How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Circle
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 6 min read
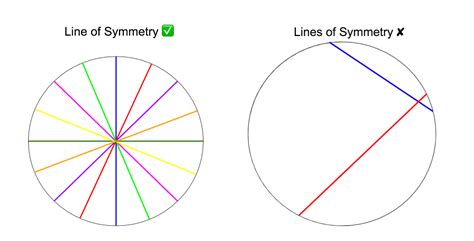
Table of Contents
- How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Circle
- Table of Contents
- How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Circle Have? An Exploration of Rotational and Reflective Symmetry
- Understanding Lines of Symmetry
- Exploring the Symmetry of Circles
- Differentiating between Lines and Axes of Symmetry
- Rotational Symmetry: A Complementary Perspective
- Contrasting with Other Shapes
- Applications of Circular Symmetry
- Beyond Lines of Symmetry: A Deeper Exploration
- Conclusion: The Infinite Symmetry of the Circle
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Circle Have? An Exploration of Rotational and Reflective Symmetry
The seemingly simple question, "How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?" opens the door to a fascinating exploration of geometry, symmetry, and the intriguing properties of circles. While the immediate answer might seem obvious, a deeper dive reveals a more nuanced understanding of symmetry and its various forms. This article will delve into the concept of lines of symmetry, explore the unique properties of circles concerning symmetry, and even touch upon rotational symmetry to provide a comprehensive understanding of this geometrical concept.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before we tackle the circle, let's establish a firm grasp on the definition of a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along this line, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This concept applies to various two-dimensional shapes, from simple triangles and squares to more complex polygons.
Key characteristics of a line of symmetry:
- Reflection: The line acts as a mirror, reflecting one half of the shape onto the other.
- Identical halves: The two halves created by the line are congruent (identical in shape and size).
- Perfect overlap: Folding the shape along the line results in a perfect overlap of the two halves.
Exploring the Symmetry of Circles
Now, let's focus on the circle, a unique geometric shape characterized by its perfect roundness. A circle is defined as the set of all points equidistant from a central point called the center. This uniform distance from the center to any point on the circumference is what gives the circle its unique properties, including its remarkable symmetry.
The question of how many lines of symmetry a circle possesses is not as straightforward as it might first appear. While many shapes have a limited number of lines of symmetry, the circle presents a special case.
To visualize the lines of symmetry in a circle, imagine drawing a line through the center of the circle. No matter which direction you draw this line, it will always divide the circle into two identical semicircles that are mirror images of each other. This means that you can draw an infinite number of lines of symmetry through the center of a circle.
Why Infinite Lines?
The key is the continuous nature of the circle. Unlike a square, which has only four lines of symmetry, or a hexagon with six, the circle possesses a continuous rotation symmetry. This means that no matter how slightly you rotate a circle around its center, it remains unchanged. This rotational symmetry is directly linked to the infinite lines of symmetry. Each line passing through the center represents a unique axis of reflection, leading to the infinite number.
Differentiating between Lines and Axes of Symmetry
It's important to clarify the distinction between "lines of symmetry" and "axes of symmetry." While often used interchangeably, there's a subtle difference:
- Lines of symmetry refer to the lines that divide a shape into identical mirror halves.
- Axes of symmetry are a broader term encompassing both lines and points of symmetry that maintain the shape's integrity when rotated or reflected.
In the context of a circle, both terms could be used, but the infinite number of lines passing through the center are more accurately described as axes of symmetry because of the inherent rotational symmetry involved.
Rotational Symmetry: A Complementary Perspective
While lines of symmetry focus on reflection, rotational symmetry considers the rotations that leave a shape unchanged. A circle exhibits perfect rotational symmetry. You can rotate a circle around its center by any angle, and it will appear identical to its original position. This continuous rotational symmetry is intrinsically linked to its infinite number of lines of symmetry. Each line of symmetry represents an axis around which a 180-degree rotation leaves the circle unchanged.
Understanding the Relationship:
The relationship between rotational and reflective symmetry in a circle is profound. The infinite number of lines of symmetry directly stems from the circle's continuous rotational symmetry. Each line of symmetry corresponds to a unique rotational axis, highlighting the interconnected nature of these two types of symmetry.
Contrasting with Other Shapes
Comparing the circle's infinite lines of symmetry with other shapes helps to further appreciate its unique characteristics:
- Square: A square possesses four lines of symmetry – two diagonal and two horizontal/vertical.
- Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle has three lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
- Rectangle: A rectangle has two lines of symmetry, both running horizontally and vertically through the center.
- Regular Polygon: A regular polygon with n sides has n lines of symmetry, each passing through a vertex and the midpoint of the opposite side.
These examples demonstrate that most shapes have a finite number of lines of symmetry. The circle stands out as the exception, possessing an infinite number.
Applications of Circular Symmetry
The concept of circular symmetry finds numerous applications in various fields:
- Engineering and Design: Circular designs are prevalent in engineering due to their strength, stability, and efficient use of materials. Wheels, gears, and rotating machinery are prime examples.
- Art and Architecture: Circular forms have long been used in art and architecture to symbolize perfection, eternity, and completeness. Many iconic structures incorporate circular elements to create visually striking and harmonious designs.
- Nature: Circles and circular patterns appear frequently in nature, from the rings of a tree trunk to the orbits of planets. This reflects the fundamental importance of circular symmetry in the natural world.
- Mathematics: Circles are fundamental in mathematics, forming the basis for various geometric concepts, trigonometric functions, and calculus.
Beyond Lines of Symmetry: A Deeper Exploration
While this article primarily focuses on lines of symmetry, the concept of symmetry extends beyond this basic definition. Other forms of symmetry exist, including:
- Point Symmetry: A shape has point symmetry if it can be rotated 180 degrees around a central point and remain unchanged. Circles possess point symmetry.
- Translational Symmetry: This type of symmetry involves repeating a pattern along a line or plane.
- Scale Symmetry: This occurs when a shape can be enlarged or reduced in size while maintaining its proportions.
Conclusion: The Infinite Symmetry of the Circle
In conclusion, the answer to the question, "How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?" is definitively infinite. This unique property arises from the circle's perfect roundness and continuous rotational symmetry. Each line passing through the center acts as an axis of reflection, creating an infinite number of lines of symmetry. Understanding this infinite symmetry provides a deeper appreciation for the circle's fundamental role in geometry, mathematics, and various other disciplines. The exploration of this concept highlights the beauty and complexity embedded within seemingly simple geometric shapes. The circle's infinite lines of symmetry serve as a testament to the elegant interplay between geometry and symmetry, showcasing the profound mathematical properties of this fundamental shape.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Are The Common Multiples Of 6 And 8
Mar 19, 2025
-
Predict The Product Of The Following Reaction
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Zeros In A Billion Dollars
Mar 19, 2025
-
Molar Mass Of Ba Oh 2
Mar 19, 2025
-
Label The Diagram Of The Female Reproductive System
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In A Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
