How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Square Have
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
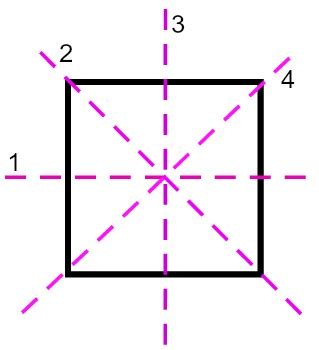
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Square Have? A Deep Dive into Geometry
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of elements. Understanding lines of symmetry is crucial in various fields, from designing aesthetically pleasing logos to comprehending the intricacies of geometric shapes. This article delves into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the number of lines of symmetry possessed by a square. We'll explore the definition of symmetry, delve into the properties of a square, and systematically identify all its lines of symmetry. We’ll also touch on the broader implications of understanding symmetry in various disciplines.
Defining Lines of Symmetry
Before we tackle the square, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This implies that each point on one side of the line has a corresponding point on the other side, equidistant from the line of symmetry. Not all shapes possess lines of symmetry, and some may have multiple lines of symmetry.
Properties of a Square: A Foundation for Symmetry
A square is a two-dimensional geometric shape with four sides of equal length and four angles, each measuring 90 degrees (right angles). These properties are critical in determining its lines of symmetry. The equality of sides and the presence of right angles create a high degree of regularity and balance, leading to multiple lines of symmetry. Understanding these defining characteristics is the key to unlocking the number of lines of symmetry a square possesses.
Identifying the Lines of Symmetry in a Square: A Step-by-Step Approach
Let's systematically identify the lines of symmetry in a square. We'll visualize a square and methodically locate each line that divides it into two identical mirrored halves.
1. Vertical Line of Symmetry:
Imagine drawing a straight line vertically down the center of the square. This line divides the square into two congruent rectangles, which are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the square along this line, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This is one line of symmetry.
2. Horizontal Line of Symmetry:
Now, let's consider a horizontal line drawn across the middle of the square. This line also bisects the square into two identical rectangles that are mirror images. Folding along this line would result in a perfect overlap of the two halves. This is our second line of symmetry.
3. and 4. Diagonal Lines of Symmetry:
The beauty of a square lies in its additional lines of symmetry that are not parallel to its sides. Draw a diagonal line from one corner to the opposite corner. This line divides the square into two congruent triangles that are mirror images. Repeat this process for the other diagonal, connecting the remaining two opposite corners. Both these diagonal lines act as lines of symmetry. These are the third and fourth lines of symmetry.
The Final Count: Four Lines of Symmetry
Therefore, a square possesses a total of four lines of symmetry: one vertical, one horizontal, and two diagonal lines. This relatively high number of lines of symmetry contributes to the square's balanced and aesthetically pleasing appearance, making it a popular shape in design and architecture.
Symmetry Beyond the Square: Exploring Other Shapes
Understanding the symmetry of a square provides a strong foundation for exploring the symmetry of other geometric shapes. Let's briefly compare the symmetry of a square with other common shapes:
-
Rectangle: A rectangle, while possessing similar properties to a square (opposite sides equal), only has two lines of symmetry—one vertical and one horizontal. The lack of equal side lengths prevents diagonal lines from being lines of symmetry.
-
Circle: A circle has infinite lines of symmetry. Any line passing through the center of the circle will divide it into two identical halves.
-
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry—one through each vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
-
Regular Pentagon: A regular pentagon (five equal sides) has five lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
Applications of Symmetry: From Art to Science
The concept of symmetry extends far beyond the realm of pure geometry. Its applications are widespread and crucial in various fields:
-
Art and Design: Symmetry is a fundamental principle in art, architecture, and design. Symmetrical compositions are often perceived as more balanced and aesthetically pleasing. Many logos, patterns, and artistic creations utilize symmetry to create visually appealing designs.
-
Nature: Symmetry is abundant in nature. From the symmetrical wings of butterflies to the balanced structure of flowers and the geometric patterns found in snowflakes, nature showcases the beauty and functionality of symmetry.
-
Science and Engineering: Symmetry plays a crucial role in physics, chemistry, and engineering. Understanding symmetrical properties can simplify complex calculations and enhance the efficiency of designs. For example, the symmetrical design of airplanes and cars contributes to their stability and aerodynamic performance.
-
Mathematics: Symmetry is a key concept in numerous mathematical fields, including group theory, abstract algebra, and topology. The study of symmetry helps mathematicians understand the underlying structures and relationships within mathematical systems.
Advanced Concepts Related to Symmetry
While this article focuses on lines of symmetry, the broader concept of symmetry encompasses several other types:
-
Rotational Symmetry: This refers to a shape's ability to be rotated about a central point by a certain angle and still appear unchanged. A square, for instance, exhibits rotational symmetry of order 4, meaning it can be rotated 90 degrees, 180 degrees, 270 degrees, and 360 degrees and still look identical.
-
Translational Symmetry: This refers to a pattern that repeats itself in a regular manner across a surface. Think of wallpaper patterns or repeating geometric designs.
-
Scale Symmetry: This type of symmetry relates to the scaling or resizing of a shape without changing its overall form. Fractals, for example, exhibit scale symmetry.
Conclusion: The Significance of Symmetry
The seemingly simple question of "How many lines of symmetry does a square have?" opens up a fascinating exploration of symmetry's profound significance in mathematics, art, nature, and various scientific disciplines. The four lines of symmetry found within a square demonstrate the inherent balance and regularity of this fundamental geometric shape. This understanding extends far beyond simple geometry, highlighting the importance of symmetry in understanding the world around us and in creating aesthetically pleasing and functionally effective designs. By appreciating the intricacies of symmetry, we can better appreciate the beauty and order present in both the natural and man-made worlds. Further exploration of different types of symmetry and their applications will continue to unveil the rich and varied aspects of this fundamental mathematical concept.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Explain Why Your Relation Is A Function
Mar 14, 2025
-
The Terminal Electron Acceptor In Aerobic Respiration Is
Mar 14, 2025
-
Whats The Difference Between Alternator And Generator
Mar 14, 2025
-
What Does Xlv Mean In Roman Numbers
Mar 14, 2025
-
Is Melting Ice Chemical Or Physical Change
Mar 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does The Square Have . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
