What Is A Vertices In A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
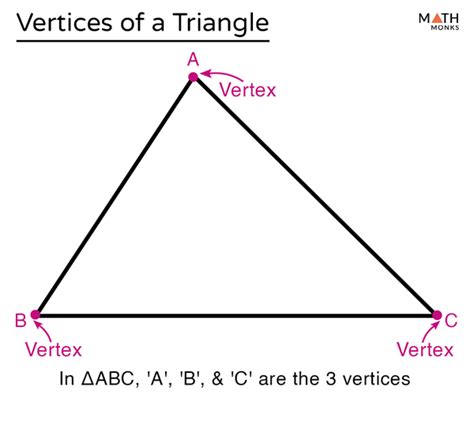
Table of Contents
What is a Vertex in a Triangle? A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the fundamental components of geometric shapes is crucial for mastering various mathematical concepts. This comprehensive guide delves into the definition of a vertex in a triangle, exploring its properties, significance, and applications across different mathematical fields. We'll also explore related concepts to provide a complete understanding.
Defining a Vertex in a Triangle
A vertex (plural: vertices) is a point where two or more lines or edges meet to form a corner or angle. In the context of a triangle, a vertex is simply one of the three points where two sides of the triangle intersect. These points are fundamental to defining the shape and properties of the triangle. Each vertex is uniquely identified by the intersection of two distinct sides.
Think of a triangle as a three-sided polygon. Each of these sides is a line segment, and where two of these line segments join, you have a vertex. It's a crucial element that determines the triangle's angles and overall structure.
Properties of Vertices in a Triangle
Vertices are not just points; they hold significant properties contributing to the overall characteristics of the triangle:
1. Angle Formation:
Each vertex forms an interior angle of the triangle. The measure of this angle is crucial in classifying the triangle (e.g., acute, obtuse, right-angled). The sum of the interior angles of any triangle always equals 180 degrees. This property is fundamental to solving numerous geometrical problems.
2. Side Intersection:
Each vertex represents the intersection point of two sides of the triangle. This point of intersection uniquely identifies the vertex and provides a starting point for many calculations related to the triangle's area and perimeter.
3. Coordinates in a Cartesian Plane:
When a triangle is plotted on a Cartesian plane (a coordinate system), each vertex has its own unique coordinates (x, y). These coordinates are essential for performing various geometric calculations using analytical geometry. You can calculate the distance between vertices, the midpoint of a side, and even the area using the coordinates.
4. Centroids and Other Points of Concurrency:
Several important points within a triangle are defined by the relationships between its vertices. These include:
- Centroid: The point of intersection of the three medians of a triangle (a median connects a vertex to the midpoint of the opposite side). The centroid is the center of mass of the triangle.
- Circumcenter: The point where the perpendicular bisectors of the three sides intersect. This point is equidistant from all three vertices, and the circle passing through all three vertices (the circumcircle) has its center at the circumcenter.
- Incenter: The point where the three angle bisectors of the triangle intersect. This point is equidistant from all three sides, and the circle inscribed within the triangle (the incircle) has its center at the incenter.
- Orthocenter: The point where the three altitudes of the triangle intersect. An altitude is a line segment from a vertex perpendicular to the opposite side.
Types of Triangles Based on Vertices and Angles
The properties of the angles formed at the vertices are used to classify triangles:
- Acute Triangle: All three angles at the vertices are less than 90 degrees.
- Right-Angled Triangle: One of the angles at a vertex is exactly 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
- Obtuse Triangle: One of the angles at a vertex is greater than 90 degrees.
Applications of Vertex Understanding
Understanding vertices and their properties is essential in various fields:
1. Geometry and Trigonometry:
Vertices are fundamental to solving various geometric problems, including:
- Calculating the area of a triangle: Various formulas, such as Heron's formula and the formula using coordinates, rely on the vertices' positions.
- Determining the lengths of sides: Using the Law of Cosines and the Law of Sines, one can determine the lengths of sides using the angles at the vertices and the known side lengths.
- Solving problems involving similar triangles: The ratios of corresponding sides and angles are crucial in solving these problems.
2. Computer Graphics and Computer-Aided Design (CAD):
In computer graphics and CAD, objects are represented as collections of polygons, including triangles. Vertices define the points that make up the polygon's corners and are crucial in creating and manipulating 3D models and images. Understanding vertex manipulation is critical for tasks such as 3D modeling, animation, and game development.
3. Physics and Engineering:
In physics and engineering, understanding vertices and their properties is crucial for various structural analysis applications. For instance, in structural engineering, the vertices represent the points where members of a truss (a structural framework) meet. Analyzing the forces and stresses at these vertices is crucial for ensuring structural integrity.
4. Cartography and Geography:
In cartography and geographic information systems (GIS), triangles are often used to represent geographical areas, and the vertices define the boundaries of these areas. These vertices are essential for accurate spatial calculations and analysis.
Beyond Triangles: Vertices in Other Polygons
The concept of a vertex extends beyond triangles to other polygons. A polygon is a closed, two-dimensional figure with straight sides. A vertex in any polygon is the point where two sides meet. The number of vertices in a polygon is always equal to the number of sides. For example:
- A quadrilateral (four-sided polygon) has four vertices.
- A pentagon (five-sided polygon) has five vertices.
- A hexagon (six-sided polygon) has six vertices.
- And so on...
The properties and applications of vertices in polygons are similar to those in triangles, although the complexities increase with the number of sides.
Advanced Concepts Related to Vertices
Further exploration into advanced topics related to vertices can lead to a deeper understanding of geometry:
- Vertex coordinates in different coordinate systems: Understanding how vertices are represented in polar coordinates, spherical coordinates, and other coordinate systems is essential in various applications.
- Vertex normals in computer graphics: In 3D computer graphics, a vertex normal is a vector that is perpendicular to the surface at a given vertex. This is crucial for lighting calculations and realistic rendering.
- Vertex coloring in graph theory: In graph theory, vertices are often colored to solve problems related to graph coloring and scheduling.
- Delaunay triangulation: This is a method for creating a triangulation of a set of points such that no point is inside the circumcircle of any triangle. This has applications in various fields, including geographic information systems and computer graphics.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of a vertex in a triangle is fundamental to grasping various geometric principles. Vertices are not merely points; they are the building blocks of triangles and represent the intersection of two sides, forming the angles that characterize the triangle's type. The properties of vertices, along with related concepts like centroids, circumcenters, and incenters, play a critical role in solving a wide array of geometric problems, and their applications extend far beyond theoretical mathematics, impacting fields such as computer graphics, engineering, and cartography. By mastering this fundamental concept, you pave the way for deeper exploration into more complex geometric principles.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Is A Result Of Glycolysis
May 09, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 40
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Inches In 12 Meters
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Chromosomes Does A Fly Have
May 09, 2025
-
What Are The Smallest Parts Of An Atom
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is A Vertices In A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.