship between these two crucial concepts in number theory.
The Significance of LCM in Real-World Applications
While the LCM of 3 and 7 might seem like a trivial mathematical exercise, the concept of LCM has far-reaching applications in various fields:
1. Fraction Simplification and Arithmetic
The LCM plays a vital role in adding and subtracting fractions. To add or subtract fractions with different denominators, we must find the LCM of the denominators and then express each fraction with this common denominator. This ensures accurate and efficient calculation. For example, adding 1/3 and 1/7 requires finding the LCM of 3 and 7 (which is 21), transforming the fractions to 7/21 and 3/21 respectively, and then adding them to obtain 10/21.
2. Scheduling and Cyclical Events
LCM finds practical use in scheduling repetitive events. Imagine two machines operating on cycles of 3 and 7 days respectively. To determine when both machines will be down for maintenance simultaneously, we need to find the LCM of 3 and 7, which is 21. This indicates that both machines will be down together every 21 days. This principle extends to various scheduling problems, from factory production lines to public transportation schedules.
3. Music Theory and Harmony
In music theory, LCM is used to understand the relationships between different musical intervals and to determine when different musical patterns will coincide. For example, the relationship between two musical notes that are 3 and 7 semitones apart can be analyzed using their LCM.
4. Computer Science and Algorithms
The LCM is also used in several computer algorithms, such as finding the least common multiple of a series of numbers, which has applications in cryptography, database management and more.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
While our focus has been on the LCM of 3 and 7, the concept extends to more than two numbers. The process remains similar, but the complexity increases. For example, to find the LCM of 3, 7, and 5, you would either list multiples, use prime factorization (finding the highest power of each prime factor present in the numbers), or employ more advanced algorithms designed for multiple numbers. Understanding the principles for two numbers provides a strong foundation for tackling problems involving multiple numbers.
Conclusion: The Power of Simplicity in Mathematics
The LCM of 3 and 7, seemingly simple at first glance, reveals the underlying power and practical utility of fundamental mathematical concepts. Understanding LCM is not just about memorizing formulas; it's about grasping the principles of divisibility, prime factorization, and the interconnectedness of mathematical ideas. From simplifying fractions to solving complex scheduling problems, the LCM plays a significant role across various disciplines, underscoring the enduring relevance of even the most basic mathematical concepts. This comprehensive exploration of the LCM of 3 and 7 offers a firm foundation for tackling more complex problems and appreciating the beauty and practicality of mathematics. The ability to efficiently calculate LCMs is an essential skill for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of arithmetic and its applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 12 And 16
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Is 30 In Roman Numerals
Mar 15, 2025
-
How Many Ft Is 72 Inches
Mar 15, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 12 And 18
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Are The Horizontal Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
