Is Combination The Same As Synthesis Chemistry
Juapaving
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
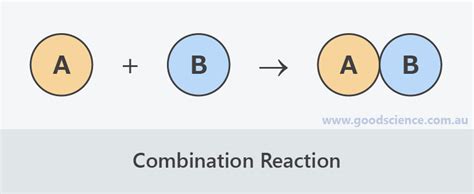
Table of Contents
Is Combination the Same as Synthesis Chemistry? Unpacking the Nuances
The terms "combination reaction" and "synthesis reaction" are often used interchangeably in chemistry, leading to confusion among students and even seasoned professionals. While they are closely related and frequently describe the same process, subtle differences exist. This article will delve deep into the definitions, explore the similarities and differences, provide examples, and clarify the nuances between combination and synthesis reactions in chemistry.
Understanding Combination Reactions
A combination reaction, also known as a synthesis reaction (the terms are frequently used synonymously), is a fundamental type of chemical reaction where two or more reactants combine to form a single, more complex product. The general form of a combination reaction can be represented as:
A + B → AB
where A and B are the reactants, and AB represents the single product formed. This process often involves the formation of new chemical bonds between the reactants. The key characteristic is the combination of simpler substances into a more complex one.
Key Characteristics of Combination Reactions:
- Two or more reactants: The reaction always involves at least two separate reactants. These can be elements or compounds.
- Single product: The reaction yields only one product.
- Bond formation: New chemical bonds are formed between the atoms of the reactants to produce the product.
- Often exothermic: Many combination reactions release energy in the form of heat, indicating they are exothermic processes. However, some are endothermic, requiring energy input.
- Changes in physical properties: The product typically has different physical properties (melting point, boiling point, color, etc.) compared to the reactants.
Understanding Synthesis Reactions
The term synthesis reaction is essentially a broader term that encompasses combination reactions. It refers to any chemical reaction where a more complex substance is created from simpler substances. This broader definition allows for reactions involving more than two reactants or reactions where a product is formed through a series of intermediate steps. A synthesis reaction can be a direct combination, but it doesn't have to be.
Key Characteristics of Synthesis Reactions:
- Formation of a complex molecule: A more complex molecule or compound is always formed as the product.
- Multiple reactants (possible): While many synthesis reactions involve two reactants (just like combination reactions), they can theoretically involve more than two.
- Multiple steps (possible): Synthesis reactions may proceed through several steps or intermediate stages, whereas combination reactions are usually single-step processes.
- Often used in organic chemistry: The term "synthesis" is widely employed in organic chemistry, where the creation of complex molecules is a central theme.
Similarities Between Combination and Synthesis Reactions
The overlap between combination and synthesis reactions is substantial. In many cases, they are practically interchangeable terms describing the same fundamental process: the formation of a single, more complex product from simpler reactants. Here's a summary of the similarities:
- Product formation: Both types of reactions result in the formation of a single, more complex product.
- Bond formation: In both, new chemical bonds are formed between atoms of the reactants.
- Mass conservation: Both reactions obey the law of conservation of mass – the total mass of the reactants equals the total mass of the product(s).
- Examples: Many examples perfectly fit the description of both a combination reaction and a synthesis reaction.
Differences Between Combination and Synthesis Reactions
Despite their significant overlap, some subtle differences exist:
- Scope: Synthesis is a broader term. Combination reactions are a specific type of synthesis reaction. All combination reactions are synthesis reactions, but not all synthesis reactions are combination reactions.
- Number of reactants: While combination reactions typically involve two reactants, synthesis reactions can involve more.
- Mechanism: Combination reactions often involve a direct combination of reactants, while synthesis reactions might involve multiple steps or intermediate compounds.
- Complexity: Synthesis reactions, in their broader sense, can involve significantly more complex processes than simple combination reactions.
Examples Illustrating the Nuances
Let's analyze specific examples to highlight the distinctions:
Example 1: The formation of water
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
This is a classic example of a combination reaction (and therefore also a synthesis reaction). Two simpler reactants (hydrogen gas and oxygen gas) combine to form a single, more complex product (water). This is a direct combination with no intermediate steps.
Example 2: Formation of magnesium oxide
2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO
Similar to the water formation, this is a straightforward combination reaction and a synthesis reaction. Magnesium and oxygen directly combine to produce magnesium oxide.
Example 3: Synthesis of aspirin
The synthesis of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is a more complex example. It involves multiple steps and intermediate compounds. While the overall process is a synthesis reaction (a complex molecule is formed from simpler ones), it wouldn't be accurately described as a simple combination reaction because it doesn't involve a direct combination of two reactants.
Example 4: Formation of ammonia
N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH₃
This is another classic example of a combination reaction (and synthesis reaction) where nitrogen and hydrogen combine to form ammonia. This reaction, however, requires specific conditions (high pressure and temperature) and a catalyst to proceed efficiently.
Conclusion: Context is Key
While the terms "combination reaction" and "synthesis reaction" are frequently used interchangeably, particularly in introductory chemistry, it's crucial to understand their nuances. Combination reaction represents a specific type of synthesis reaction—one involving the direct combination of two or more reactants to form a single product. Synthesis reaction, however, is a more general term encompassing any process where a more complex substance is formed from simpler ones, potentially involving multiple steps or reactants. The most accurate terminology depends heavily on the specific chemical reaction being described and the context. In most cases, using "synthesis reaction" will cover the majority of scenarios without losing accuracy. However, using the term "combination reaction" when appropriate highlights the direct and simple nature of the reaction. Always consider the mechanism and the number of reactants and intermediate steps involved to choose the most precise and accurate terminology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
A Body Of Land Completely Surrounded By Water
Apr 05, 2025
-
Difference Between Glycogen Starch And Cellulose
Apr 05, 2025
-
Can Pure Substances Be Separated By Chemical Means
Apr 05, 2025
-
Describe The Steps Of The Carbon Cycle
Apr 05, 2025
-
Is 49 A Prime Number Or A Composite Number
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Combination The Same As Synthesis Chemistry . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
