How To Get The Diameter Of A Sphere
Juapaving
Mar 09, 2025 · 6 min read
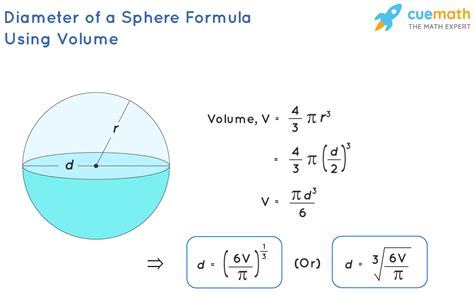
Table of Contents
How to Get the Diameter of a Sphere: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the diameter of a sphere is a fundamental task across numerous fields, from engineering and physics to mathematics and everyday life. Whether you're measuring a marble, a basketball, or a celestial body, understanding the different methods available is crucial. This comprehensive guide will explore various techniques, from simple measurements to more complex calculations, equipping you with the knowledge to accurately determine the diameter of any sphere.
Understanding the Fundamentals: Diameter, Radius, and Circumference
Before diving into the methods, let's clarify the key terms:
- Diameter: The straight line passing from side to side through the center of a sphere. It's the longest distance across the sphere.
- Radius: The distance from the center of the sphere to any point on its surface. The radius is half the diameter (Diameter = 2 * Radius).
- Circumference: The distance around the sphere's outer edge. For a sphere, it's calculated as Circumference = 2 * π * Radius or Circumference = π * Diameter.
Method 1: Direct Measurement with Calipers
This is the simplest and most direct method, particularly suitable for smaller spheres where physical access is possible. Vernier calipers or digital calipers are precision measuring instruments that provide highly accurate measurements.
Steps:
- Ensure Proper Calibration: Before starting, verify that the calipers are properly calibrated and zeroed.
- Secure the Sphere: Gently place the sphere between the jaws of the calipers.
- Close the Jaws: Slowly close the jaws until they firmly contact the sphere at opposite points.
- Read the Measurement: Read the measurement displayed on the calipers. This reading directly provides the diameter of the sphere.
Advantages: This method is straightforward, provides precise measurements, and requires minimal calculations.
Disadvantages: It's not suitable for large spheres or spheres that are inaccessible for direct measurement. Also, the accuracy depends on the precision of the calipers and the user's skill.
Method 2: Measuring the Circumference and Calculating the Diameter
If direct measurement isn't feasible, you can determine the diameter by measuring the circumference and then applying the formula. A flexible measuring tape is ideal for this method.
Steps:
- Wrap the Tape: Carefully wrap the measuring tape around the widest part of the sphere, ensuring a snug fit.
- Record the Circumference: Note the measurement from the tape, which represents the circumference of the sphere.
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula: Diameter = Circumference / π (where π is approximately 3.14159).
Advantages: This method is suitable for larger spheres where direct measurement is difficult or impossible.
Disadvantages: The accuracy depends on the precision of the measuring tape and the ability to accurately measure the circumference. Any slight inaccuracy in circumference measurement will directly impact the calculated diameter.
Method 3: Using the Sphere's Volume and Calculating the Diameter
If you know the volume of the sphere, you can calculate its diameter using the following formula:
Volume of a sphere = (4/3) * π * r³
Where 'r' is the radius. To find the diameter, follow these steps:
- Rearrange the Formula: Solve the volume formula for the radius: r = ³√[(3 * Volume) / (4 * π)]
- Calculate the Radius: Substitute the known volume into the rearranged formula to calculate the radius.
- Calculate the Diameter: Multiply the calculated radius by 2 to obtain the diameter (Diameter = 2 * r).
Advantages: Useful when the volume of the sphere is known, but direct measurement is difficult.
Disadvantages: Requires accurate knowledge of the sphere's volume, which might need to be determined through other methods, such as water displacement. This introduces potential errors in the calculation.
Method 4: Using the Sphere's Surface Area and Calculating the Diameter
Similar to the volume method, if the surface area of the sphere is known, you can calculate its diameter.
Surface area of a sphere = 4 * π * r²
Follow these steps:
- Rearrange the Formula: Solve the surface area formula for the radius: r = √[Surface Area / (4 * π)]
- Calculate the Radius: Substitute the known surface area into the rearranged formula to obtain the radius.
- Calculate the Diameter: Multiply the calculated radius by 2 (Diameter = 2 * r).
Advantages: Suitable when the surface area is known, rather than the volume.
Disadvantages: Accurate knowledge of the surface area is crucial. Inaccuracies in the surface area measurement will directly affect the final diameter calculation.
Method 5: Advanced Techniques for Irregular Spheres
For spheres that are not perfectly spherical (e.g., slightly deformed or irregular shapes), the above methods might not provide entirely accurate results. In such cases, more advanced techniques are needed:
- 3D Scanning: Using 3D scanning technology to create a digital model of the sphere allows for precise measurements of its diameter at various points, providing a more comprehensive understanding of its dimensions.
- Image Processing and Computer Vision: Sophisticated image analysis techniques can be used to process images of the sphere and accurately determine its diameter, even if the sphere is partially obscured or irregular in shape.
- Geometric Modeling and Approximation: If the irregularities are minor, geometric modeling can create an approximation of a perfect sphere, allowing for reasonably accurate diameter calculation using the traditional methods.
These advanced methods typically require specialized equipment and expertise.
Choosing the Right Method
The best method for determining the diameter of a sphere depends on several factors, including:
- Size of the sphere: Direct measurement is best for small spheres, while circumference measurement or volume/surface area calculations are more suitable for larger ones.
- Accessibility of the sphere: If the sphere is easily accessible, direct measurement is the preferred choice.
- Available tools and equipment: The availability of calipers, measuring tapes, or other specialized equipment will influence the method selection.
- Accuracy requirements: The required level of accuracy will determine the choice of method and the precision of the measuring instruments.
By considering these factors, you can choose the most appropriate method for your specific needs.
Error Analysis and Minimizing Inaccuracies
Regardless of the chosen method, it's important to consider potential sources of error and take steps to minimize them:
- Calibration of Instruments: Always ensure that your measuring instruments (calipers, measuring tapes) are properly calibrated and zeroed before each measurement.
- Multiple Measurements: Take multiple measurements at different points on the sphere and average the results to minimize the impact of individual errors.
- Environmental Factors: Be aware of factors like temperature fluctuations that might affect the accuracy of measurements.
- Human Error: Minimize human error through careful and precise measurements.
- Instrument Resolution: Understand the resolution of your measuring instrument and acknowledge its limitations in accuracy.
By paying close attention to detail and accounting for potential errors, you can significantly improve the accuracy of your diameter determination.
Applications of Sphere Diameter Measurement
The ability to accurately determine the diameter of a sphere is critical in many different fields:
- Manufacturing: Ensuring the precise dimensions of spherical components in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and medicine.
- Astronomy: Determining the sizes of planets, stars, and other celestial bodies.
- Physics and Engineering: Calculating volumes, surface areas, and other properties of spherical objects in various scientific and engineering applications.
- Sports: Measuring the size and specifications of sports equipment like balls.
- Medicine: Measuring the size of cells, organs, and other structures in medical imaging and analysis.
- Everyday Life: Simple tasks like determining the size of marbles, beads, or other spherical objects.
Understanding the various methods and their applications provides a comprehensive approach to accurately and effectively measuring the diameter of a sphere, regardless of its size, accessibility, or intended use. Remember to choose the most appropriate method for your specific circumstances, and always strive for accurate and reliable results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 12
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Cubic Inches In A Cubic Ft
Mar 10, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 7
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Many Feet In 50 Metres
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Are The Components Of A Nucleotide
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Get The Diameter Of A Sphere . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
