Lines Of Symmetry Of An Octagon
Juapaving
Mar 07, 2025 · 5 min read
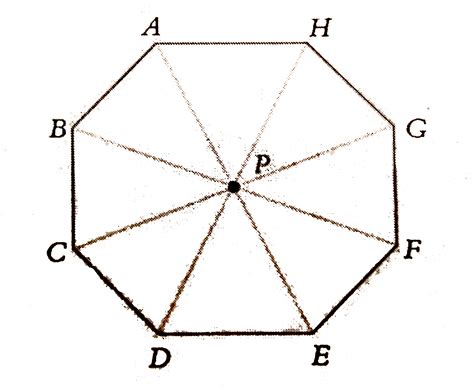
Table of Contents
Lines of Symmetry of an Octagon: A Comprehensive Guide
The world of geometry is filled with fascinating shapes, each possessing unique properties. Among these, the octagon, an eight-sided polygon, holds a special place due to its diverse symmetries. Understanding the lines of symmetry in an octagon is crucial for various applications, from art and design to advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the lines of symmetry of an octagon, exploring its different types and providing a clear understanding of their significance.
What is a Line of Symmetry?
Before we dive into the specifics of octagons, let's establish a clear understanding of what a line of symmetry is. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection or axis of symmetry, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This concept applies to various shapes, including regular and irregular polygons, and even more complex figures.
Types of Octagons
Octagons can be categorized into two main types: regular and irregular. This categorization is crucial because it directly impacts the number and orientation of their lines of symmetry.
Regular Octagon
A regular octagon has eight equal sides and eight equal angles. This uniformity leads to a higher degree of symmetry compared to its irregular counterpart. The angles of a regular octagon each measure 135 degrees. This regularity is key to understanding its lines of symmetry.
Irregular Octagon
An irregular octagon, on the other hand, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. This lack of uniformity significantly reduces the number of lines of symmetry, if any exist at all. Most irregular octagons possess zero lines of symmetry.
Lines of Symmetry in a Regular Octagon
A regular octagon possesses a remarkable amount of symmetry. It has a total of eight lines of symmetry. These lines can be categorized into two types:
1. Lines of Symmetry Through Opposite Vertices
Four lines of symmetry pass through opposite vertices (corners) of the octagon. These lines connect a vertex to the vertex directly opposite it, bisecting the octagon into two congruent quadrilaterals. Imagine drawing a line from one corner to the corner directly opposite; this is a line of symmetry. Since there are four pairs of opposite vertices, there are four lines of symmetry of this type.
2. Lines of Symmetry Through Midpoints of Opposite Sides
The other four lines of symmetry pass through the midpoints of opposite sides. These lines bisect each pair of parallel sides, dividing the octagon into two congruent shapes. Each line connects the midpoint of one side to the midpoint of the opposite side.
Visualizing the Lines of Symmetry
To better understand the lines of symmetry, imagine a regular octagon drawn on a piece of paper. You can fold the paper along each of the eight lines of symmetry, and the two halves will perfectly overlap. This visual demonstration effectively illustrates the concept of mirror symmetry.
Mathematical Proof of Lines of Symmetry
The existence of these eight lines of symmetry can be proven mathematically. The rotational symmetry of a regular octagon is also a factor. A regular octagon has rotational symmetry of order 8, meaning it can be rotated 45 degrees (360/8) about its center and still look identical. Each line of symmetry is related to a specific rotational symmetry.
Applications of Understanding Octagonal Symmetry
The understanding of octagonal symmetry is not just a theoretical exercise; it finds numerous practical applications across diverse fields:
1. Art and Design
Artists and designers frequently utilize octagonal symmetry in their creations. The balanced and aesthetically pleasing nature of the octagon makes it a popular choice for various designs, from mosaics and tiling patterns to architectural structures. Understanding its lines of symmetry allows for the creation of visually harmonious and balanced compositions.
2. Architecture and Engineering
Octagonal structures are found in various architectural marvels throughout history. The symmetrical nature of the octagon makes it structurally sound and allows for efficient design and construction. The understanding of its lines of symmetry plays a vital role in ensuring the structural integrity and aesthetic appeal of such buildings.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Development
In computer graphics and game development, octagonal shapes are often employed to create various elements within virtual worlds. Understanding the lines of symmetry allows for efficient rendering and animation of such objects, reducing computational load and improving performance. Symmetrical objects require less memory and processing power.
4. Crystallography and Material Science
The symmetrical nature of octagons is relevant to crystallography and material science. Certain crystals exhibit octagonal symmetry in their structures, impacting their physical and chemical properties. Understanding these symmetries is crucial for predicting and controlling material behavior.
Distinguishing Between Regular and Irregular Octagons Through Symmetry
The number of lines of symmetry is a key differentiator between regular and irregular octagons. While a regular octagon boasts eight lines of symmetry, an irregular octagon might have zero, one, two, or even four lines of symmetry, depending on its specific shape. The absence or reduced number of lines of symmetry directly reflects the lack of uniform sides and angles in an irregular octagon.
Exploring Higher-Order Polygons and their Symmetry
The exploration of octagonal symmetry extends our understanding to higher-order polygons. As the number of sides increases, the complexity of the symmetry also increases. Understanding the patterns and principles of symmetry in octagons provides a solid foundation for analyzing the symmetry in other polygons, such as decagons, dodecagons, and beyond. The concepts discussed here can be applied and expanded upon to investigate these more complex shapes.
Conclusion: The Significance of Symmetry in Octagons
The lines of symmetry in an octagon are not merely abstract geometrical concepts. They are fundamental properties that influence the shape's visual appeal, structural integrity, and its applications across various disciplines. Understanding these lines allows us to appreciate the beauty and practicality of octagonal symmetry, whether in artistic creations, architectural marvels, or scientific discoveries. The exploration of octagonal symmetry offers a fascinating journey into the world of geometric properties and their far-reaching implications. From simple visual observation to complex mathematical proofs, the lines of symmetry in a regular octagon provide a rich source of learning and understanding. The ability to discern the symmetry within a shape allows us to appreciate the inherent order and beauty found throughout the natural and man-made world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are Horizontal Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is The Formula For Potassium Oxide
Mar 09, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Not An Si Base Unit
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Country Is Called The Land Of The Rising Sun
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Are All The Factors For 40
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lines Of Symmetry Of An Octagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
