Lcm Of 3 6 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
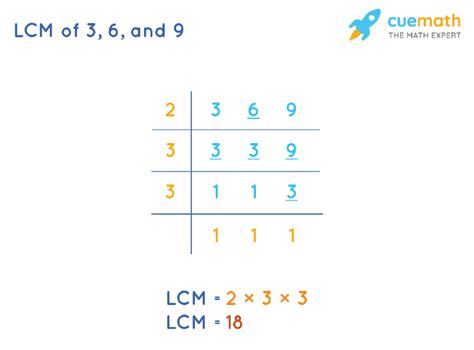
Table of Contents
Finding the LCM of 3, 6, and 9: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems in algebra and beyond. This article delves deep into finding the LCM of 3, 6, and 9, explaining multiple methods and exploring the underlying mathematical principles. We’ll also explore the broader applications of LCMs and how they relate to other mathematical concepts like the greatest common divisor (GCD).
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into calculating the LCM of 3, 6, and 9, let's clarify what the LCM actually represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the numbers in the set as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12… and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15… The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method for finding the LCM, especially for smaller numbers like 3, 6, and 9, is by listing their multiples.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30…
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36…
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36…
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest number common to all three lists is 18. Therefore, the LCM of 3, 6, and 9 is 18.
This method is simple and intuitive, making it ideal for understanding the concept of LCM. However, it becomes less efficient when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more powerful and efficient method for calculating the LCM, especially for larger numbers. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. Prime factors are numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...).
Let's find the prime factorization of 3, 6, and 9:
- 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- 6: 2 x 3
- 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
Now, to find the LCM using prime factorization, we follow these steps:
- Identify the prime factors: The prime factors involved are 2 and 3.
- Find the highest power of each prime factor: The highest power of 2 is 2¹ (from the factorization of 6), and the highest power of 3 is 3² (from the factorization of 9).
- Multiply the highest powers: Multiply 2¹ and 3² together: 2 x 3 x 3 = 18
Therefore, the LCM of 3, 6, and 9 is 18. This method provides a systematic and efficient approach, even when dealing with more complex numbers.
Method 3: Using the GCD (Greatest Common Divisor)
The LCM and GCD are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
This formula holds true for any two integers 'a' and 'b'. While it's not directly applicable to finding the LCM of three numbers simultaneously, we can use it iteratively. First, find the LCM of two numbers, and then find the LCM of that result and the third number.
Let's illustrate this with 3, 6, and 9:
- Find the LCM of 3 and 6: Using the listing method or prime factorization, the LCM(3, 6) = 6.
- Find the GCD of 3 and 6: The GCD(3, 6) = 3.
- Verify the formula: LCM(3, 6) * GCD(3, 6) = 6 * 3 = 18. This matches 3 * 6 = 18, confirming the calculation.
- Find the LCM of 6 and 9: Using the listing method or prime factorization, the LCM(6, 9) = 18.
Therefore, the LCM of 3, 6, and 9 is 18. This method demonstrates the interconnectedness of LCM and GCD.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM finds numerous applications across various fields:
- Fraction addition and subtraction: Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires finding the LCM of the denominators.
- Scheduling problems: Determining when events will occur simultaneously (e.g., buses arriving at a stop, machines completing cycles) involves calculating the LCM of their respective periods.
- Modular arithmetic: LCM is used extensively in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory dealing with remainders.
- Music theory: LCM helps determine the least common period of repeating musical patterns.
- Computer science: LCM plays a role in algorithms related to scheduling and synchronization of tasks.
Beyond 3, 6, and 9: Extending the Concepts
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of any number of integers. For larger sets of numbers, the prime factorization method proves particularly efficient. For example, finding the LCM of 12, 18, and 24:
- Prime factorization:
- 12 = 2² x 3
- 18 = 2 x 3²
- 24 = 2³ x 3
- Highest powers: The highest power of 2 is 2³, and the highest power of 3 is 3².
- Multiply: 2³ x 3² = 8 x 9 = 72. Therefore, the LCM(12, 18, 24) = 72.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Understanding the least common multiple is essential for various mathematical applications. This article has provided a comprehensive guide to calculating the LCM, focusing on the specific example of 3, 6, and 9, while also exploring more general methods applicable to any set of integers. Mastering these techniques will empower you to solve a wider range of mathematical problems and deepen your understanding of number theory. Remember, practice is key to developing fluency in these calculations. Try working through different examples, experimenting with various methods, and observing their efficiency in different contexts. The more you practice, the more confident and proficient you will become in finding the LCM of any set of numbers.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Surface Area Of A Hemisphere Calculator
Mar 25, 2025
-
Put Numbers In Order From Least To Greatest
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Energy Levels Does Sodium Have
Mar 25, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between An Alternator And A Generator
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is Air A Compound Or A Mixture
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 3 6 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
