Which Of The Following Is Not An Si Base Unit
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
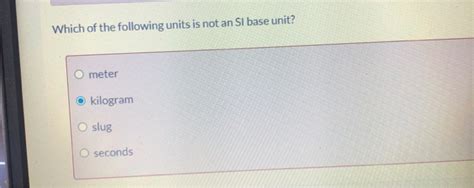
Table of Contents
Which of the Following is NOT an SI Base Unit? A Comprehensive Guide
The International System of Units (SI), also known as the metric system, is the world's most widely used system of measurement. Understanding its fundamental building blocks – the SI base units – is crucial for anyone working with scientific measurements or engineering calculations. This article delves deep into the seven SI base units, explaining what they are, what they measure, and crucially, exploring which units are not included in this fundamental set.
The Seven Pillars of Measurement: Understanding SI Base Units
The SI system is built upon seven base units, each representing a fundamental physical quantity. These are not derived from other units; they are the foundation upon which all other units are constructed. Let's explore each one:
1. The Meter (m): The Standard for Length
The meter defines length. Originally based on the Earth's circumference, it's now defined with incredible precision using the speed of light in a vacuum. This ensures consistency and accuracy across the globe. Think of measuring the length of a table, the distance between cities, or even the vast expanse of interstellar space – the meter is the unit of choice.
2. The Kilogram (kg): Mass, Not Weight
The kilogram represents mass, a measure of the amount of matter in an object. Crucially, it's different from weight, which is a measure of the force of gravity on an object. While weight changes depending on location (e.g., on the Moon, you weigh less), mass remains constant. From weighing groceries to measuring the mass of planets, the kilogram plays a vital role.
3. The Second (s): Time's Constant Tick
The second measures time intervals. Initially defined using the Earth's rotation, its definition has evolved to be far more precise, using atomic clocks based on the cesium atom's resonant frequency. The second is fundamental to everything from measuring the speed of a car to tracking the lifespan of stars.
4. The Ampere (A): The Flow of Electrical Charge
The ampere is the unit of electric current, representing the flow of electric charge. It's crucial in understanding electricity and electronics, from the current in a household circuit to the power of a supercomputer. One ampere corresponds to a specific rate of charge flow.
5. The Kelvin (K): Measuring Temperature
The Kelvin is the unit of thermodynamic temperature. Unlike the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales, the Kelvin scale starts at absolute zero, the theoretical point where all molecular motion ceases. This makes it particularly useful in scientific calculations and understanding thermodynamic processes.
6. The Mole (mol): Counting Particles
The mole measures the amount of substance. It's a specific number of particles (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.), approximately 6.022 x 10²³ (Avogadro's number). This unit is essential in chemistry and related fields, allowing us to relate macroscopic measurements to the microscopic world of atoms and molecules.
7. The Candela (cd): Measuring Luminous Intensity
The candela measures luminous intensity, the perceived brightness of a light source in a specific direction. It's crucial in lighting design, photography, and other fields where light intensity is a key factor. Unlike simply measuring the total light output, the candela focuses on the brightness as perceived by the human eye.
Identifying Units that are NOT SI Base Units
Now that we've established the seven SI base units, let's look at some units and determine why they aren't fundamental:
1. The Newton (N): The Newton is the unit of force. While incredibly important, it's derived from the base units of mass (kilogram), length (meter), and time (second): 1 N = 1 kg⋅m/s². It's a combination, not a fundamental unit.
2. The Joule (J): The Joule is the unit of energy or work. Again, it’s a derived unit, defined as 1 kg⋅m²/s². This shows its dependence on the base units of mass, length, and time.
3. The Pascal (Pa): The Pascal is the unit of pressure. It's also a derived unit, equal to 1 N/m², which further breaks down to kg⋅m⁻¹⋅s⁻². Its reliance on other units excludes it from the base unit category.
4. The Hertz (Hz): The Hertz is the unit of frequency, representing cycles per second. It is a derived unit, simply equal to s⁻¹, highlighting its dependence on the base unit of time.
5. The Liter (L): Although commonly used, the liter is a unit of volume. While convenient, it's not an SI base unit. Its equivalent in SI base units is the cubic meter (m³), highlighting its derived nature.
6. The Degree Celsius (°C): Degree Celsius is a unit of temperature, but it is not a base unit. The Kelvin (K) is the SI base unit for temperature. Celsius is simply a shifted scale of Kelvin (°C = K - 273.15).
7. The Electronvolt (eV): The electronvolt, a unit of energy, is frequently used in atomic and nuclear physics. However, it's not an SI base unit and is derived from fundamental constants and the base units of charge and voltage.
Why the Distinction Between Base and Derived Units Matters
The distinction between SI base units and derived units is critical for several reasons:
-
Consistency: The use of base units ensures a consistent and universally understood system of measurement. Derived units are clearly defined by their relationship to the base units.
-
Accuracy: Base units are defined with exceptional precision, ensuring accurate measurements. This accuracy propagates through derived units, making calculations more reliable.
-
Simplicity: By building upon a small set of base units, the entire system remains elegant and easily manageable. The relationships between derived units and base units are well-defined and straightforward.
Expanding on the Importance of SI Units in Various Fields
The implications of understanding SI base units are far-reaching and impact numerous fields:
-
Science: SI units are fundamental in scientific research and experimentation, allowing for clear communication of results and reproducible experiments across different labs and countries.
-
Engineering: Engineers use SI units extensively in design, construction, and manufacturing to ensure accuracy and safety in projects ranging from bridges to microchips.
-
Medicine: Accurate measurements are crucial in medicine, from dosage calculations to diagnostic equipment. SI units ensure consistency and accuracy in these critical applications.
-
Commerce: International trade relies on standardized units of measurement. The widespread adoption of SI simplifies trade and reduces potential confusion.
-
Technology: From the development of smartphones to the design of spacecraft, SI units are essential for ensuring the functionality and reliability of technological advancements.
Conclusion: Mastering the Fundamentals of Measurement
Understanding which units are SI base units and which are derived is crucial for anyone working with measurements, especially in science, engineering, and related fields. The seven SI base units form the bedrock of a globally recognized system, ensuring consistency, accuracy, and clarity in all measurements. By appreciating the fundamental nature of these units and how derived units are constructed from them, we can unlock a more profound understanding of the world around us and foster clearer communication within the scientific and engineering communities. This knowledge empowers us to perform calculations correctly, interpret data accurately, and ultimately, to contribute to a more precise and efficient world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Mountain Range Separates Europe From Asia
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Oxidized And Reduced In Cellular Respiration
Mar 09, 2025
-
What Is Greater Mb Or Gb
Mar 09, 2025
-
Is Water A Renewable Or A Nonrenewable Resource
Mar 09, 2025
-
Common Factors Of 12 And 9
Mar 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Which Of The Following Is Not An Si Base Unit . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
