Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 2
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 4 min read
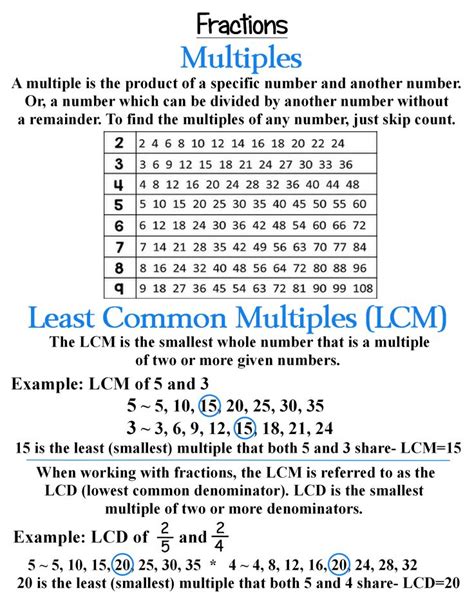
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 7 and 2: A Deep Dive
The concept of the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental cornerstone in number theory and has widespread applications across various mathematical fields and real-world scenarios. Understanding LCM is crucial for solving problems involving fractions, ratios, and rhythmic patterns, among other things. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 7 and 2, explaining the underlying principles and offering various methods to arrive at the solution. We'll also explore the broader significance of LCM and its practical applications.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The Least Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that can be divided evenly by all the numbers in the set without leaving a remainder. For instance, the LCM of 3 and 4 is 12 because 12 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 3 and 4.
Methods for Calculating LCM
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM of two or more numbers. Let's explore the most common ones:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This straightforward method involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
Example (LCM of 7 and 2):
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, ...
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, ...
The smallest multiple common to both lists is 14. Therefore, the LCM of 7 and 2 is 14.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method uses the prime factorization of each number to find the LCM. Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors (numbers divisible only by 1 and themselves).
Example (LCM of 7 and 2):
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 2: 2 (2 is a prime number)
To find the LCM using prime factorization:
- Identify the prime factors: The prime factors are 2 and 7.
- Take the highest power of each prime factor: The highest power of 2 is 2<sup>1</sup> = 2, and the highest power of 7 is 7<sup>1</sup> = 7.
- Multiply the highest powers: LCM(7, 2) = 2 x 7 = 14
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) of two numbers are related through a simple formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
where |a x b| represents the absolute value of the product of a and b.
Example (LCM of 7 and 2):
- Find the GCD of 7 and 2: The GCD of 7 and 2 is 1 because 1 is the only common divisor of both numbers.
- Apply the formula: LCM(7, 2) = (7 x 2) / 1 = 14
Comparing the Methods
All three methods yield the same result: the LCM of 7 and 2 is 14. The listing multiples method is simple for small numbers but becomes cumbersome for larger numbers. The prime factorization method is efficient for larger numbers, while the GCD method is particularly useful when the GCD is already known.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The LCM finds practical applications in various contexts:
1. Scheduling and Timing
Imagine two buses arrive at a bus stop at different intervals. One bus arrives every 7 minutes, and the other arrives every 2 minutes. The LCM (14 minutes) tells us when both buses will arrive at the bus stop simultaneously again.
2. Fraction Operations
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial to finding a common denominator for the calculation.
3. Rhythmic Patterns and Music
In music, the LCM helps determine when rhythmic patterns will coincide. For instance, two musical phrases with lengths of 7 and 2 beats will align perfectly after 14 beats.
4. Gear Ratios
In mechanical engineering, gear ratios often involve finding the LCM to determine the synchronized rotation of gears.
5. Calendars and Dates
LCM calculations can help determine when specific events occur on the same day of the week or month after a certain period.
Advanced Concepts Related to LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond just two numbers. You can calculate the LCM of three or more integers using the same principles outlined above (especially the prime factorization method). Moreover, the LCM plays a role in more advanced mathematical concepts such as modular arithmetic and abstract algebra.
Conclusion: The Power of the Least Common Multiple
The LCM, though seemingly a simple concept, holds immense significance in mathematics and its applications. Understanding the various methods for calculating the LCM and its real-world applications equips you with a powerful tool to solve a wide range of problems across various disciplines. From scheduling and music to engineering and beyond, the LCM helps us understand patterns, synchronize events, and manage complexities efficiently. The simple example of finding the LCM of 7 and 2, while seemingly trivial, serves as a foundational stepping stone to understanding this fundamental mathematical concept and its broader implications. Mastering the LCM opens doors to a deeper appreciation of mathematics and its ability to solve practical problems in our everyday lives.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Has A Rhombus
Mar 06, 2025
-
Two Equal Sides Of A Triangle
Mar 06, 2025
-
Si Unit Of Measurement For Acceleration
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is A Factor Of 96
Mar 06, 2025
-
Which Element Has The Highest Ionization Potential
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 2 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
