What Is 30 In Roman Numerals
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
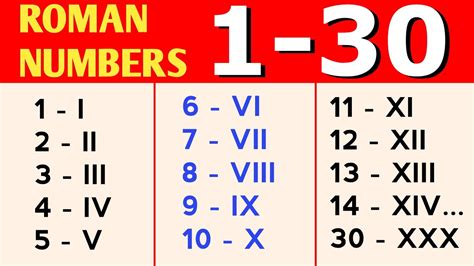
Table of Contents
- What Is 30 In Roman Numerals
- Table of Contents
- What is 30 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeration
- Understanding the Roman Numeral System
- Core Symbols and their Values
- The Additive and Subtractive Principles
- Deconstructing 30 in Roman Numerals: XXX
- Beyond 30: Exploring Larger and Smaller Numbers
- Numbers below 30:
- Numbers above 30:
- Applications of Roman Numerals
- Limitations of the Roman Numeral System
- Converting between Roman Numerals and Decimal Numbers
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
What is 30 in Roman Numerals? A Deep Dive into Roman Numeration
The question, "What is 30 in Roman numerals?" seems simple at first glance. The answer, XXX, is easily memorized. However, a deeper exploration reveals fascinating insights into the Roman numeral system, its history, its applications, and even its limitations. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the initial question but will also provide a thorough understanding of Roman numerals, empowering you to confidently convert numbers to and from this ancient system.
Understanding the Roman Numeral System
The Roman numeral system, developed in ancient Rome, uses combinations of letters to represent numbers. Unlike the decimal system (base-10) we use today, which is positional, the Roman system is additive and subtractive. This means the value of a symbol depends not only on the symbol itself but also on its position relative to other symbols.
Core Symbols and their Values
The foundation of the Roman numeral system lies in seven core symbols:
- I = 1
- V = 5
- X = 10
- L = 50
- C = 100
- D = 500
- M = 1000
These symbols, representing powers of 10 and their midpoints, allow for the representation of a wide range of numbers.
The Additive and Subtractive Principles
The core principle of Roman numerals is addition. When a symbol is placed after a symbol of equal or greater value, their values are added. For example:
- VI = 6 (5 + 1)
- XV = 15 (10 + 5)
- CXX = 120 (100 + 10 + 10)
However, the system also employs a subtractive principle. When a symbol of lesser value precedes a symbol of greater value, the lesser value is subtracted from the greater. This rule applies only to specific pairs:
- IV = 4 (5 - 1)
- IX = 9 (10 - 1)
- XL = 40 (50 - 10)
- XC = 90 (100 - 10)
- CD = 400 (500 - 100)
- CM = 900 (1000 - 100)
This subtractive principle enhances efficiency by avoiding lengthy additive sequences. For example, writing 9 as "VIIII" is less elegant than "IX".
Deconstructing 30 in Roman Numerals: XXX
Now, let's return to our original question: What is 30 in Roman numerals?
The answer is simply XXX. This is because we use the additive principle:
- X = 10
- XX = 20 (10 + 10)
- XXX = 30 (10 + 10 + 10)
There's no need for subtractive notation here; the straightforward additive approach yields the correct representation.
Beyond 30: Exploring Larger and Smaller Numbers
Understanding how 30 is represented in Roman numerals allows us to explore broader applications. Let's consider some examples:
Numbers below 30:
- I = 1
- II = 2
- III = 3
- IV = 4
- V = 5
- VI = 6
- VII = 7
- VIII = 8
- IX = 9
- X = 10
- XI = 11
- XII = 12
- XIII = 13
- XIV = 14
- XV = 15
- XVI = 16
- XVII = 17
- XVIII = 18
- XIX = 19
- XX = 20
- XXI = 21
- XXII = 22
- XXIII = 23
- XXIV = 24
- XXV = 25
- XXVI = 26
- XXVII = 27
- XXVIII = 28
- XXIX = 29
Numbers above 30:
- XL = 40
- L = 50
- LX = 60
- LXX = 70
- LXXX = 80
- XC = 90
- C = 100
- CC = 200
- CCC = 300
- CD = 400
- D = 500
- DC = 600
- DCC = 700
- DCCC = 800
- CM = 900
- M = 1000
- MM = 2000
- MMM = 3000
Applications of Roman Numerals
Though less prevalent in everyday mathematics, Roman numerals persist in various contexts:
- Clock faces: Many analog clocks use Roman numerals for the hours (typically I through XII).
- Outlines and lists: Roman numerals are often employed for outlining major sections of a document, providing a clear hierarchical structure.
- Copyright dates: Some copyright notices utilize Roman numerals, particularly in more formal or traditional settings.
- Movie sequels: Film series sometimes use Roman numerals to number their sequels (e.g., "Star Wars Episode V").
- Super Bowl numbers: The Super Bowl is numbered using Roman numerals.
- Chapter numbering in books: Some books, especially older or classic texts, use Roman numerals for chapter numbers.
Limitations of the Roman Numeral System
While elegant in its simplicity, the Roman numeral system has limitations compared to the decimal system:
- No zero: The Roman system lacks a symbol for zero, a fundamental concept in modern mathematics.
- Cumbersome for large numbers: Representing very large numbers becomes increasingly cumbersome and less efficient compared to the concise representation possible in the decimal system.
- Ambiguity: Without clear rules about spacing or grouping, interpretations can become ambiguous.
- Arithmetic operations: Performing arithmetic operations, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division, using Roman numerals is significantly more challenging compared to the decimal system.
Converting between Roman Numerals and Decimal Numbers
Converting between Roman numerals and decimal numbers requires understanding the additive and subtractive principles. Here's a basic approach:
Converting from Roman numerals to decimal:
- Identify each Roman numeral symbol and its corresponding value.
- Apply the additive and subtractive principles, considering the position of each symbol.
- Add the values to obtain the decimal equivalent.
Converting from decimal to Roman numerals:
- Break down the decimal number into powers of 10 (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones).
- Identify the corresponding Roman numeral symbols for each power of 10.
- Combine the symbols using the additive and subtractive principles to obtain the Roman numeral representation.
Conclusion
While the question, "What is 30 in Roman numerals?" has a simple answer (XXX), exploring the broader context reveals the intricacies and historical significance of the Roman numeral system. Understanding its principles, applications, and limitations allows for a deeper appreciation of this ancient system and provides the knowledge to navigate conversions between Roman numerals and the decimal system we use daily. Though largely superseded by the efficiency of the decimal system for complex calculations, Roman numerals remain a compelling example of an historical numeration system with continued relevance in specific contexts. Their persistence underlines their enduring cultural significance and their continued practical application.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find Out Perimeter Of A Rectangle
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 11
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Two Types Of Currents
Mar 16, 2025
-
Alternative Forms Of The Same Gene Are Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Is Heavier A Pound Or A Kilogram
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is 30 In Roman Numerals . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
