Is 83 A Prime Or Composite Number
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
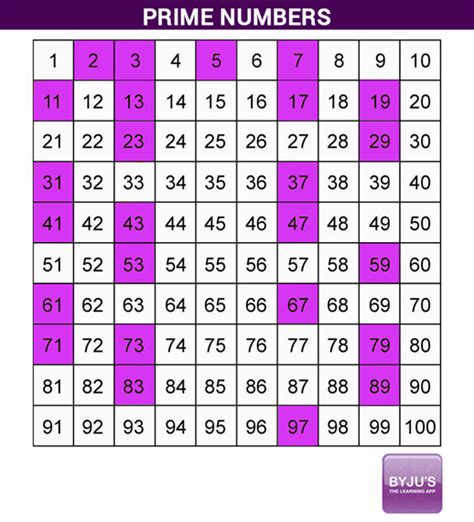
Table of Contents
Is 83 a Prime or Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Determining whether a number is prime or composite is a fundamental concept in number theory. While seemingly simple for small numbers, the process can become more complex as numbers grow larger. This article will thoroughly explore whether 83 is a prime or composite number, explaining the underlying principles and providing a comprehensive understanding of prime and composite numbers. We'll also touch upon some advanced concepts and practical applications.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we delve into the specifics of 83, let's define our key terms:
Prime Number: A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This means it's only divisible by 1 and itself without leaving a remainder. Examples include 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, and so on.
Composite Number: A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number. In other words, it has at least one positive divisor other than 1 and itself. Examples include 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 9 (3 x 3), and so on.
The Number 1: The number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This is a crucial distinction often overlooked.
Determining if 83 is Prime or Composite
To determine if 83 is prime or composite, we need to check if it's divisible by any number other than 1 and itself. The most straightforward approach is to test for divisibility by all prime numbers less than the square root of 83. Why the square root? Because if a number has a divisor greater than its square root, it must also have a divisor smaller than its square root.
The square root of 83 is approximately 9.11. Therefore, we only need to check for divisibility by prime numbers less than 9.11: 2, 3, 5, and 7.
- Divisibility by 2: 83 is not divisible by 2 because it's an odd number.
- Divisibility by 3: The sum of the digits of 83 is 8 + 3 = 11, which is not divisible by 3. Therefore, 83 is not divisible by 3.
- Divisibility by 5: 83 does not end in 0 or 5, so it's not divisible by 5.
- Divisibility by 7: 83 divided by 7 is approximately 11.86, leaving a remainder. Therefore, 83 is not divisible by 7.
Since 83 is not divisible by any prime number less than its square root, we can conclude that 83 is a prime number.
Advanced Techniques for Primality Testing
While the trial division method works well for smaller numbers like 83, it becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers. For larger numbers, more sophisticated primality tests are employed:
-
Fermat Primality Test: This probabilistic test uses Fermat's Little Theorem to determine if a number is likely prime. While it's not foolproof (some composite numbers can pass the test), it's efficient for large numbers.
-
Miller-Rabin Primality Test: This is a more robust probabilistic test that improves upon the Fermat test by reducing the probability of false positives (composite numbers incorrectly identified as prime).
-
AKS Primality Test: This is a deterministic polynomial-time algorithm that definitively determines whether a number is prime or composite. While theoretically efficient, it's often less practical than probabilistic tests for extremely large numbers due to its computational complexity.
These advanced tests are crucial in cryptography and other fields where dealing with very large prime numbers is essential.
The Significance of Prime Numbers
Prime numbers are fundamental building blocks of number theory and have far-reaching implications in various fields:
-
Cryptography: The security of many encryption algorithms relies on the difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors. RSA encryption, for example, heavily utilizes this principle.
-
Computer Science: Prime numbers play a crucial role in hash functions, data structures, and random number generation.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers are used in error-correcting codes, which are essential for reliable data transmission.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers form the basis of many concepts in abstract algebra, including modular arithmetic and finite fields.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The seemingly abstract concept of prime numbers has surprisingly tangible applications:
-
Secure Online Transactions: Every time you make an online purchase, prime numbers are working behind the scenes to secure your data. The encryption protocols that protect your sensitive information rely heavily on prime numbers.
-
Data Compression: Efficient data compression algorithms often leverage prime numbers to optimize the compression process.
-
Network Security: Prime numbers contribute to the security of network communication protocols, safeguarding your data from unauthorized access.
Conclusion: 83 – A Prime Example
We've definitively established that 83 is a prime number. This seemingly simple determination highlights the fundamental importance of prime numbers in mathematics and their widespread applications in various fields. Understanding prime numbers is key to understanding many aspects of modern technology and security. From secure online transactions to sophisticated algorithms, prime numbers are silently but powerfully shaping our digital world. Further exploration into number theory and its applications will reveal the fascinating depth and breadth of this crucial mathematical concept. The seemingly simple question of whether 83 is prime or composite opens the door to a world of intricate mathematical beauty and practical applications. Remember, the quest to understand prime numbers is an ongoing journey, and the more we explore, the more we uncover the secrets they hold.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between Political And Geographical Map
Mar 14, 2025
-
Words That Have Ai In Them
Mar 14, 2025
-
Simplify The Square Root Of 160
Mar 14, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Square
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Is An Organized Collection Of Data
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 83 A Prime Or Composite Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
