List All The Factors Of 21
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
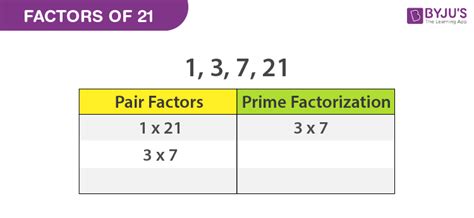
Table of Contents
Decomposing 21: A Deep Dive into its Factors and Number Theory Implications
The seemingly simple number 21 holds a surprising depth when explored through the lens of number theory. Understanding its factors isn't just about simple division; it opens doors to concepts like prime factorization, divisibility rules, and even their applications in cryptography and computer science. This article will comprehensively explore all factors of 21, delving into the mathematical concepts behind them and highlighting their broader significance.
What are Factors?
Before we dive into the specifics of 21, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is any integer that divides the number evenly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if we can divide a number by another number without getting a fraction or decimal, the second number is a factor of the first. For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3, and 6, because 6 ÷ 1 = 6, 6 ÷ 2 = 3, 6 ÷ 3 = 2, and 6 ÷ 6 = 1.
Finding the Factors of 21: A Systematic Approach
To find all the factors of 21, we can systematically check each integer from 1 up to 21. However, a more efficient approach involves recognizing that factors always come in pairs. If 'a' is a factor of 'n', then 'n/a' is also a factor. This significantly reduces the number of checks we need to perform.
Let's apply this method to 21:
- 1: 21 divided by 1 is 21, so 1 and 21 are factors.
- 3: 21 divided by 3 is 7, so 3 and 7 are factors.
- 7: We've already found 7 as a factor in the previous step.
- 21: This is the number itself, and it's a factor of itself (as every number is).
Therefore, the complete set of factors of 21 are 1, 3, 7, and 21.
Prime Factorization: Unveiling the Building Blocks
The concept of prime factorization is crucial in understanding the fundamental structure of numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
21 can be expressed as the product of two prime numbers: 3 and 7. Therefore, the prime factorization of 21 is 3 x 7. This representation is unique; every composite number (a number that is not prime) has only one prime factorization. This uniqueness is a cornerstone of number theory and has profound implications in various mathematical fields.
Divisibility Rules: Shortcuts to Factor Identification
Divisibility rules provide quick ways to determine if a number is divisible by certain integers without performing the actual division. These rules can be particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers. For 21, we can utilize the following divisibility rules:
-
Divisibility by 3: A number is divisible by 3 if the sum of its digits is divisible by 3. In the case of 21, 2 + 1 = 3, which is divisible by 3, confirming that 21 is divisible by 3.
-
Divisibility by 7: There's no single simple rule for divisibility by 7, but we can test it directly. 21 ÷ 7 = 3, confirming that 7 is a factor.
These rules expedite the process of finding factors, especially when dealing with more complex numbers.
Beyond the Factors: Exploring Number Theory Concepts
The factors of 21 provide a springboard for exploring various number theory concepts:
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD):
The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. Finding the GCD is essential in various mathematical applications. For instance, the GCD of 21 and another number, let's say 42, can be determined using methods like the Euclidean algorithm. In this case, GCD(21, 42) = 21, because 21 is the largest number that divides both 21 and 42 evenly.
Least Common Multiple (LCM):
The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. The LCM is often used when working with fractions or solving problems involving periodic events. The LCM of 21 and 14, for example, is 42.
Perfect Numbers and Abundant Numbers:
The sum of the proper divisors (all factors excluding the number itself) of a number can help classify it into categories like perfect, deficient, or abundant numbers. For 21, the sum of its proper divisors (1 + 3 + 7) is 11. Since this sum (11) is less than the number itself (21), 21 is considered a deficient number. A perfect number is when this sum equals the number itself, and an abundant number is when the sum is greater.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios
The seemingly abstract concept of factors finds surprising applications in real-world scenarios:
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization, directly related to finding factors, forms the basis of many modern encryption algorithms like RSA. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the key to the security of these systems.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for finding factors and prime numbers are crucial in various computer science applications, such as database optimization and code optimization. Efficient factorization algorithms are continuously being researched and improved.
-
Scheduling and Resource Allocation: LCM and GCD calculations are often used in solving problems related to scheduling tasks or allocating resources efficiently. This could include synchronizing repeating events or optimizing the use of resources in a system.
-
Geometry and Measurement: Factors play a role in determining the dimensions of shapes and objects, especially when dealing with area, volume, or surface area calculations.
Conclusion: The Unexpected Depth of a Simple Number
The seemingly simple question of "What are the factors of 21?" opens up a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. From the fundamental concept of prime factorization to its implications in cryptography and computer science, understanding the factors of a number provides valuable insights into the structure and properties of numbers. This exploration demonstrates how even seemingly simple mathematical entities can have a significant impact on various fields, highlighting the interconnectedness and power of mathematical ideas. The seemingly unassuming number 21, with its four factors, serves as a compelling example of this depth and complexity. Its seemingly simple factorization leads to a much deeper exploration of number theory, reinforcing the importance of fundamental mathematical concepts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 40 Percent Of 32
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Valence Electrons Are In Potassium
Mar 26, 2025
-
When Gas Turns Into A Liquid
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 14 Meters
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about List All The Factors Of 21 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
