Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 4 And 5
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
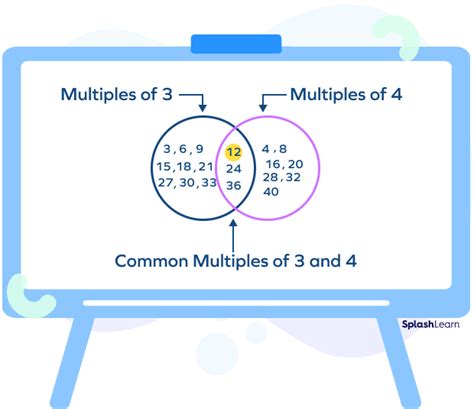
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Secrets of the Lowest Common Multiple: A Deep Dive into LCM(3, 4, 5)
Finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, relegated to the dusty corners of elementary school math. However, understanding the LCM, particularly in the context of seemingly straightforward numbers like 3, 4, and 5, opens doors to a richer appreciation of number theory and its applications in various fields. This comprehensive guide will explore the LCM(3, 4, 5), delving into its calculation, practical applications, and the underlying mathematical principles that govern it.
What is the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)?
Before we tackle the specific case of LCM(3, 4, 5), let's establish a firm understanding of what the LCM actually represents. The lowest common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. This concept finds applications in diverse areas, from scheduling tasks to solving complex engineering problems.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
Several methods exist for determining the LCM, each offering its own advantages depending on the complexity of the numbers involved. Let's explore the most common techniques:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method is intuitive and straightforward, particularly for smaller numbers. We simply list out the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 60. Therefore, LCM(3, 4, 5) = 60. This method is effective for small numbers but becomes cumbersome for larger ones.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method leverages the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, which states that every integer greater than 1 can be uniquely represented as a product of prime numbers. This method is generally more efficient for larger numbers.
-
Find the prime factorization of each number:
- 3 = 3
- 4 = 2²
- 5 = 5
-
Identify the highest power of each prime factor:
- The prime factors are 2, 3, and 5.
- The highest power of 2 is 2².
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹.
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹.
-
Multiply the highest powers together:
- LCM(3, 4, 5) = 2² * 3 * 5 = 4 * 3 * 5 = 60
This method provides a systematic and efficient approach, particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are intimately related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers equals the product of the two numbers themselves. This relationship can be extended to more than two numbers, although the calculation becomes more involved. For our example:
-
Find the GCD of 3, 4, and 5: The GCD of 3, 4, and 5 is 1, as they share no common factors other than 1.
-
Use the relationship LCM(a, b, c) * GCD(a, b, c) = a * b * c (for three numbers):
- LCM(3, 4, 5) * 1 = 3 * 4 * 5
- LCM(3, 4, 5) = 60
This method highlights the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD, offering an alternative perspective on the calculation.
Applications of LCM
The seemingly simple concept of the LCM finds surprisingly diverse applications across various fields:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have three tasks: one that repeats every 3 days, another every 4 days, and a third every 5 days. When will all three tasks coincide? The answer is the LCM(3, 4, 5) = 60 days. This principle is crucial in scheduling meetings, production cycles, and various other time-dependent activities.
2. Fractions and Arithmetic
When adding or subtracting fractions, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential to find a common denominator, simplifying the calculation. Understanding the LCM helps streamline fractional arithmetic and makes it significantly easier.
3. Music Theory
Musical intervals and harmonies are often expressed as ratios of frequencies. The LCM plays a role in determining when different musical notes or chords will harmonize perfectly, creating consonant sounds.
4. Engineering and Construction
In engineering and construction projects, the LCM is used in determining the optimal timing for certain processes or the synchronization of different components. This ensures efficient and synchronized operation.
5. Computer Science
The LCM concept appears in various algorithms and data structures in computer science, particularly in areas involving scheduling, synchronization, and resource management.
LCM and its Significance in Number Theory
The LCM is a fundamental concept in number theory, a branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of integers. Its relationship with the GCD, prime factorization, and modular arithmetic underscores its importance in deeper mathematical explorations. Understanding the LCM provides a gateway to understanding more advanced number-theoretic concepts.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Related Concepts
The concept of LCM extends to more complex scenarios:
-
LCM of more than three numbers: The methods described above can be generalized to find the LCM of any number of integers. The prime factorization method remains a particularly efficient approach.
-
LCM and modular arithmetic: The LCM plays a crucial role in solving congruences and systems of congruences in modular arithmetic, a powerful tool in cryptography and other areas.
-
LCM in abstract algebra: The concept of LCM generalizes to more abstract algebraic structures, extending its reach beyond the realm of integers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Relevance of LCM(3, 4, 5)
While LCM(3, 4, 5) = 60 might seem like a simple result, the journey to understanding its calculation and its myriad applications highlights the depth and power of seemingly basic mathematical concepts. This seemingly simple problem provides a springboard for exploring more complex mathematical ideas and showcases the practical relevance of number theory in various fields. By mastering the concept of LCM, we gain not just a computational skill, but a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness and elegance of mathematics. This understanding empowers us to tackle more challenging problems and opens doors to advanced mathematical explorations. The journey from a simple LCM calculation to a broader understanding of number theory is a testament to the rich and rewarding nature of mathematical inquiry.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 91
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is Carbon Metal Nonmetal Or Metalloid
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Percentage Of 2 3rds
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Prime Factorization Of 63
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Are The Building Blocks Of All Matter
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 4 And 5 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
