Difference Between Political And Geographical Map
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
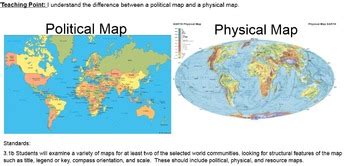
Table of Contents
Delving into the Differences: Political vs. Geographical Maps
Maps are fundamental tools for understanding our world. They provide visual representations of geographical locations, political boundaries, and a myriad of other spatial data. However, not all maps are created equal. Two distinct types, political and geographical maps, serve different purposes and utilize varying visual elements. Understanding their key differences is crucial for anyone seeking to interpret and utilize cartographic information effectively. This comprehensive guide will explore the nuances separating political and geographical maps, highlighting their respective strengths, limitations, and applications.
The Essence of Geographical Maps: A Focus on Nature
Geographical maps, also known as physical maps, primarily showcase the Earth's natural features. They are designed to illustrate the planet's physical landscape, providing a detailed picture of its topography, landforms, and geographical phenomena. Think mountains, rivers, deserts, plains, oceans, and lakes – these are the stars of a geographical map.
Key Elements of Geographical Maps:
- Landforms: Mountains, hills, valleys, plains, plateaus, and other significant land formations are meticulously depicted using contour lines, shading, and color gradients to represent elevation changes.
- Hydrography: Rivers, lakes, oceans, seas, and other bodies of water are shown with varying levels of detail, depending on the map's scale and purpose. Major waterways are usually clearly marked, while smaller streams might be omitted on smaller-scale maps.
- Vegetation: Forests, grasslands, deserts, and other vegetation types are often represented using different colors or symbols, providing insights into the distribution of plant life.
- Climate: While not always explicitly shown, geographical maps can indirectly convey climatic information through the representation of vegetation zones, elevation, and proximity to water bodies.
- Natural Resources: Some geographical maps may also highlight the distribution of natural resources such as minerals, oil, or forests.
Purpose and Applications:
Geographical maps are invaluable for a multitude of purposes, including:
- Environmental Studies: Understanding the distribution of natural resources, analyzing ecosystems, and assessing environmental risks.
- Urban Planning: Identifying suitable locations for development, considering topography and drainage patterns.
- Navigation: Though less precise than specialized navigational charts, geographical maps can provide a general sense of location and route planning.
- Educational Purposes: Teaching geography, geology, and environmental science, providing a visual context for understanding spatial relationships.
- Tourism and Recreation: Planning travel routes, identifying points of interest like national parks or scenic overlooks.
Political Maps: Charting the Human Landscape
In contrast to geographical maps, political maps emphasize human-created boundaries and divisions. Their primary focus is on showcasing the geopolitical organization of the world, highlighting countries, states, provinces, and other administrative regions. These maps are less concerned with natural features and more interested in the political structures imposed upon the landscape.
Key Elements of Political Maps:
- International Boundaries: Clearly defined lines marking the borders between countries. The style and thickness of these lines can vary, sometimes reflecting the historical significance or disputed nature of the border.
- National Capitals: Major cities, especially national capitals, are typically marked with a distinct symbol, often a star or a filled circle.
- Administrative Divisions: Sub-national divisions such as states, provinces, or counties are often depicted, usually with different colors or patterns to distinguish them.
- Cities and Towns: Important urban areas are represented, often with their names and sizes proportionate to their population.
- Transportation Networks: Roads, railways, and airports are frequently included, providing information on connectivity and infrastructure.
Purpose and Applications:
Political maps serve a wide range of purposes, frequently used for:
- International Relations: Understanding geopolitical relationships, analyzing alliances, and identifying potential conflict zones.
- Political Analysis: Studying voting patterns, analyzing electoral districts, and understanding the distribution of political power.
- Strategic Planning: Military operations, resource allocation, and economic development initiatives often rely heavily on political map analysis.
- Journalism and Media: Reporting on current events, presenting political news, and providing visual context for geopolitical discussions.
- Education: Teaching civics, history, and political science, providing a visual representation of governmental structures.
Key Differences Summarized: A Table for Clarity
To further clarify the distinctions, let's summarize the core differences in a concise table:
| Feature | Geographical Map | Political Map |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Earth's natural features | Human-created boundaries and political divisions |
| Key Elements | Landforms, hydrography, vegetation, climate | International boundaries, capitals, administrative divisions |
| Data Represented | Physical geography | Political geography |
| Colors/Symbols | Primarily represent elevation, vegetation | Primarily represent political entities |
| Scale | Can vary widely, from local to global | Can vary widely, from local to global |
| Applications | Environmental studies, urban planning, education | International relations, political analysis, journalism |
Hybrid Maps: Blending the Best of Both Worlds
While political and geographical maps represent distinct approaches to cartography, it's important to note that many maps incorporate elements of both. These hybrid maps offer a more comprehensive understanding of a region by integrating both physical and political information. They often depict natural features alongside political boundaries, providing a richer visual context. For example, a map showing the distribution of population density overlaid on a topographical map would be considered a hybrid map.
The Role of Scale and Detail: A Crucial Consideration
The scale of a map significantly impacts its level of detail and the type of information it can effectively convey. Large-scale maps, showing smaller areas in greater detail, are better suited for illustrating specific geographical features or political subdivisions within a limited region. Small-scale maps, covering larger areas with less detail, are more appropriate for presenting overall geographical patterns or broad political divisions across continents or even the globe. The choice of scale directly influences the effectiveness of both political and geographical maps.
Advanced Cartographic Techniques and Their Impact
Modern cartography utilizes advanced techniques like GIS (Geographic Information Systems) and remote sensing to create highly sophisticated and detailed maps. These technologies allow for the integration of vast amounts of data, enabling the creation of maps that are both visually appealing and information-rich. For instance, 3D models, interactive maps, and data visualizations are becoming increasingly common, offering dynamic and engaging ways to understand geographical and political information.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Map for the Right Purpose
The selection of either a political or geographical map, or a hybrid thereof, depends entirely on the specific information required. When focusing on the natural landscape and its physical features, a geographical map is the ideal choice. Conversely, for visualizing political divisions, administrative boundaries, and human-created structures, a political map serves its purpose better. Understanding the fundamental differences between these map types is paramount for effectively interpreting and using cartographic data across diverse disciplines and applications. By appreciating the unique strengths of each type, we can unlock a deeper understanding of our world's complex interplay of nature and human organization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Is A Correct Description Of The Polygon
Mar 15, 2025
-
Lcm Of 8 12 And 4
Mar 15, 2025
-
Is A Kilo More Than A Pound
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Difference Between Political And Geographical Map . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
