Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 5 min read
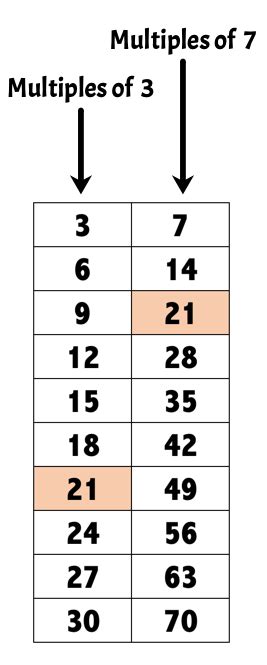
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 3 and 7: A Deep Dive
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding LCMs is crucial for simplifying fractions, solving problems involving ratios and proportions, and even tackling more advanced mathematical concepts. This comprehensive article will delve into the LCM of 3 and 7, exploring various methods of calculation and demonstrating its practical applications. We'll go beyond a simple answer, providing a thorough understanding of the underlying principles and expanding on related mathematical ideas.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
Before we jump into the specific LCM of 3 and 7, let's establish a clear understanding of what LCM means. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the integers as factors.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16... Multiples of 3 are: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, hence the LCM(2,3) = 6.
Calculating the LCM of 3 and 7: Different Approaches
There are several ways to calculate the LCM of 3 and 7. Let's explore the most common methods:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward approach, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35...
As you can see, the smallest number that appears in both lists is 21. Therefore, the LCM(3,7) = 21.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is particularly useful for larger numbers or when dealing with more than two numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
Since 3 and 7 are both prime numbers and have no common factors other than 1, their LCM is simply their product.
Therefore, LCM(3,7) = 3 x 7 = 21
3. Using the Formula: LCM(a,b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a,b)
This method utilizes the greatest common divisor (GCD) of the two numbers. The GCD is the largest positive integer that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. For 3 and 7, the GCD is 1 (as they are coprime – they share no common factors other than 1).
- GCD(3,7) = 1
Applying the formula: LCM(3,7) = (3 x 7) / 1 = 21
Why is the LCM Important?
Understanding and calculating the LCM is not merely an academic exercise; it has significant practical applications in various areas:
1. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential. The LCM becomes the common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
For example, to add 1/3 + 1/7, we find the LCM of 3 and 7, which is 21. Then we rewrite the fractions with the common denominator:
(7/21) + (3/21) = 10/21
2. Real-world Applications: Scheduling and Cyclical Events
The LCM finds applications in scheduling problems. Imagine two buses that leave a station at different intervals. One bus leaves every 3 hours, and the other leaves every 7 hours. The LCM(3,7) = 21 indicates that both buses will depart simultaneously again after 21 hours. This principle extends to various cyclical events, from planetary alignments to machine maintenance schedules.
3. Music Theory: Harmonics and Musical Intervals
In music theory, the LCM plays a role in understanding harmonics and musical intervals. The frequencies of musical notes are often related by ratios, and the LCM helps determine when these frequencies align, creating harmonious sounds.
4. Computer Science: Algorithm Optimization
In certain algorithms and computer programs, finding the LCM can be crucial for optimizing performance. For instance, in tasks involving synchronization or cycle detection, calculating the LCM efficiently can lead to faster execution times.
Exploring Coprime Numbers and their LCM
The numbers 3 and 7 are examples of coprime numbers (also known as relatively prime numbers). Coprime numbers are two integers that have no common factors other than 1. This property significantly simplifies the calculation of their LCM. The LCM of two coprime numbers is simply their product. This is a crucial observation that simplifies many LCM calculations.
The concept of coprimality extends beyond the LCM calculation. It appears in several areas of number theory, including cryptography and modular arithmetic, which form the foundation for secure online communication and data encryption.
Expanding on the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
While this article focuses on the LCM of 3 and 7, the concept extends to finding the LCM of three or more numbers. The prime factorization method becomes particularly useful in such cases. You find the prime factorization of each number, and the LCM is constructed by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations.
For example, let's find the LCM of 3, 7, and 5:
- Prime factorization of 3: 3
- Prime factorization of 7: 7
- Prime factorization of 5: 5
LCM(3, 7, 5) = 3 x 7 x 5 = 105
Conclusion: The Significance of Understanding LCM
The least common multiple, while seemingly a simple concept, is a fundamental building block in various mathematical fields and practical applications. Understanding how to calculate the LCM, particularly using different methods, is essential for solving problems across various disciplines. The example of the LCM(3,7) = 21 serves as a clear illustration of the principles involved and highlights the significance of this concept in both theoretical and practical contexts. This article has provided a comprehensive overview, going beyond the simple calculation to delve into the underlying principles, related concepts, and practical applications, enhancing your understanding of this vital mathematical tool.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Junction Between Two Neurons Is Known As The
Mar 10, 2025
-
Units For Area Moment Of Inertia
Mar 10, 2025
-
Four Letter Words From A To Z
Mar 10, 2025
-
How Big Is 5cm By 5cm
Mar 10, 2025
-
5 Letter Words Ending With On
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 3 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
