Least Common Multiple Of 21 And 28
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 4 min read
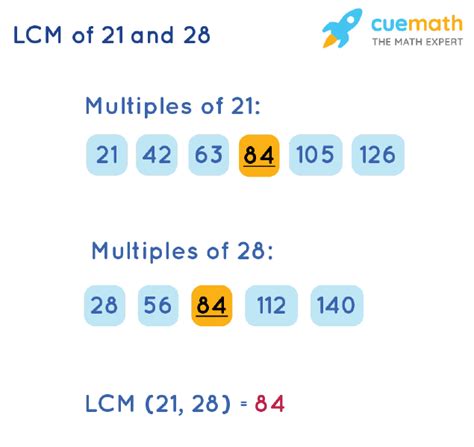
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 21 and 28: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to find the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems in areas like scheduling and music theory. This article delves deep into the process of calculating the LCM of 21 and 28, exploring multiple methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We’ll also explore the broader context of LCMs and their significance.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest number divisible by both 2 and 3.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 21 and 28
There are several effective methods to determine the LCM of two numbers, including 21 and 28. We will explore three common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to both.
Multiples of 21: 21, 42, 63, 84, 105, 126, 147, 168, 189, 210...
Multiples of 28: 28, 56, 84, 112, 140, 168, 196, 224, 252, 280...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 84. Therefore, the LCM(21, 28) = 84.
This method is simple to understand but can become cumbersome for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of all prime factors present.
Prime Factorization of 21: 21 = 3 x 7
Prime Factorization of 28: 28 = 2 x 2 x 7 = 2² x 7
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2² = 4
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7
Therefore, LCM(21, 28) = 2² x 3 x 7 = 4 x 3 x 7 = 84.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. That is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 21 and 28. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
28 = 21 x 1 + 7 21 = 7 x 3 + 0
The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 7.
Now we can use the formula:
LCM(21, 28) = (21 x 28) / GCD(21, 28) = (21 x 28) / 7 = 84
This method is efficient and relies on a well-established algorithm for finding the GCD.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM finds applications in various fields:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. The LCM of the denominators becomes the common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
2. Scheduling Problems
Imagine two buses depart from the same station at different intervals. The LCM of their departure intervals helps determine when they will depart simultaneously again.
3. Music Theory
In music, the LCM helps in determining the least common period of two or more musical phrases with differing lengths. This is vital for creating harmonious and well-structured musical pieces.
4. Gear Ratios
In mechanical engineering, the LCM helps calculate the least common rotational period for interconnected gears with different numbers of teeth. This aids in determining the optimal gear ratio for a specific application.
5. Cyclic Processes
In various cyclical processes, whether in nature or engineering, the LCM assists in determining when events will coincide or repeat.
Choosing the Best Method
The best method for finding the LCM depends on the context and the numbers involved.
- For smaller numbers, the listing multiples method is simple and intuitive.
- For larger numbers or when dealing with multiple numbers, the prime factorization method is generally more efficient and systematic.
- The GCD method is efficient if you already know or can easily determine the GCD.
Conclusion
Determining the least common multiple of 21 and 28, which we've found to be 84, demonstrates a fundamental mathematical concept with widespread applications. Understanding the different methods for calculating the LCM allows for a flexible and efficient approach depending on the specific scenario. Mastering the LCM is a valuable skill that extends beyond basic arithmetic into various practical and theoretical fields. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving scheduling problems, or exploring the intricacies of music theory, the concept of the LCM remains a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. The consistent application of these methods ensures accuracy and efficiency in solving LCM-related problems, emphasizing the importance of understanding the underlying principles. This comprehensive guide equipped you with the knowledge and tools necessary to tackle various LCM problems confidently.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is All The Factors Of 56
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Gas Is Released During Photosynthesis
Mar 14, 2025
-
Round The Number To The Nearest Thousandth
Mar 14, 2025
-
Digestion Of Starch Begins In The
Mar 14, 2025
-
Difference Between Ac And Dc Motors
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 21 And 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
