How To Determine Whether The Function Is A Polynomial Function
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
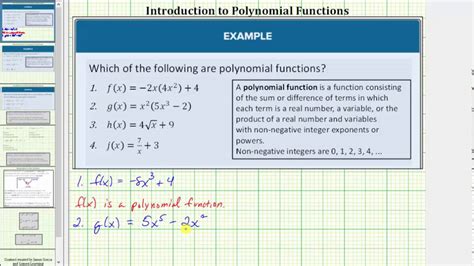
Table of Contents
How to Determine Whether a Function is a Polynomial Function
Determining whether a given function is a polynomial function is a fundamental concept in algebra and calculus. Understanding polynomial functions is crucial for many mathematical operations and applications, from solving equations to modeling real-world phenomena. This comprehensive guide will delve into the characteristics of polynomial functions, providing you with a robust understanding of how to definitively identify them.
Understanding Polynomial Functions: The Defining Characteristics
A polynomial function is a function that can be expressed in the form:
f(x) = aₙxⁿ + aₙ₋₁xⁿ⁻¹ + ... + a₂x² + a₁x + a₀
Where:
- x is the variable.
- aₙ, aₙ₋₁, ..., a₂, a₁, a₀ are constants, often called coefficients. These coefficients can be real numbers or complex numbers.
- n is a non-negative integer, representing the degree of the polynomial.
Let's break down the key characteristics that define a polynomial function:
1. Exponents Must Be Non-Negative Integers
This is the most crucial characteristic. The exponents of the variable (x) must be non-negative integers (0, 1, 2, 3, and so on). If you encounter any negative exponents, fractional exponents (like square roots or cube roots), or exponents that are not integers, the function is not a polynomial.
Examples:
- Polynomial: f(x) = 3x⁴ - 2x² + 5x - 7 (Exponents are 4, 2, 1, and 0)
- Not a Polynomial: g(x) = 2x⁻² + 4x (Negative exponent -2)
- Not a Polynomial: h(x) = x¹⁄² + 1 (Fractional exponent 1/2)
- Not a Polynomial: i(x) = 5x<sup>π</sup> + 2 (Non-integer exponent π)
2. Only Whole Number Powers of x are Allowed
Closely related to the first point, polynomial functions only involve whole number powers of the variable x. This eliminates functions with variables in denominators, within radicals (roots), or as exponents.
Examples:
- Polynomial: f(x) = x³ + 2x² - 5 (Whole number exponents)
- Not a Polynomial: g(x) = 1/x + 3 (Variable in the denominator)
- Not a Polynomial: h(x) = √x + 2 (Variable under a radical)
- Not a Polynomial: i(x) = xˣ (Variable as an exponent)
3. Coefficients Can Be Real or Complex Numbers
The coefficients (the numbers in front of the x terms) can be any real number (like 2, -5, 0.75, π) or even complex numbers (numbers involving the imaginary unit 'i', where i² = -1). This doesn't affect whether the function is a polynomial; it only affects the nature of its roots (solutions).
Examples:
- Polynomial: f(x) = 2.5x³ - √2x + 1 (Real number coefficients)
- Polynomial: g(x) = (3 + 2i)x² - ix + 4 (Complex number coefficients)
4. The Function Must Be Finite
Polynomial functions are finite. This means they have a defined highest power of x (the degree). They don't have an infinite number of terms or an infinite degree.
Examples:
- Polynomial: f(x) = 7x⁵ + 3x² - 1 (Finite number of terms)
- Not a Polynomial: An infinite series like the Taylor expansion of eˣ (Infinite number of terms)
Identifying Polynomial Functions: A Step-by-Step Approach
To determine if a function is a polynomial, systematically check the following:
-
Examine the exponents: Carefully scrutinize each term in the function. Make sure all exponents of the variable are non-negative integers. If you find any negative, fractional, or non-integer exponents, the function is not a polynomial.
-
Check for variables in denominators, under radicals, or as exponents: The variable (x) should only appear in the numerator as whole number powers. If it appears in a denominator, under a square root or other radical, or as an exponent, the function is not a polynomial.
-
Verify the finiteness of the function: The function should have a limited number of terms, each with a non-negative integer exponent. Infinite series and functions with an undefined highest power of x are not polynomials.
-
Analyze the coefficients: While the type of coefficients (real or complex) doesn't determine whether it's a polynomial, analyzing them can be useful in further understanding the function's behavior.
Advanced Cases and Examples
Let's analyze some more complex examples to solidify your understanding:
Example 1:
Is f(x) = (x² + 1)(x³ - 2x) a polynomial function?
Solution: Expand the expression:
f(x) = x⁵ - 2x³ + x³ - 2x = x⁵ - x³ - 2x
All exponents are non-negative integers. Therefore, yes, f(x) is a polynomial function.
Example 2:
Is g(x) = 3x² + 2/x - 5 a polynomial function?
Solution: The presence of 'x' in the denominator (2/x) immediately indicates that this is not a polynomial function.
Example 3:
Is h(x) = √(x² + 1) a polynomial function?
Solution: The square root makes this a non-polynomial function because the variable is under a radical.
Example 4:
Is k(x) = |x| a polynomial function?
Solution: The absolute value function, |x|, cannot be expressed in the standard polynomial form. While it can be defined piecewise (as x for x ≥ 0 and -x for x < 0), it's not representable as a single polynomial expression. Thus, no, it is not a polynomial.
Example 5:
Is m(x) = eˣ a polynomial function?
Solution: The exponential function eˣ cannot be expressed in polynomial form, regardless of the coefficients. Its Taylor series representation is an infinite sum, which means it is not a polynomial.
Example 6:
Is n(x) = sin(x) a polynomial function?
Solution: The trigonometric function sin(x) also cannot be expressed as a finite sum of terms with whole number powers of x. Therefore, it's not a polynomial.
Conclusion: Mastering Polynomial Function Identification
Identifying polynomial functions requires a thorough understanding of their defining characteristics. By carefully examining the exponents, checking for variables in inappropriate locations, confirming finiteness, and analyzing the coefficients, you can accurately determine whether a given function belongs to this important class of mathematical functions. The ability to distinguish polynomial functions is fundamental to success in higher-level mathematics and its various applications. Practice consistently using the steps outlined in this guide, and you'll quickly master this essential skill. Remember to always check for negative or fractional exponents as these are immediate indicators that a function is not a polynomial. With careful attention to detail and a solid grasp of the core principles, you'll confidently navigate the world of polynomials.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Key In Database Management System
Mar 19, 2025
-
New Delhi Delhi India Latitude Longitude
Mar 19, 2025
-
How To Convert Ratios To Percentages
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Percentile And Percent
Mar 19, 2025
-
Cometh The Hour Cometh The Man
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Determine Whether The Function Is A Polynomial Function . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
