How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Square
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
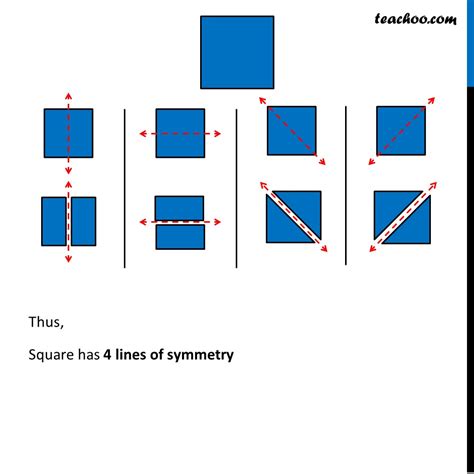
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Square Have? A Comprehensive Exploration
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and geometry, refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of parts within a whole. Understanding symmetry allows us to appreciate the beauty and order found in various shapes and patterns, from snowflakes to architectural masterpieces. This article delves into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the number of lines of symmetry a square possesses. We'll explore different types of symmetry, provide practical examples, and delve into the mathematical reasoning behind the answer.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, both halves would perfectly overlap. Not all shapes possess lines of symmetry; some might have none, while others can have multiple. The number of lines of symmetry a shape has depends on its geometric properties.
Types of Symmetry
Before diving into the specifics of a square, let's briefly touch upon other types of symmetry:
-
Reflectional Symmetry (Line Symmetry): This is the type of symmetry we're primarily concerned with in this article. It involves reflecting a shape across a line to obtain a mirror image.
-
Rotational Symmetry: This type of symmetry involves rotating a shape around a central point. A shape has rotational symmetry if it looks identical after being rotated by a certain angle less than 360 degrees.
-
Translational Symmetry: This type of symmetry involves moving a shape along a straight line without changing its orientation. You often see this in repeating patterns like wallpaper designs.
-
Point Symmetry: A shape has point symmetry if it looks identical after being rotated 180 degrees around a central point. This is also sometimes referred to as rotational symmetry of order 2.
Exploring the Symmetry of a Square
A square, a fundamental geometric shape, possesses a unique set of symmetry properties. Let's explore them systematically:
Identifying Lines of Symmetry in a Square
Consider a perfect square. To find its lines of symmetry, we need to identify lines that divide the square into two congruent (identical in shape and size) halves which are mirror images of each other.
-
Vertical Line of Symmetry: Draw a vertical line down the middle of the square. This line divides the square into two identical rectangles, each a mirror image of the other.
-
Horizontal Line of Symmetry: Draw a horizontal line across the middle of the square. Similar to the vertical line, this line creates two identical rectangles that are mirror images.
-
Diagonal Lines of Symmetry: Now, draw a line connecting opposite corners of the square. This is a diagonal line. It also divides the square into two identical triangles that are mirror images. Since there are two pairs of opposite corners, you have two such diagonal lines of symmetry.
Therefore, a square possesses a total of four lines of symmetry: one vertical, one horizontal, and two diagonal.
Visualizing the Lines of Symmetry
Imagine folding a paper square along each of these four lines. In each case, the two halves will perfectly overlap, demonstrating the reflective symmetry. This visual demonstration is a powerful way to understand the concept of lines of symmetry.
The Mathematical Proof
While visual inspection confirms the four lines of symmetry, a more rigorous mathematical approach can solidify our understanding.
The symmetry of a square stems from its properties:
- Four equal sides: This ensures that the vertical and horizontal lines of symmetry bisect the square into identical halves.
- Four right angles: This guarantees that the diagonal lines are indeed lines of symmetry, dividing the square into congruent right-angled triangles.
Any line that does not fulfill these conditions will not result in two identical mirror-image halves. Therefore, four, and only four, lines can meet this criterion for a square.
Comparing Symmetry in Other Shapes
Let's briefly compare the lines of symmetry in other common shapes:
-
Rectangle (non-square): A rectangle has two lines of symmetry – one vertical and one horizontal.
-
Circle: A circle possesses infinite lines of symmetry, as any line passing through its center divides it into two identical halves.
-
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry – one from each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon has five lines of symmetry – one from each vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has six lines of symmetry – three lines connecting opposite vertices, and three lines connecting midpoints of opposite sides.
The number of lines of symmetry generally increases with the increase in the order of rotational symmetry of regular polygons.
Applications of Symmetry
Understanding lines of symmetry is not just an academic exercise; it has numerous practical applications:
-
Art and Design: Artists and designers utilize symmetry to create balanced and aesthetically pleasing compositions. From logos to architectural designs, symmetry is a fundamental principle.
-
Nature: Symmetry is prevalent in nature, found in snowflakes, flowers, and many other natural formations. Understanding symmetry allows us to appreciate the underlying mathematical order in the natural world.
-
Engineering and Architecture: Symmetrical designs often provide structural stability and balance in engineering and architecture.
-
Computer Graphics: Symmetry plays a significant role in computer graphics, particularly in creating 3D models and animations. Understanding symmetry allows for more efficient and effective design processes.
Conclusion: The Definitive Answer
In conclusion, a square has precisely four lines of symmetry: one vertical, one horizontal, and two diagonal. This fact is not only demonstrable through visual inspection and folding but is also supported by a rigorous mathematical understanding of the square's properties. The concept of lines of symmetry extends far beyond the realm of geometry, impacting various fields, from art and design to engineering and nature itself. Understanding symmetry deepens our appreciation of order, balance, and the inherent beauty found in shapes and patterns around us. We hope this comprehensive exploration has provided a thorough understanding of the lines of symmetry in a square.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Simplify The Square Root Of 169
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Algebraic Expression Is A Trinomial
Mar 15, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 9 And 16
Mar 15, 2025
-
Animals That Can Breathe Underwater And On Land
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Is A Correct Description Of The Polygon
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry On A Square . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
