How Many Valence Electrons Are Found In Phosphorus
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
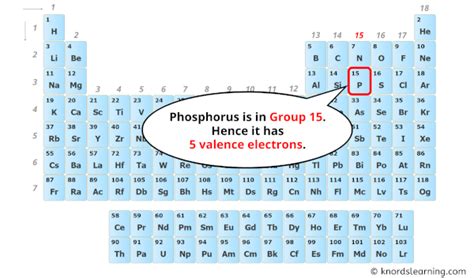
Table of Contents
How Many Valence Electrons Are Found in Phosphorus? A Deep Dive into Atomic Structure
Phosphorus, a crucial element for life, plays a vital role in biological processes and industrial applications. Understanding its atomic structure, particularly its valence electrons, is key to comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. This article will delve into the details of phosphorus's electron configuration, explaining exactly how many valence electrons it possesses and why this number is so significant.
Understanding Valence Electrons
Before we focus on phosphorus specifically, let's clarify what valence electrons are. Valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are the most loosely bound to the nucleus and are therefore the ones involved in chemical bonding. They determine an element's reactivity, its ability to form chemical bonds with other atoms, and the types of bonds it forms (ionic, covalent, etc.). The number of valence electrons directly influences an element's chemical properties and its position within the periodic table.
Phosphorus's Position in the Periodic Table
Phosphorus is located in Group 15 (or VA) of the periodic table, also known as the pnictogens. Elements within the same group share similar valence electron configurations, leading to similar chemical behaviors. This grouping provides a valuable clue to determining the number of valence electrons in phosphorus.
Determining Phosphorus's Electron Configuration
To accurately determine the number of valence electrons, we need to examine phosphorus's electron configuration. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, meaning a neutral phosphorus atom has 15 protons and 15 electrons. These electrons are distributed across different energy levels (shells) around the nucleus according to the Aufbau principle and Hund's rule.
The electron configuration of phosphorus is: 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p³.
Let's break this down:
- 1s²: Two electrons in the first energy level (shell), in the 's' subshell.
- 2s²: Two electrons in the second energy level, in the 's' subshell.
- 2p⁶: Six electrons in the second energy level, in the 'p' subshell.
- 3s²: Two electrons in the third energy level, in the 's' subshell.
- 3p³: Three electrons in the third energy level, in the 'p' subshell.
Identifying the Valence Electrons
The valence electrons are those in the outermost shell, which in phosphorus's case is the third energy level (n=3). This shell contains both the 3s and 3p electrons. Therefore, phosphorus has a total of five valence electrons (2 from 3s and 3 from 3p).
This configuration explains phosphorus's chemical behavior. It often forms three covalent bonds to achieve a stable octet (eight electrons in its outermost shell), although it can also form five bonds under certain circumstances.
The Significance of Five Valence Electrons
The presence of five valence electrons significantly impacts phosphorus's properties and reactivity:
-
Covalent Bonding: Phosphorus readily forms covalent bonds with other atoms to share electrons and achieve a stable electron configuration. This is evident in numerous phosphorus compounds like phosphine (PH₃) and phosphorus pentachloride (PCl₅).
-
Oxidation States: Phosphorus exhibits a range of oxidation states, primarily -3, +3, and +5, reflecting its ability to gain or lose electrons. This versatility is crucial in its diverse chemical applications.
-
Allotropes: Phosphorus exists in several allotropic forms, including white phosphorus, red phosphorus, and black phosphorus. These allotropes differ in their physical and chemical properties due to variations in their bonding arrangements, which are directly influenced by the presence of five valence electrons.
-
Biological Importance: The five valence electrons contribute to phosphorus's essential role in biological systems. It's a crucial component of DNA, RNA, ATP (adenosine triphosphate – the energy currency of cells), and phospholipids (major components of cell membranes). Its chemical versatility allows it to participate in a wide array of biochemical reactions.
-
Industrial Applications: The chemical reactivity stemming from its five valence electrons makes phosphorus vital in various industrial processes. It’s used in fertilizers, detergents, flame retardants, and the production of certain metals.
Phosphorus Compounds and Valence Electrons
Let's examine a few examples of phosphorus compounds to illustrate the role of its valence electrons in bonding:
1. Phosphine (PH₃): In phosphine, phosphorus forms three single covalent bonds with three hydrogen atoms. Each hydrogen atom shares one electron with phosphorus, contributing to phosphorus's octet. Phosphorus uses three of its five valence electrons in this bonding, leaving a lone pair of electrons.
2. Phosphorus Pentachloride (PCl₅): In this compound, phosphorus forms five covalent bonds with five chlorine atoms. This is possible because phosphorus can utilize its 3s and 3p orbitals, along with vacant 3d orbitals, to accommodate more than eight electrons in its valence shell, a phenomenon known as expanded octet.
3. Phosphates (PO₄³⁻): In phosphate ions, phosphorus forms four covalent bonds with four oxygen atoms. The negative charge on the ion reflects the extra electrons acquired to complete the octet.
Exceptions and Further Considerations
While the rule of five valence electrons generally holds true for phosphorus, there are subtle complexities to consider:
-
Excited States: Under certain conditions, phosphorus atoms can be promoted to an excited state, where one or more electrons are moved to a higher energy level. This can affect its bonding behavior and lead to different oxidation states.
-
Hybridization: The orbitals involved in bonding can hybridize, mixing to form new orbitals with different shapes and energies. This hybridization further influences the geometry and properties of phosphorus compounds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, phosphorus, with its five valence electrons, is a remarkably versatile element. These valence electrons dictate its reactivity, bonding behavior, and the formation of diverse compounds. Understanding the number and arrangement of these electrons is essential to fully appreciate phosphorus's pivotal role in biological processes, industrial applications, and the wider world of chemistry. Its position in the periodic table and its electron configuration provide a clear framework for comprehending its significant chemical characteristics and the numerous ways it interacts with other elements. The concept of valence electrons is fundamental to understanding chemical bonding and reactivity, and phosphorus serves as a perfect example of how this seemingly simple concept underpins the complexity and diversity of chemical behavior.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Air Moves From High To Low Pressure
Apr 02, 2025
-
The Smallest Particle Of An Element Is A N
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Many Neutrons Does A Hydrogen Atom Have
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is Nickel Used For In Everyday Life
Apr 02, 2025
-
A Tetrad Is Made Up Of
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Valence Electrons Are Found In Phosphorus . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
