Is The Square Root Of 17 A Rational Number
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
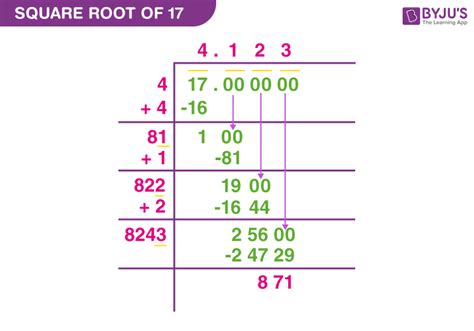
Table of Contents
Is the Square Root of 17 a Rational Number? A Deep Dive into Irrationality
The question of whether the square root of 17 is a rational number is a fundamental one in mathematics, touching upon the core concepts of number systems and their properties. Understanding this seemingly simple question requires a grasp of rational and irrational numbers, prime factorization, and proof by contradiction. Let's delve into this fascinating topic.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Before we tackle the square root of 17 specifically, let's establish a clear definition of rational and irrational numbers.
Rational Numbers: A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, and q is not equal to zero. Examples include 1/2, 3/4, -5/7, and even integers like 4 (which can be expressed as 4/1). The key characteristic is the ability to represent the number as a ratio of two integers. When expressed as decimals, rational numbers either terminate (e.g., 0.75) or repeat infinitely with a repeating pattern (e.g., 0.333...).
Irrational Numbers: Irrational numbers, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. Famous examples include π (pi) and e (Euler's number). The square root of many numbers, including the square root of 17, falls into this category.
Investigating the Square Root of 17
Now, let's focus on the square root of 17 (√17). To determine if it's rational, we'll employ a common mathematical technique: proof by contradiction.
Proof by Contradiction: Assuming √17 is Rational
Let's assume that √17 is a rational number. If this is true, it can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, q ≠ 0, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning p and q share no common factors other than 1; the fraction is reduced).
So, we have:
√17 = p/q
Squaring both sides, we get:
17 = p²/q²
Rearranging the equation, we obtain:
17q² = p²
This equation tells us that p² is a multiple of 17. Since 17 is a prime number, this implies that p itself must also be a multiple of 17. We can express this as:
p = 17k (where k is an integer)
Substituting this back into the equation 17q² = p², we get:
17q² = (17k)²
17q² = 289k²
Dividing both sides by 17, we get:
q² = 17k²
This equation shows that q² is also a multiple of 17, and since 17 is prime, q must also be a multiple of 17.
The Contradiction
Here's where the contradiction arises. We initially assumed that p/q was in its simplest form, meaning p and q share no common factors. However, we've just shown that both p and q are multiples of 17, meaning they do share a common factor of 17. This contradicts our initial assumption.
Conclusion of the Proof
Because our initial assumption (that √17 is rational) leads to a contradiction, the assumption must be false. Therefore, √17 is not a rational number; it is an irrational number.
Further Exploration: Irrationality and Prime Numbers
The proof above highlights a crucial connection between irrational numbers and prime numbers. The primality of 17 plays a vital role in establishing the irrationality of its square root. This relationship extends to other square roots of prime numbers. The square root of any prime number is always irrational. This is because if the square root were rational, it would lead to a similar contradiction as shown above.
Approximating Irrational Numbers
While we can't express √17 as a precise fraction, we can approximate its value. Using a calculator, we find that √17 ≈ 4.123. This is an approximation; the decimal representation of √17 continues infinitely without repeating. Various mathematical methods exist for calculating increasingly accurate approximations of irrational numbers like √17.
Practical Implications and Applications
Understanding irrational numbers, even seemingly abstract ones like √17, has practical implications in various fields:
-
Geometry: Irrational numbers often appear in geometric calculations involving lengths, areas, and volumes. For example, the diagonal of a square with side length 1 is √2, an irrational number.
-
Physics: Many physical phenomena involve irrational numbers. For instance, the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter (π) is irrational and crucial in physics and engineering.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for approximating irrational numbers are essential in computer graphics, simulations, and scientific computing.
Expanding the Concept: Other Irrational Numbers
The techniques used to prove the irrationality of √17 can be extended to prove the irrationality of other numbers. Similar proofs can be constructed for square roots of other non-perfect squares, demonstrating a wider class of irrational numbers.
The Importance of Mathematical Proof
The proof by contradiction presented above is a powerful example of rigorous mathematical reasoning. It's not enough to simply observe that the decimal representation of √17 appears non-repeating; a formal proof is needed to definitively establish its irrationality. This emphasizes the importance of precise mathematical methods in establishing fundamental truths about numbers and their properties.
Conclusion: The Beauty of Irrationality
The fact that the square root of 17 is irrational might seem like a minor detail, but it speaks to the richness and complexity of the number system. Irrational numbers, while not easily expressible as simple fractions, are fundamental components of mathematics and have profound implications across various scientific and technological fields. Understanding their properties and the methods for proving their irrationality deepens our appreciation for the elegance and beauty of mathematics. The exploration of √17 serves as a gateway to understanding broader concepts within number theory and mathematical proof.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Two Numbers Multiply To 36
Mar 14, 2025
-
Why Are Noble Gasses Not Reactive
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Mass Number Of Calcium
Mar 14, 2025
-
Why Earth Is Called Blue Planet
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization For 22
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Square Root Of 17 A Rational Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
