What Is All The Factors Of 56
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
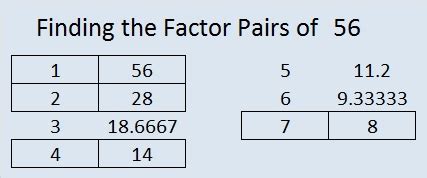
Table of Contents
What are all the factors of 56? A Deep Dive into Factorization
Finding all the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the process reveals fundamental concepts in number theory and has practical applications in various fields like cryptography and computer science. This article will comprehensively explore the factors of 56, illustrating the methods used to find them and touching upon related mathematical concepts.
Understanding Factors
Before diving into the factors of 56, let's establish a clear definition. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, if you can divide a number by another number and get a whole number as the result, the number you divided by is a factor.
For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Finding the Factors of 56: A Systematic Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of 56. Let's explore the most common methods:
1. Listing Factors Pairwise
This method involves systematically listing pairs of numbers that multiply to give 56. We start with 1 and work our way up:
- 1 x 56 = 56
- 2 x 28 = 56
- 4 x 14 = 56
- 7 x 8 = 56
This method gives us the factors: 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28, and 56.
2. Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a powerful technique for finding all the factors of a number. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, etc.). Prime factorization involves expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
Let's find the prime factorization of 56:
56 can be divided by 2: 56 = 2 x 28 28 can be divided by 2: 28 = 2 x 14 14 can be divided by 2: 14 = 2 x 7 7 is a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 56 is 2 x 2 x 2 x 7 = 2³ x 7.
Once we have the prime factorization, we can easily find all the factors. We do this by considering all possible combinations of the prime factors:
- 2⁰ x 7⁰ = 1
- 2¹ x 7⁰ = 2
- 2² x 7⁰ = 4
- 2³ x 7⁰ = 8
- 2⁰ x 7¹ = 7
- 2¹ x 7¹ = 14
- 2² x 7¹ = 28
- 2³ x 7¹ = 56
This method confirms that the factors of 56 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 8, 14, 28, and 56.
3. Using Division
This method involves dividing 56 by each whole number starting from 1 until you reach the square root of 56 (approximately 7.48). For each number that divides 56 evenly, you'll find a pair of factors.
- 56 ÷ 1 = 56 (Factors: 1 and 56)
- 56 ÷ 2 = 28 (Factors: 2 and 28)
- 56 ÷ 4 = 14 (Factors: 4 and 14)
- 56 ÷ 7 = 8 (Factors: 7 and 8)
Once you pass the square root, you'll simply be repeating the pairs in reverse order.
Properties of Factors of 56
Let's examine some key properties related to the factors we've found:
-
Number of Factors: 56 has eight factors. This is relatively straightforward to determine from the list.
-
Even and Odd Factors: All the factors of 56 except for 7 are even. This is because 56 itself is an even number (divisible by 2) and its prime factorization includes only the even prime number 2 and the odd prime number 7.
-
Sum of Factors: Adding all the factors together (1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 8 + 14 + 28 + 56) gives us a total of 120. The sum of factors is a significant concept in number theory, particularly related to perfect numbers and abundant numbers.
-
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD): The GCD of two or more numbers is the largest number that divides all of them without leaving a remainder. For example, the GCD of 56 and 28 is 28 because 28 is the largest factor common to both numbers.
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest number that is a multiple of all of them. The LCM of 56 and 14, for example, is 56 because 56 is a multiple of both 14 and 56.
Applications of Factorization
Understanding factors and factorization is not merely an academic exercise. It has numerous practical applications across various disciplines:
1. Cryptography
Factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography. Many encryption algorithms rely on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors. The security of RSA encryption, a widely used public-key cryptosystem, depends on the computational infeasibility of factoring very large composite numbers.
2. Computer Science
Factorization algorithms are used in various computer science applications, such as:
-
Data compression: Efficient data compression algorithms often utilize factorization to identify patterns and redundancies in data.
-
Graph theory: Factorization concepts find use in analyzing graph structures and finding efficient algorithms for graph traversal.
-
Scheduling and optimization: Factorization techniques can contribute to optimizing resource allocation and scheduling problems.
3. Number Theory
Factorization is a fundamental concept in number theory, the branch of mathematics dealing with the properties of whole numbers. It underpins many theorems and further research in areas like prime number distribution and modular arithmetic.
Conclusion: Beyond the Factors of 56
While this article focused specifically on the factors of 56, the methods and concepts explored are applicable to finding the factors of any whole number. Understanding factorization is key to gaining a deeper appreciation of number theory and its significant role in various scientific and technological fields. From simple arithmetic exercises to the complex algorithms underlying modern cryptography, the seemingly simple act of finding factors has far-reaching implications. The prime factorization of 56 (2³ x 7), in particular, serves as a fundamental illustration of how a number's prime factors reveal its complete set of divisors, offering a comprehensive understanding of its multiplicative structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Bond Holds Nitrogen Bases Together
Mar 14, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Examples Of Plasmas
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Slime A Non Newtonian Fluid
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Type Of Triangle Has Two Equal Sides
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Function Of Areolar Tissue
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is All The Factors Of 56 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
