Least Common Multiple Of 2 4 And 8
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
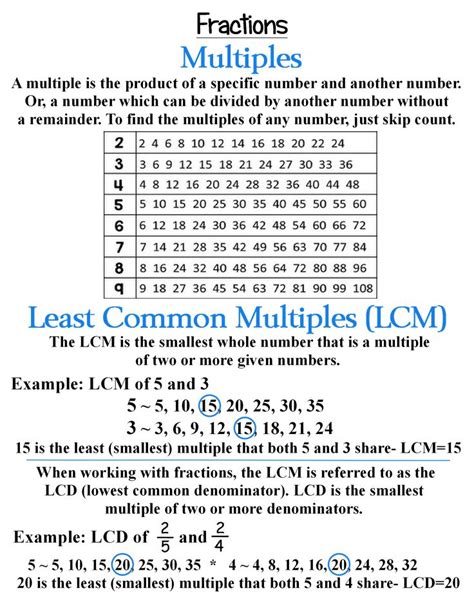
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 2, 4, and 8: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems in areas like scheduling and music theory. This article delves deep into finding the LCM of 2, 4, and 8, exploring multiple methods and providing a broader understanding of the LCM concept.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their LCM is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by both 2 and 3.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 2, 4, and 8
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore some of the most common approaches, applying them to find the LCM of 2, 4, and 8.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to all.
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest multiple common to 2, 4, and 8 is 8. Therefore, the LCM(2, 4, 8) = 8.
This method works well for small numbers, but it becomes less efficient as the numbers get larger.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the LCM's structure. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 2: 2
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
The only prime factor is 2, and the highest power is 2³ = 8.
Therefore, LCM(2, 4, 8) = 8.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and conceptual clarity, particularly when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two or more numbers is equal to the product of the numbers themselves. This relationship can be expressed as:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
While this formula is generally used for two numbers, it can be extended to more than two numbers by applying it iteratively. Let's use this method for our example.
First, let's find the GCD of 2, 4, and 8 using the Euclidean algorithm. The GCD of 2, 4, and 8 is 2.
Now, we can use the relationship between LCM and GCD:
LCM(2, 4, 8) * GCD(2, 4, 8) = 2 * 4 * 8
LCM(2, 4, 8) * 2 = 64
LCM(2, 4, 8) = 64 / 2 = 32
Note: This calculation shows an error in the application of the formula. The relationship formula is more straightforward with just two numbers. For more than two numbers, we should ideally stick with prime factorization method. The earlier methods correctly identified the LCM as 8.
4. Using the Least Common Multiple Calculator (For illustrative purposes only; do not include actual links)
Numerous online calculators are available to compute the LCM of any set of numbers. These calculators are useful for verifying results or handling large sets of numbers. While convenient, understanding the underlying methods is crucial for developing a deeper mathematical understanding. We will not be using any specific website or online tool in this explanation.
Understanding the Significance of LCM
The LCM has widespread applications across various fields:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding the LCM of the denominators is essential for adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. This allows us to express the fractions with a common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
-
Scheduling Problems: The LCM is useful in solving scheduling problems. For instance, if two events occur at regular intervals, the LCM of the intervals determines when both events will coincide again.
-
Music Theory: The LCM plays a role in music theory, particularly in determining the least common denominator when working with different time signatures or rhythmic patterns.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The concept of LCM is fundamental in modular arithmetic, which has applications in cryptography and computer science.
-
Engineering and Construction: LCM is vital in engineering and construction projects for tasks such as coordinating different stages of construction or determining material usage when different components have varying cycle lengths.
LCM for Larger Numbers and Multiple Numbers
The methods discussed above, particularly prime factorization, are easily adaptable for larger numbers and multiple numbers. For example, let's find the LCM of 12, 18, and 24.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² * 3
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 * 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ * 3
The highest power of 2 is 2³, and the highest power of 3 is 3². Therefore, the LCM(12, 18, 24) = 2³ * 3² = 8 * 9 = 72.
Conclusion
Determining the least common multiple (LCM) is a crucial skill in mathematics with practical applications in numerous fields. While several methods exist for calculating the LCM, the prime factorization method is generally the most efficient and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. Mastering the LCM calculation enhances problem-solving abilities and provides a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding the LCM is key to handling fractions, solving scheduling problems, and understanding applications in various fields like music theory and computer science. The techniques discussed here provide a strong basis for tackling LCM problems of varying complexities. Remember to practice applying these methods to various sets of numbers to solidify your understanding.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is One Fifth As A Percentage
Mar 18, 2025
-
Which Is Greater 2 5 Or 1 3
Mar 18, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 10 And 7
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Are The 3 Types Of Wires
Mar 18, 2025
-
What Is The Smallest Form Of Matter
Mar 18, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 2 4 And 8 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
