What Is Prime Factorization Of 63
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 5 min read
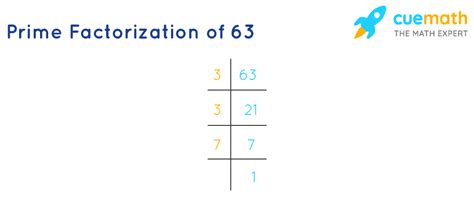
Table of Contents
What is Prime Factorization of 63? A Deep Dive into Prime Numbers and Factorization
Prime factorization, a cornerstone of number theory, is the process of breaking down a composite number into its prime number components. Understanding prime factorization is crucial not only for mathematical calculations but also for various applications in cryptography, computer science, and other fields. This article will delve into the concept of prime factorization, focusing specifically on the prime factorization of 63, and explore related concepts along the way.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before we tackle the prime factorization of 63, let's establish a firm grasp on what constitutes a prime number. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. In simpler terms, it's a number that's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. The first few prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Note that 1 is not considered a prime number.
Key characteristics of prime numbers:
- Divisibility: Only divisible by 1 and itself.
- Infinitude: There are infinitely many prime numbers. This was proven by Euclid centuries ago.
- Distribution: The distribution of prime numbers is a fascinating topic in its own right, and mathematicians continue to study its patterns.
Understanding Composite Numbers
A composite number is a positive integer that has at least one positive divisor other than 1 and itself. In essence, it's a number that can be factored into smaller positive integers. For instance, 6 is a composite number because it's divisible by 2 and 3 (besides 1 and 6). Every composite number can be uniquely expressed as a product of prime numbers – this is the essence of the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
The Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic
This theorem forms the bedrock of prime factorization. It states that every integer greater than 1 is either a prime number itself or can be represented as a unique product of prime numbers, disregarding the order of the factors. This uniqueness is a crucial aspect, ensuring there's only one way to express a composite number as a product of primes.
For example:
- 12 = 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3)
- 18 = 2 x 3 x 3 (or 2 x 3²)
- 35 = 5 x 7
This theorem makes prime factorization a powerful tool for solving various mathematical problems.
Finding the Prime Factorization of 63
Now, let's determine the prime factorization of 63. We can use several methods to achieve this:
Method 1: Factor Tree
A factor tree is a visual method to break down a number into its prime factors. We start by finding any two factors of 63. A simple choice is 7 and 9.
63
/ \
7 9
/ \
3 3
We see that 7 is a prime number. However, 9 is not prime; it's 3 x 3. Therefore, the prime factorization of 63 is 3 x 3 x 7, or 3² x 7.
Method 2: Repeated Division
This method involves repeatedly dividing the number by its smallest prime factor until we reach 1.
- Start with 63. The smallest prime number is 2, but 63 is not divisible by 2.
- The next prime number is 3. 63 ÷ 3 = 21.
- 21 is also divisible by 3. 21 ÷ 3 = 7.
- 7 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 63 is 3 x 3 x 7, or 3² x 7.
Both methods lead to the same result: the prime factorization of 63 is 3² x 7.
Applications of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, while seemingly a simple concept, has far-reaching implications in various fields:
1. Cryptography
The security of many modern encryption methods relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring very large composite numbers into their prime factors. The RSA algorithm, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, uses this principle. Factoring extremely large numbers is computationally intensive, making it practically impossible to break the encryption in a reasonable timeframe.
2. Computer Science
Prime numbers play a vital role in hash tables, a fundamental data structure used for efficient data retrieval. Prime numbers help minimize collisions in hash tables, ensuring quicker access to data.
3. Number Theory
Prime factorization is fundamental to various number theory concepts, including modular arithmetic, which is used in cryptography and other areas.
4. Other Applications
Prime factorization finds applications in various other fields, including:
- Coding Theory: Used in error-correcting codes.
- Abstract Algebra: Forms the basis for various algebraic structures.
- Probability and Statistics: Used in certain probabilistic models.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Deeper Concepts
While we've focused on the prime factorization of 63, exploring related concepts enhances understanding:
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): Finding the GCD of two numbers involves finding the largest number that divides both without leaving a remainder. Prime factorization simplifies this process. To find the GCD of two numbers, find their prime factorizations and take the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two numbers is the smallest number divisible by both. Again, prime factorization makes determining the LCM easier. Find the prime factorizations, take all the prime factors raised to the highest power, and multiply them together.
-
Sieve of Eratosthenes: This ancient algorithm is a remarkably efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified integer. Understanding this algorithm provides deeper insights into the distribution of prime numbers.
Conclusion: The Significance of Prime Factorization
Prime factorization, while seemingly a simple mathematical procedure, forms the bedrock of various advanced concepts and practical applications. Understanding the prime factorization of 63, and the broader concept of prime factorization itself, is crucial for anyone seeking a deeper understanding of mathematics and its applications in the modern world. From cryptography to computer science, the power of prime numbers continues to shape our technological landscape. The seemingly simple process of breaking down a number into its prime constituents holds a surprising depth and significance that continues to fascinate and challenge mathematicians and computer scientists alike. The unique factorization of every composite number guarantees the reliability and security of many crucial systems we rely on daily. Further exploration of prime numbers and their properties promises to unlock even more profound discoveries in the future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Three Types Of Ecological Pyramids
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Magnitude Of Displacement
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization For 140
Mar 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 24 And 12
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Leeward Side Of A Mountain
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is Prime Factorization Of 63 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
