Lines Of Symmetry For A Circle
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
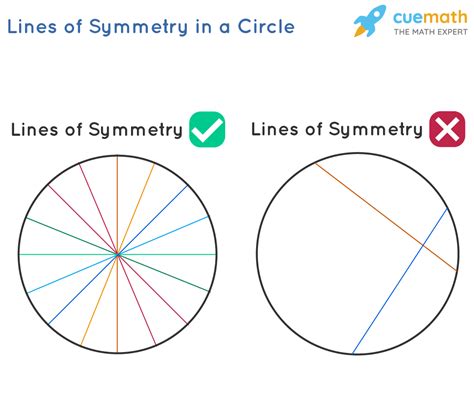
Table of Contents
Lines of Symmetry for a Circle: A Comprehensive Exploration
The circle, a timeless and elegant geometric shape, holds a unique position in mathematics due to its infinite lines of symmetry. Unlike squares, rectangles, or triangles with a finite number of symmetry lines, the circle boasts an unparalleled property: every diameter acts as a line of symmetry. This article delves deep into the concept of lines of symmetry, specifically focusing on circles, exploring its implications in geometry, art, and beyond.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before diving into the specifics of circles, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two congruent halves, meaning the two halves are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap.
Different shapes possess different numbers of lines of symmetry. A square, for instance, has four lines of symmetry: two diagonals and two lines passing through the midpoints of opposite sides. An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, each connecting a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side. A rectangle (excluding squares) typically has two lines of symmetry, running through the midpoints of opposite sides.
The Infinite Symmetry of the Circle
This is where the circle truly stands apart. Unlike polygons with a defined number of sides and consequently a finite number of lines of symmetry, a circle possesses infinite lines of symmetry. Every diameter of the circle acts as a line of symmetry. A diameter is a line segment that passes through the center of the circle and connects two points on the circumference.
Why infinite? Consider this: you can draw an infinite number of diameters in a circle, each one dividing the circle into two perfectly congruent semicircles. Each of these diameters represents a line of symmetry. No matter where you draw a diameter, it will always bisect the circle into mirror-image halves. This inherent property of the circle highlights its unique geometric characteristics.
Exploring the Properties of Circular Symmetry
The infinite lines of symmetry of a circle lead to several fascinating mathematical and visual properties:
1. Rotational Symmetry: A Complementary Feature
Besides its reflectional symmetry, the circle also exhibits rotational symmetry. This means that the circle can be rotated about its center by any angle, and it will appear unchanged. This is a direct consequence of its infinite lines of symmetry. Each rotation about the center can be associated with a diameter acting as a line of reflection. The combination of reflectional and rotational symmetry makes the circle a highly symmetrical shape.
2. Applications in Geometry and Mathematics
The infinite lines of symmetry of a circle have significant applications within various branches of mathematics:
- Coordinate Geometry: The circle's equation in Cartesian coordinates, (x-a)² + (y-b)² = r², highlights its symmetrical nature. The center (a, b) acts as the point of symmetry, and any line passing through this center represents a line of symmetry.
- Trigonometry: Circular functions like sine, cosine, and tangent are fundamentally linked to the circle's geometry, making its symmetry crucial in understanding their periodic nature.
- Calculus: The concept of symmetry finds application in integral calculus, particularly in simplifying calculations involving even and odd functions. The circle's symmetry can significantly simplify calculations related to its area or circumference.
3. Visual and Artistic Significance
The circle's inherent symmetry has captivated artists and designers for millennia. Its perfect form and balanced proportions evoke feelings of harmony, completeness, and perfection.
- Art and Design: From ancient mandalas to modern minimalist designs, the circle and its symmetry are fundamental elements in various art forms. The infinite lines of symmetry allow for endless possibilities in creating visually appealing and balanced compositions.
- Architecture: Circular structures, often incorporating radial symmetry, have been used throughout history, showcasing the inherent beauty and structural strength of circular forms. The Pantheon in Rome is a prime example of this architectural application.
- Nature: Circles and near-circular shapes are frequently found in nature, ranging from the sun and moon to the rings of Saturn and the ripples in a pond. The symmetry inherent in these forms showcases the mathematical elegance present in the natural world.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Advanced Concepts
The concept of lines of symmetry for a circle extends beyond the basic understanding of diameters. Let's explore some advanced aspects:
1. Symmetry and Transformations
The lines of symmetry of a circle can be understood within the broader context of geometric transformations. Each line of symmetry represents a reflection across that line. The combination of multiple reflections generates various other transformations, showcasing the richness of the circle's symmetry properties.
2. Symmetry in Higher Dimensions
While we've focused on two-dimensional circles, the concept of symmetry extends to higher dimensions. A sphere in three-dimensional space possesses an infinite number of planes of symmetry, each plane passing through the sphere's center. This concept can be generalized to higher dimensions, further highlighting the pervasive nature of circular symmetry in various mathematical contexts.
3. Applications in Computer Graphics and Animation
The circle's symmetry is heavily utilized in computer graphics and animation. Algorithms for generating circular shapes and patterns leverage the properties of its symmetry to optimize computational efficiency. This efficient generation is crucial for applications ranging from creating realistic 3D models to designing user interfaces.
Conclusion: The Enduring Elegance of Circular Symmetry
The infinite lines of symmetry possessed by a circle are a testament to its profound mathematical significance and aesthetic appeal. From its applications in various branches of mathematics to its impact on art, design, and architecture, the circle's symmetry continues to inspire and fascinate. The exploration of circular symmetry offers a glimpse into the elegance and power of geometric principles, highlighting the interplay between mathematics and the visual world. Understanding the concept of infinite lines of symmetry within a circle provides a foundational understanding of symmetry in general, paving the way for exploring more complex geometrical concepts and applications across diverse fields. The circle, with its infinite lines of symmetry, remains a symbol of perfection and balance, a testament to the beauty and power of mathematical principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Melting Of Wax A Physical Or Chemical Change
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are Rows On The Periodic Table Called
Mar 16, 2025
-
Is Carbon Tetrachloride Ionic Or Covalent
Mar 16, 2025
-
Write The Formula For Sulfurous Acid
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials Required For Photosynthesis
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lines Of Symmetry For A Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
