Is Air A Compound Mixture Or Element
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
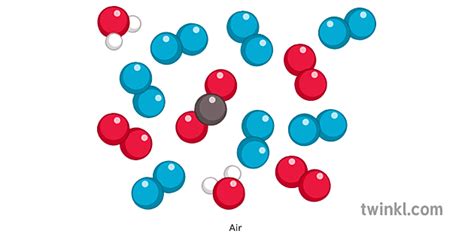
Table of Contents
Is Air a Compound, Mixture, or Element? A Deep Dive into Atmospheric Composition
The question of whether air is a compound, mixture, or element is a fundamental one in chemistry and atmospheric science. The simple answer is that air is a mixture, but understanding why requires a deeper exploration of its composition, the differences between compounds, mixtures, and elements, and the properties that define each. This article will delve into these aspects, providing a comprehensive understanding of air's nature and its constituent components.
Understanding the Basics: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Before classifying air, let's establish clear definitions of the three fundamental categories of matter:
Elements
An element is a pure substance consisting only of atoms that all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei. Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter, and they cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), and iron (Fe). The periodic table organizes all known elements.
Compounds
A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different elements are chemically bonded together in a fixed ratio. This bonding creates a new substance with properties different from its constituent elements. The properties of a compound are consistent regardless of the source. For example, water (H₂O) is a compound formed by the chemical bonding of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. It has distinctly different properties than hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. Compounds can only be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical reactions.
Mixtures
A mixture is a combination of two or more substances that are not chemically bonded. The substances retain their individual chemical properties, and their proportions can vary. Mixtures can be homogeneous (uniform composition throughout, like saltwater) or heterogeneous (non-uniform composition, like sand and water). Mixtures can be separated into their constituent components by physical methods, such as filtration, distillation, or evaporation.
The Composition of Air: A Closer Look
Air is a homogeneous mixture of various gases, primarily nitrogen and oxygen. While its composition can vary slightly depending on location (altitude, proximity to pollution sources, etc.), the major components remain consistent. Let's examine the principal constituents:
Major Components of Air
-
Nitrogen (N₂): Approximately 78% of Earth's atmosphere is nitrogen gas. This diatomic molecule is relatively inert, meaning it doesn't readily react with other substances. Its presence in air is crucial for maintaining the balance of the Earth's atmosphere.
-
Oxygen (O₂): Oxygen makes up about 21% of the atmosphere. This diatomic molecule is essential for respiration in most living organisms and plays a vital role in combustion processes.
-
Argon (Ar): Argon constitutes around 0.93% of air. It's a noble gas, meaning it's very unreactive.
Minor Components of Air
Besides the major components, air also contains several trace gases in much smaller quantities:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): While a minor component (around 0.04%), CO₂ plays a significant role in the Earth's climate system as a greenhouse gas. Its concentration is increasing due to human activities.
-
Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Methane (CH₄), Krypton (Kr), Hydrogen (H₂), Nitrous Oxide (N₂O), Xenon (Xe), Ozone (O₃): These gases are present in trace amounts but can have significant environmental impacts, particularly ozone (which plays a crucial role in the stratosphere's ozone layer, protecting us from harmful UV radiation).
-
Water Vapor (H₂O): The concentration of water vapor in the air is highly variable, depending on factors such as temperature and location. It can range from near zero to several percent.
-
Aerosols: Air also contains tiny solid and liquid particles suspended in the air, known as aerosols. These include dust, pollen, sea salt, and pollutants.
Why Air is a Mixture, Not a Compound
The key distinction lies in the nature of the interactions between the components of air. In a compound, elements are chemically bonded, forming a new substance with distinct properties. In air, however, the gases are simply mixed together; they are not chemically bonded. This is evident in several ways:
-
Variable Composition: The proportions of gases in air can vary depending on location and other factors. This variability is a characteristic of mixtures, not compounds. Compounds always have a fixed composition.
-
Retention of Individual Properties: Each gas in air retains its individual chemical properties. For instance, oxygen in air still supports combustion, and nitrogen remains relatively inert. If these gases were chemically bonded, they would exhibit new properties, different from the individual gases.
-
Physical Separation: The components of air can be separated by physical methods, such as fractional distillation of liquid air. This is a hallmark of mixtures. Separating a compound requires chemical reactions.
The Importance of Air's Composition
The specific composition of air is crucial for life on Earth and for many natural processes. The balance of nitrogen and oxygen is essential for respiration and the functioning of many biological systems. The presence of trace gases, even in small amounts, plays significant roles in climate regulation and atmospheric chemistry. Changes in air composition, such as increases in carbon dioxide, can have significant consequences for the environment and human society.
The Role of Nitrogen in Air
Nitrogen's inertness is beneficial. If it were more reactive, it would quickly combine with other elements, potentially disrupting the delicate balance of the atmosphere and biological systems. However, certain bacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for plants, initiating the nitrogen cycle, essential for plant growth and the overall ecosystem.
The Crucial Role of Oxygen
Oxygen's reactivity is vital for respiration. It's essential for the metabolic processes of most living organisms, providing the energy needed to sustain life. However, its high reactivity also means it can participate in combustion and other reactions that can be both beneficial and harmful.
The Impact of Trace Gases
Trace gases, like carbon dioxide and methane, contribute to the greenhouse effect, trapping heat in the atmosphere and influencing global temperatures. While the greenhouse effect is essential for maintaining a habitable temperature on Earth, excessive increases in greenhouse gas concentrations can lead to global warming and climate change. Ozone, while a pollutant at ground level, plays a crucial protective role in the stratosphere by absorbing harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Conclusion: Air as a Vital Mixture
In conclusion, air is definitively a mixture, not a compound or an element. Its composition, a complex blend of gases and aerosols, is far from uniform, but it maintains a remarkable stability that supports life on Earth. Understanding the nature of air as a mixture, its component parts, and the interactions between them is essential for appreciating the intricate workings of the Earth's atmosphere and for addressing environmental challenges related to air quality and climate change. The relative proportions of each component, particularly those trace gases, contribute to the delicate balance of the atmosphere and are subject to constant monitoring and scientific study. Continued research into atmospheric composition will be vital for understanding and mitigating the effects of human activities on our planet's atmosphere.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Centimeters Is 1 Inch
Mar 26, 2025
-
Are Ionic Compounds Solid At Room Temperature
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Much Is 18 Cm In Inches
Mar 26, 2025
-
Oxidation Reduction Reactions In Cellular Respiration
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Direction Does Dna Polymerase Read
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Air A Compound Mixture Or Element . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
